Abstract
Purpose
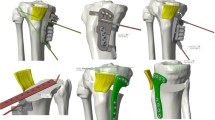
Double level osteotomy (DLO) (femoral and tibial) is a technically demanding procedure for which pre-operative planning accuracy and intraoperative correction are key factors. The aim of this study was to assess the accuracy of the achieved correction using patient-specific cutting guides (PSCGs) compared to the planned correction, its ability to maintain joint line obliquity (JLO), and to evaluate clinical outcomes and level of patient satisfaction at a follow-up of two years.
Methods
A single-centre, prospective observational study including 22 patients who underwent DLO by PSCGs between 2014 and 2018 was performed. Post-operative alignment was evaluated and compared with the target angular values to define the accuracy of the correction for the hip-knee-ankle angle (ΔHKA), medial proximal tibial angle (ΔMPTA), lateral distal femoral angle (ΔLDFA), and posterior proximal tibial angle (ΔPPTA). Pre- and post-operative JLO was also evaluated. At two year follow-up, changes in the KOOS sub-scores and patient satisfaction were recorded. The Mann–Whitney U test with 95% confidence interval (95% CI) was used to evaluate the differences between two variables; the paired Student’s t test was used to estimate evolution of functional outcomes.
Results
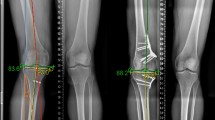
The mean ΔHKA was 1.3 ± 0.5°; the mean ΔMPTA was 0.98 ± 0.3°; the mean ΔLDFA was 0.94 ± 0.2°; ΔPPTA was 0.45 ± 0.4°. The orientation of the joint line was preserved with a mean difference in the JLO of 0.4 ± 0.2. At last follow-up, it was recorded a significant improvement in all KOOS scores, and 19 patients were enthusiastic, two satisfied, and one moderately satisfied.
Conclusion
Performing a DLO using PSCGs produces an accurate correction, without modification of the joint line orientation and with good functional outcomes at two year follow-up


Similar content being viewed by others
Availability of data and material
Copy of the initial spreadsheet kept available.
References
Conventry MB (2001) Osteotomy of the upper portion of the tibia for degenerative arthritis of the knee. A preliminary report by Mark B. Conventry, MD. From the Section of Orthopedic Surgery, Mayo Clinic and Mayo Foundation, Rochester, Minnesota. 1965. J Bone Joint Surg Am 83:1426
Ferner F, Lutter C, Dickschas J, Strecker W (2019) Medial open wedge vs. lateral closed wedge high tibial osteotomy - indications based on the findings of patellar height, leg length, torsional correction and clinical outcome in one hundred cases. Int Orthop 43:1379–1386. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00264-018-4155-9
Amendola A, Bonasia DE (2010) Results of high tibial osteotomy: review of the literature. Int Orthop 34:155–160. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00264-009-0889-8
Seil R, van Heerwaarden R, Lobenhoffer P, Kohn D (2013) The rapid evolution of knee osteotomies. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc Off J ESSKA 21:1–2. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00167-012-2175-3
Saragaglia D, Chedal-Bornu B, Rouchy RC et al (2016) Role of computer-assisted surgery in osteotomies around the knee. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc Off J ESSKA 24:3387–3395. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00167-016-4302-z
Sharma L, Song J, Felson DT et al (2001) The role of knee alignment in disease progression and functional decline in knee osteoarthritis. JAMA 286:188–195. https://doi.org/10.1001/jama.286.2.188
Dugdale TW, Noyes FR, Styer D (1992) Preoperative planning for high tibial osteotomy. The effect of lateral tibiofemoral separation and tibiofemoral length. Clin Orthop 248–264
Sailhan F, Jacob L, Hamadouche M (2017) Differences in limb alignment and femoral mechanical-anatomical angles using two dimension versus three dimension radiographic imaging. Int Orthop 41:2009–2016. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00264-017-3428-z
Donnez M, Ollivier M, Munier M et al (2018) Are three-dimensional patient-specific cutting guides for open wedge high tibial osteotomy accurate? An in vitro study. J Orthop Surg 13:171. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13018-018-0872-4
Ke S, Ran T, He Y et al (2020) Does patient-specific instrumentation increase the risk of notching in the anterior femoral cortex in total knee arthroplasty? A comparative prospective trial. Int Orthop 44:2603–2611. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00264-020-04779-4
Thienpont E, Schwab PE, Fennema P (2014) A systematic review and meta-analysis of patient-specific instrumentation for improving alignment of the components in total knee replacement. Bone Jt J 96-B:1052–1061. https://doi.org/10.1302/0301-620X.96B8.33747
Haglin JM, Eltorai AEM, Gil JA et al (2016) Patient-specific orthopaedic implants. Orthop Surg 8:417–424. https://doi.org/10.1111/os.12282
Jacquet C, Sharma A, Fabre M et al (2019) Patient-specific high-tibial osteotomy’s “cutting-guides” decrease operating time and the number of fluoroscopic images taken after a Brief Learning Curve. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc Off J ESSKA. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00167-019-05637-6
Jacquet C, Chan-Yu-Kin J, Sharma A et al (2019) "More accurate correction using “patient-specific” cutting guides in opening wedge distal femur varization osteotomies. Int Orthop 43:2285–2291. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00264-018-4207-1
Chaouche S, Jacquet C, Fabre-Aubrespy M et al (2019) Patient-specific cutting guides for open-wedge high tibial osteotomy: safety and accuracy analysis of a hundred patients continuous cohort. Int Orthop 43:2757–2765. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00264-019-04372-4
Gómez-Palomo JM, Meschian-Coretti S, Esteban-Castillo JL et al (2020) Double level osteotomy assisted by 3D printing technology in a patient with blount disease: a case report. JBJS Case Connect 10:e0477. https://doi.org/10.2106/JBJS.CC.19.00477
Munier M, Donnez M, Ollivier M et al (2017) Can three-dimensional patient-specific cutting guides be used to achieve optimal correction for high tibial osteotomy? Pilot study. Orthop Traumatol Surg Res OTSR 103:245–250. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.otsr.2016.11.020
Dijkman BG, Sprague S, Schemitsch EH, Bhandari M (2010) When is a fracture healed? Radiographic and clinical criteria revisited. J Orthop Trauma 24(Suppl 1):S76-80. https://doi.org/10.1097/BOT.0b013e3181ca3f97
Benjamin A (1969) Double osteotomy for the painful knee in rheumatoid arthritis and osteoarthritis. J Bone Joint Surg Br 51:694–699
Babis GC, An K-N, Chao EYS et al (2002) Double level osteotomy of the knee: a method to retain joint-line obliquity. Clinical results. J Bone Joint Surg Am 84:1380–1388. https://doi.org/10.2106/00004623-200208000-00013
Saragaglia D, Roberts J (2005) Navigated osteotomies around the knee in 170 patients with osteoarthritis secondary to genu varum. Orthopedics 28:s1269-1274
Maurer F, Wassmer G (2006) High tibial osteotomy: does navigation improve results? Orthopedics 29:S130-132
Saragaglia D, Blaysat M, Mercier N, Grimaldi M (2012) Results of forty two computer-assisted double level osteotomies for severe genu varum deformity. Int Orthop 36:999–1003. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00264-011-1363-y
Lee D-H, Park S-C, Park H-J, Han S-B (2016) Effect of soft tissue laxity of the knee joint on limb alignment correction in open-wedge high tibial osteotomy. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc Off J ESSKA 24:3704–3712. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00167-015-3682-9
Predescu V, Grosu A-M, Gherman I et al (2021) Early experience using patient-specific instrumentation in opening wedge high tibial osteotomy. Int Orthop. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00264-021-04964-z
Pérez-Mañanes R, Burró JA, Manaute JR et al (2016) 3D surgical printing cutting guides for open-wedge high tibial osteotomy: do it yourself. J Knee Surg 29:690–695. https://doi.org/10.1055/s-0036-1572412
Cerciello S, Ollivier M, Corona K et al (2020) CAS and PSI increase coronal alignment accuracy and reduce outliers when compared to traditional technique of medial open wedge high tibial osteotomy: a meta-analysis. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc Off J ESSKA. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00167-020-06253-5
Schröter S, Nakayama H, Yoshiya S et al (2019) Development of the double level osteotomy in severe varus osteoarthritis showed good outcome by preventing oblique joint line. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg 139:519–527. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00402-018-3068-9
Micicoi G, Grasso F, Kley K, et al (2021) Osteotomy around the knee is planned toward an anatomical bone correction in less than half of patients. Orthop Traumatol Surg Res OTSR 102897. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.otsr.2021.102897
Nakayama H, Schröter S, Yamamoto C et al (2018) Large correction in opening wedge high tibial osteotomy with resultant joint-line obliquity induces excessive shear stress on the articular cartilage. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc Off J ESSKA 26:1873–1878. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00167-017-4680-x
Akamatsu Y, Nejima S, Tsuji M et al (2021) Joint line obliquity was maintained after double-level osteotomy, but was increased after open-wedge high tibial osteotomy. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc Off J ESSKA. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00167-020-06430-6
Song J-H, Bin S-I, Kim J-M, Lee B-S (2020) What is an acceptable limit of joint-line obliquity after medial open wedge high tibial osteotomy? Analysis based on midterm results. Am J Sports Med 48:3028–3035. https://doi.org/10.1177/0363546520949552
Nakayama H, Iseki T, Kanto R et al (2020) Physiologic knee joint alignment and orientation can be restored by the minimally invasive double level osteotomy for osteoarthritic knees with severe varus deformity. Knee Surg Sports Traumatol Arthrosc Off J ESSKA 28:742–750. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00167-018-5103-3
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
MO, LH, and CJ designed the protocol. MO, LH, and KK gathered the patients’ data anonymously. FG, KK, and RK performed database analysis. CJ, MO, and FG wrote the initial draft. MO, CJ, FG, KK, RK, GM, and PM edited the different version of the draft. MO, CJ, FG, KK, RK, LH, GM, and PM approved the submitted and final versions.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate and to publish
Patient consent was collected pre-operatively after they were informed of the procedure in accordance with the principles of the Declaration of Helsinki. Local Ethical Committee approval was obtained prior to study’s initiation (Comité Informatique et Liberté (CIL)/Assistance Publique des Hopitaux de Marseille (AP-HM)/Registration Number 2019–127)).
Conflict of interest
MO is educational consultant for New-Clip, Stryker, and Arthrex. KK is educational consultant for New-Clip. CJ, RK, FG, PM, GM, and LH have no relevant financial or non-financial interests to disclose.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Grasso, F., Martz, P., Micicoi, G. et al. Double level knee osteotomy using patient-specific cutting guides is accurate and provides satisfactory clinical results: a prospective analysis of a cohort of twenty-two continuous patients. International Orthopaedics (SICOT) 46, 473–479 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00264-021-05194-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00264-021-05194-z