Abstract
Purpose
Acetabular fractures are accompanied by complications such as post-traumatic osteoarthritis (OA) of the hip and avascular necrosis (AVN) of the femoral head. The aim of the study was to evaluate improvement of life quality and functional recovery after total hip arthroplasty (THA) in patients with post-traumatic OA and AVN.
Methods
We retrospectively reviewed 23 patients with post-traumatic OA of the hip and AVN of the femoral head who undergone THA, out of 63 patients who were previously surgically treated for acetabular fractures. Final functional outcomes are defined according to the Merle dʼAubigné score, and the pain intensity according to VAS from 0 to 10.
Results
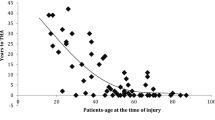
Out of 63 patients with acetabular fractures from 2008 to 2018, we analyzed 23 (36.5%) patients, with an average age of 51.5 ± 13.8 years, who required THA due to post-traumatic OA and AVN of the femoral head. THA was done after the average of 4.28 years (range 1 to 8) from previous acetabular osteosynthesis. According to Merle dʼAubigné score, final functional outcomes before THA were moderate with average points of 4.86 (4–6). Post-THA final functional outcomes were excellent with an average point of 10.04 (10–12) (p < 0.001). The ratio of VAS before and after THA was 9.04:1.95(p < 0.001).
Conclusion
THA is a method which gives the best results in the treatment of post-traumatic OA of the hip and AVN of the femoral head after previous osteosynthesis of the acetabular fracture. After THA, life quality and functional status of a patient are significantly improved.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Wang T, Sun J, Zha J, Wang C, Xi Z (2018) Delayed total hip arthroplasty after failed treatment of acetabular fractures: an 8- to 17-year follow-up study. J Orthop Surg Res 13:208. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13018-018-0909-8
Weber M, Berry DJ, Harmsen WS (1998) Total hip arthroplasty after operative treatment of an acetabular fracture. J Bone Joint Surg Am 80(9):1295–1305. https://doi.org/10.2106/00004623-199809000-00008
von Roth P, Abdel PM, Harmsen WS, Berry JD (2015) Total hip arthroplasty after operatively treated acetabular fracture: a concise follow-up, at a mean of twenty years, of a previous report. J Bone Joint Surg Am 97(4):288–291. https://doi.org/10.2106/JBJS.N.00871
Jindal K, Aggarwal S, Kumar P, Kumar V (2019) Complications in patients of acetabular fractures and the factors affecting the quality of reduction in surgically treated cases. J Clin Orthop Trauma 10(5):884–889. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcot.2019.02.012
Matta JM, Merritt PO (1988) Displaced acetabular fractures. Clin Orthop Rel Res 230:83–97
Ziran N, Soles GLS, Matta JM (2019) Outcomes after surgical treatment of acetabular fractures: a review. Patient Saf Surg 13:16. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13037-019-0196-2
Hougaard K, Thomsen PB (1986) Traumatic posterior dislocation of the hip- prognostic factors influencing the incidence of avascular necrosis of the femoral head. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg 106(1):32–35. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00435649
Ahmed G, Shiraz S, Riaz M, Ibrahim T (2017) Late versus early reduction in traumatic hip dislocations: a meta-analysis. Eur J Orthop Surg Traumatol 27(8):1109–1116. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00590-017-1988-7
Taheriazam A, Saeidinia A (2019) Conversion to total hip arthroplasty in posttraumatic arthritis: short-term clinical outcomes. Orthop Res Rev 11:41–46. https://doi.org/10.2147/ORR.S184590
Wu ES, Jauregui JJ, Banerjee S, Cherian JJ, Mont MA (2015) Outcomes of delayed total hip arthroplasty in patients with a previous ipsilateral acetabular fracture. Expert Rev Med Devices 12(3):297–306. https://doi.org/10.1586/17434440.2015.1026327
Biau DJ, Brand RA (2009) Robert Merle d’Aubigné, 1900-1989. Clin Orthop Relat Res 467(1):2–6. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11999-008-0571-2
Lequesne MG (1997) The algofunctional indices for hip and knee osteoarthritis. J Rheumatol 24(4):779–781
Morison Z, Moojen DJ, Nauth A, Hall J, McKee MD, Waddell JP, Schemitsch EH (2016) Total hip arthroplasty after acetabular fracture is associated with lower survivorship and more complications. Clin Orthop Relat Res 474(2):392–398. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11999-015-4509-1
Stibolt RD Jr, Patel HA, Huntley SR, Lehtonen EJ, Shah AB, Naranje SM (2018) Total hip arthroplasty for posttraumatic osteoarthritis following acetabular fracture: a systematic review of characteristics, outcomes, and complications. Chin J Traumatol 21(3):176–181. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cjtee.2018.02.004
Kumar P, Sen RK, Kumar V, Dadra A (2016) Quality of life following total hip arthroplasty in patients with acetabular fractures, previously managed by open reduction and internal fixation. Chin J Traumatol 19(4):206–208. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cjtee.2015.07.012
Rollmann FM, Holstein HJ, Pohlemann T, Herath CS, Histing T, Braun JB, Schmal H, Putzeys G, Marintschev I, Aghayev E (2019) Predictors for secondary hip osteoarthritis after acetabular fractures- a pelvic registry study. Int Orthop 43(9):2167–2173. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00264-018-4169-3
Sierra RJ, Mabry TM, Sems SA (2013) Acetabular fractures: the role of total hip replacement. Bone Joint J 95- B(11 Suppl A):11–16. https://doi.org/10.1302/0301-620X.95B11.32897
Giunta JC, Tronc C, Kerschbaumer G, Milaire M, Ruatti S, Tonetti J, Boudissa M (2019) Outcomes of acetabular fractures in the elderly: a five year retrospective study of twenty seven patients with primary total hip replacement. Int Orthop 43(10):2383–2389. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00264-018-4204-4
Pavelka T, Houcek P (2009) Complications associated with the surgical treatment of acetabular fractures. Acta Chir Orthop Traumatol Cech 76(3):186–193
Steven KD, Phillips TC, Joseph MR, Michael TA (2016) Achieving anatomic acetabular fracture reduction- when is the best time to operate? J Orthop Trauma 30(8):426–431. https://doi.org/10.1097/BOT.0000000000000576
Moed BR, Willson Carr SE, Watson JT (2002) Results of operative treatment of fractures of the posterior wall of the acetabulum. J Bone Joint Surg Am 84-A:752–758. https://doi.org/10.2106/00004623-200205000-00008
Pantazopoulos T, Nicolopoulos CS, Babis GC, Theodoropoulos T (1993) Surgical treatment of acetabular posterior wall fractures. Injury 24:319–323. https://doi.org/10.1016/0020-1383(93)90055-b
Meena UK, Tripathy SK, Sen RK, Aggarwal S, Behera P (2013) Predictors of postoperative outcome for acetabular fractures. Orthop Traumatol Surg Res 99(8):929–935. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.otsr.2013.09.004
Rommens PM, Ingelfinger P, Nowak TE, Kuhn S, Hessmann MH (2011) Traumatic damage to the cartilage influences outcome of anatomically reduced acetabular fractures: a medium- term retrospective analysis. Injury 42(10):1043–1048. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.injury.2011.03.058
Alonso JE, Volgas DA, Giordano V, Stannard JP (2000) A review of the treatment of hip dislocation associated with acetabular fractures. Clin Orthop 377:32–43. https://doi.org/10.1097/00003086-200008000-00007
Acknowledgments
This manuscript is supported by the Medical Faculty of Niš, Serbia, internal project titled “Total hip arthroplasty after earlier acetabular fractures” and the project “Virtual human osteoarticular system and its application in preclinical and clinical practice” (project no. III41017) funded by the Ministry of Education, Science and Technological Development of the Republic of Serbia.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Ethical approval
All procedures performed in study involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional research committee and with the 1964 Helsinki declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards.
Informed consent
Informed consent was obtained from all patients included in the study.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Milenkovic, S., Mitkovic, M., Mitkovic, M. et al. Total hip arthroplasty after acetabular fracture surgery. International Orthopaedics (SICOT) 45, 871–876 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00264-020-04676-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00264-020-04676-w