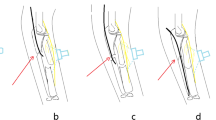
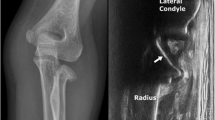
Abstract
Purpose
This study aimed to evaluate the feasibility of reduction under ultrasonographic (US) guidance with Kirschner wires (K-wires) and fixation with elastic stable intramedullary nails (ESINs) in the treatment of radial neck fractures (RNFs).
Methods
This retrospective study included 50 children treated for Judet types III and IV RNFs at our hospital from September 2015 to November 2018. Patients were divided into two groups: group A (without US) and group B (with US). Group A patients were treated using the Métaizeau technique; one K-wire was used for reduction under the guidance of X-ray fluoroscopy. Group B patients were treated using the same technique, but under the guidance of US. Post-operative radiographs, elbow function, and complications were analyzed.
Results
All patients were followed up over a period of 12 months. Five patients in group A had posterior interosseous nerve (PIN) injury, whereas no patient in group B had PIN injury (p = 0.016). The use of US guidance resulted in lower radiation exposure and shorter operation time. According to the Mayo Elbow Performance Index, there was no significant difference between the two groups (p = 0.814), including post-operative complications (radial head necrosis, fracture displacement, or stiffness).
Conclusion
US guidance during surgery is feasible to treat Judet type III and IV RNFs. US guidance can significantly reduce X-ray radiation exposure and the risk of PIN injury.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Nicholson LT, Skaggs DL (2019) Proximal radius fractures in children. J Am Acad Orthop Surg 27:e876–876e886
Du X, Yu L, Xiong Z, Chen G, Zou J, Wu X, Xiong B, Wang B (2019) Percutaneous leverage reduction with two Kirschner wires combined with the Métaizeau technique versus open reduction plus internal fixation with a single Kirschner-wire for treating Judet IV radial neck fractures in children. J Int Med Res 47:5497–5507
Lee JE, Kim JB, Choi ES (2017) Ultrasonography-guided reduction of pediatric radial neck fractures. BMC Musculoskelet Disord 18:516
Malahias MA, Manolopoulos PP, Kadu V, Shahpari O, Fagkrezos D, Kaseta MK (2018) Bedside ultrasonography for early diagnosis of occult radial head fractures in emergency room: a CT-comparative diagnostic study. Arch Bone Jt Surg 6:539–546
Rowlands R, Rippey J, Tie S, Flynn J (2017) Bedside ultrasound vs X-ray for the diagnosis of forearm fractures in children. J Emerg Med 52:208–215
Tokarski J, Avner JR, Rabiner JE (2018) Reduction of radiography with point-of-care elbow ultrasonography for elbow trauma in children. J Pediatr 198:214–219.e2
Ali AA, Solomon DM, Hoffman RJ (2016) Femur fracture diagnosis and management aided by point-of-care ultrasonography. Pediatr Emerg Care 32:192–194
Kozaci N, Ay MO, Avci M, Beydilli I, Turhan S, Donertas E, Ararat E (2017) The comparison of radiography and point-of-care ultrasonography in the diagnosis and management of metatarsal fractures. Injury 48:542–547
Bellavia MA, Cambise C, Coraci D, Maccauro G, Valassina A, Padua L (2017) Ultrasound is a useful tool to evaluate nerve involvement in children with supracondylar humerus fractures. Muscle Nerve 56:E18–18E20
Kaiser M, Eberl R, Castellani C, Kraus T, Till H, Singer G (2016) Judet type-IV radial neck fractures in children: comparison of the outcome of fractures with and without bony contact. Acta Orthop 87:529–532
Cossio A, Cazzaniga C, Gridavilla G, Gallone D, Zatti G (2014) Paediatric radial neck fractures: one-step percutaneous reduction and fixation. Injury 45(Suppl 6):S80–S84
Broberg MA, Morrey BF (1986) Results of delayed excision of the radial head after fracture. J Bone Joint Surg Am 68:669–674
Li XT, Shen XT, Wu X, Chen XL (2019) A novel transverse ultrasonography technique for minimally displaced lateral humeral condyle fractures in children. Orthop Traumatol Surg Res 105:557–562
Qiao F, Jiang F (2019) Closed reduction of severely displaced radial neck fractures in children. BMC Musculoskelet Disord 20:567
Soldado F, Knorr J, Haddad S, Diaz-Gallardo P, Palau-Gonzalez J, Mascarenhas VV, Karmali S, de Gauzy JS (2015) Ultrasound-guided percutaneous medial pinning of pediatric supracondylar humeral fractures to avoid ulnar nerve injury. Arch Bone Jt Surg 3:169–172
Karthick SR, Gopinathan NR, Vashisht S, Pattabiraman K (2020) Arthrogram assisted reduction of radial neck fracture in a child with unossified radial head - a case report and review of literature. J Clin Orthop Trauma 11:324–327
Connolly B, Racadio J, Towbin R (2006) Practice of ALARA in the pediatric interventional suite. Pediatr Radiol 36(Suppl 2):163–167
Su Y, Nan G (2019) Evaluation of a better approach for open reduction of severe Gartland type III supracondylar humeral fracture. J Investig Surg:1–7
Wellsh BM, Kuzma JM (2016) Ultrasound-guided pediatric forearm fracture reductions in a resource-limited ED. Am J Emerg Med 34:40–44
Song KS, Kim BS, Lee SW (2015) Percutaneous leverage reduction for severely displaced radial neck fractures in children. J Pediatr Orthop 35:e26–e30
Cha SM, Shin HD, Kim KC, Han SC (2012) Percutaneous reduction and leverage fixation using K-wires in paediatric angulated radial neck fractures. Int Orthop 36:803–809
Çevik N, Cansabuncu G, Akalın Y, Otuzbir A, Öztürk A, Özkan Y (2018) Functional and radiological results of percutaneous K-wire aided Métaizeau technique in the treatment of displaced radial neck fractures in children. Acta Orthop Traumatol Turc 52:428–434
Choi WS, Han KJ, Lee DH, Lee GE, Kweon HJ, Cho JH (2017) Stepwise percutaneous leverage technique to avoid posterior interosseous nerve injury in pediatric radial neck fracture. J Orthop Trauma 31:e151–151e157
Metaizeau JP, Lascombes P, Lemelle JL, Finlayson D, Prevot J (1993) Reduction and fixation of displaced radial neck fractures by closed intramedullary pinning. J Pediatr Orthop 13:355–360
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
The ethics committee of The Second Affiliated Hospital of Shandong First Medical University approved this study.
Informed consent
Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Level of Evidence: III
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Su, Y., Jin, C., Duan, X. et al. Treatment of displaced radial neck fractures under ultrasonographic guidance in children. International Orthopaedics (SICOT) 44, 2337–2342 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00264-020-04630-w
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00264-020-04630-w