Abstract
Purpose
This study examined the hip morphology of paediatric patients with mucopolysaccharidosis (MPS) type IVA (MPS IVA).
Methods
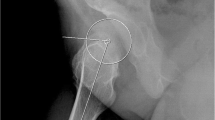
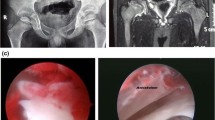
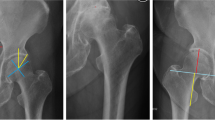
This was a retrospective chart review of 42 hips in 21 children with MPS IVA. Pelvic radiographs and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) scans of 42 hips and arthrograms of 13 hips were analysed. The bony, cartilaginous and labral coverage of the acetabulum was determined by acetabular index (AI), centre edge angle (CEA) and femoral head coverage (FHC).
Results
The mean age at the time of radiography was 66.3 ± 21.7 months. The bony, cartilaginous and labral AI in the MRI assessment were 36.3 ± 5.3, 18.3 ± 4.7 and 12.1 ± 4.6 degrees, respectively. The inter-class correlation coefficients (ICCs) for the bony AI, CEA and FHC measurements on radiographs and MRI were 0.936, 0.879 and 0.810, respectively. In the MRI assessment, labrum in 12 of 42 hips appeared as a regular triangle, and it was flat on 30/42 hips. The average arthrographic AI (AAI) was 11.1 ± 2.7 degrees. The ICCs value of AAI versus cartilaginous and labral AI on MRI indicates good agreement but higher in labral AI.
Conclusion
Hips in MPS IVA exhibited obvious cartilage and labrum compensation in response to abnormal ossification of bony acetabulum. Cartilage in MPS IVA hip increases the thickness in the longitudinal direction, while the labrum becomes flatten in the horizontal direction. The AAI may represent intraoperative labrum coverage. The femora-acetabular harmony is difficult to determine using radiography only, and pre-operative MRI and an intraoperative arthrogram are very important in a hip assessment in MPS IVA.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kobayashi H (2019) Recent trends in mucopolysaccharidosis research. J Hum Genet 64(2):127–137
Tomatsu S, Almeciga-Diaz CJ, Montano AM, Yabe H, Tanaka A, Dung VC, Giugliani R, Kubaski F, Mason RW, Yasuda E, Sawamoto K, Mackenzie W, Suzuki Y, Orii KE, Barrera LA, Sly WS, Orii T (2015) Therapies for the bone in mucopolysaccharidoses. Mol Genet Metab 114(2):94–109
White KK, Jester A, Bache CE, Harmatz PR, Shediac R, Thacker MM, Mackenzie WG (2014) Orthopedic management of the extremities in patients with Morquio A syndrome. J Child Orthop 8(4):295–304
Bixby SD, Millis MB (2019) The borderline dysplastic hip: when and how is it abnormal? Pediatr Radiol 49(12):1669–1677
Breyer SR, Muschol N, Schmidt M, Rupprecht M, Babin K, Herrmann J, Stucker R (2018) Hip morphology in MPS-1H patients: an MRI-based study. J Pediatr Orthop 38(9):478–483
Huber H, Mainard-Simard L, Lascombes P, Renaud F, Jean-Baptiste M, Journeau P (2014) Normal values of bony, cartilaginous, and labral coverage of the infant hip in MR imaging. J Pediatr Orthop 34(7):674–678
Walbron P, Muller F, Mainard-Simard L, Luc A, Journeau P (2019) Bone maturation of MRI residual developmental dysplasia of the hip with discrepancy between osseous and cartilaginous acetabular index. J Pediatr Orthop B 28(5):419–423
Siddesh ND, Shah H, Tercier S, Pai H, Nair S, Joseph B (2014) The sphericity deviation score: a quantitative radiologic outcome measure of Legg-Calve Perthes disease applicable at the stage of healing and at skeletal maturity. J Pediatr Orthop 34(5):522–528
Hachiya Y, Kubo T, Horii M, Hirasawa Y, Muramatsu K, Morita C, Ando K, Yoshizawa H (2001) Characteristic features of the acetabular labrum in healthy children. J Pediatr Orthop B 10(3):169–172
Miyake T, Tetsunaga T, Endo H, Yamada K, Sanki T, Fujiwara K, Nakata E, Ozaki T (2019) Predicting acetabular growth in developmental dysplasia of the hip following open reduction after walking age. J Orthop Sci 24(2):326–331
White KK, Sousa T (2013) Mucopolysaccharide disorders in orthopaedic surgery. J Am Acad Orthop Surg 21(1):12–22
Nowicki PD, Duhn R (2014) The use of arthrography in pediatric orthopaedic surgery. J Am Acad Orthop Surg 22(8):472–481
Tomatsu S, Fujii T, Fukushi M, Oguma T, Shimada T, Maeda M, Kida K, Shibata Y, Futatsumori H, Montano AM, Mason RW, Yamaguchi S, Suzuki Y, Orii T (2013) Newborn screening and diagnosis of mucopolysaccharidoses. Mol Genet Metab 110(1–2):42–53
Li LY, Zhang LJ, Li QW, Zhao Q, Jia JY, Huang T (2012) Development of the osseous and cartilaginous acetabular index in normal children and those with developmental dysplasia of the hip: a cross-sectional study using MRI. J Bone Joint Surg (Br) 94(12):1625–1631
Li Y, Liu Y, Zhou Q, Chen W, Li J, Yu L, Xu H, Xie D (2016) Magnetic resonance imaging evaluation of acetabular orientation in normal Chinese children. Medicine (Baltimore) 95(37):e4878
Zhou Y, Ju L, Lou Y, Wang B (2019) Analysis of acetabulum in children with developmental dysplasia of the hip by MRI scan. Medicine (Baltimore) 98(3):e14054
Horii M, Kubo T, Inoue S, Kim WC (2003) Coverage of the femoral head by the acetabular labrum in dysplastic hips: quantitative analysis with radial MR imaging. Acta Orthop Scand 74(3):287–292
Carbonell PG, Pena MO (2017) MRI assessment of the importance of the acetabular labrum: a comparative radiographic and MRI study in children's hips. J Pediatr Orthop B 26(4):289–292
Gupta A, Chandrasekaran S, Redmond JM, Hammarstedt JE, Cramer TL, Liu Y, Domb BG (2015) Does labral size correlate with degree of acetabular dysplasia? Orthop J Sports Med 3(2):2325967115572573
Kraeutler MJ, Goodrich JA, Ashwell ZR, Garabekyan T, Jesse MK, Mei-Dan O (2019) Combined lateral osseolabral coverage is normal in hips with acetabular dysplasia. Arthroscopy 35(3):800–806
Theroux MC, Nerker T, Ditro C, Mackenzie WG (2012) Anesthetic care and perioperative complications of children with Morquio syndrome. Paediatr Anaesth 22(9):901–907
Thawrani DP, Walker K, Polgreen LE, Tolar J, Orchard PJ (2013) Hip dysplasia in patients with Hurler syndrome (mucopolysaccharidosis type 1H). J Pediatr Orthop 33(6):635–643
Satsuma S, Kobayashi D, Kinugasa M, Takeoka Y, Kuroda R, Kurosaka M (2016) A new predictive indicator by arthrography for future acetabular growth following conservative treatment of developmental dysplasia of the hip. J Pediatr Orthop B 25(3):207–211
Masterson EL, Murphy PG, O'Meara A, Moore DP, Dowling FE, Fogarty EE (1996) Hip dysplasia in Hurler's syndrome: orthopaedic management after bone marrow transplantation. J Pediatr Orthop 16(6):731–733
Funding
Approval of financial support was given by the Medium and Long-Term Clinical Research Foundation of Shanghai Children’s Medical Center (Grant No. ZCQ-SCMC2018–1), the Clinical Research Cultivation Foundation of the Shanghai Shenkang Hospital Development Center (Grant No. SHDC12018X31), the Natural Science Foundation of Shanghai (Grant No. 17ZR1417900) and the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Grant No. 81801919).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
This study was approved by the Ethical Committee of the Shanghai Children’s Medical Center, Shanghai Jiao Tong University School of Medicine.
Informed consent
Informed consent was obtained from legal guardian of each participant in the study.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Zhigang Wang is the co-first author.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Miao, M., Wang, Z., Cai, H. et al. Hip morphology in mucopolysaccharidosis type IVA through radiograph, magnetic resonance imaging and arthrogram assessment. International Orthopaedics (SICOT) 44, 1677–1683 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00264-020-04600-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00264-020-04600-2