Abstract
Purpose
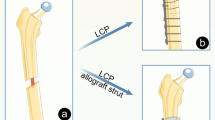
Unified classification system (UCS) type B1 periprosthetic femoral fractures are associated with many complications, and management decisions continue to be controversial. The purpose of this study was to evaluate outcomes of UCS type B1 periprosthetic femoral fractures treated by locking compression plating with strut allograft augmentation.
Materials and methods
We retrospectively reviewed 17 consecutive UCS type B1 periprosthetic femoral fractures treated by open reduction and internal fixation using a lateral locking compression plate supplemented with an anterior cortical strut allograft. There was one man and 16 women with an average age of 74 years (range, 57–92 years). All had a cementless hip arthroplasty, and eight of the arthroplasties were revisions.
Results
The mean duration of follow-up was 28 months (range, 12–74 months). All 17 fractures healed successfully at a mean of 20 weeks (range, 12–30 weeks). The mean post-operative Harris hip score was 86 points (range, 77–95 points). No mechanical complications such as failure of plate or screws and malalignment were noted. According to the graft-remodeling classification of Emerson et al., a partial bridging was observed in nine and a complete bridging in eight. Two patients required a removal of the plate due to irritation of the iliotibial band. No femoral stem loosening or deep infection was observed.
Conclusion
Our findings indicate that open reduction and internal fixation of UCS type B1 periprosthetic femoral fractures using a lateral locking compression plate supplemented with anterior cortical strut allograft provides adequate mechanical stability of fracture fixation and enhances the fracture healing.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Meek RM, Norwood T, Smith R, Brenkel IJ, Howie CR (2011) The risk of peri-prosthetic fracture after primary and revision total hip and knee replacement. J Bone Joint Surg (Br) 253(93):96–101
Lindahl H, Malchau H, Herberts P, Garellick G (2005) Periprosthetic femoral fractures: classification and demographics of 1049 periprosthetic femoral fractures from the Swedish National Hip Arthroplasty Register. J Arthroplasty 20:857–865
Sidler-Maier CC, Waddell JP (2015) Incidence and predisposing factors of periprosthetic proximal femoral fractures: a literature review. Int Orthop 39:1673–1682
Duncan CP, Masri BA (1995) Fractures of the femur after hip replacement. Instr Course Lect 44:293–304
Duncan CP, Haddad FS (2014) The Unified Classification System (UCS): improving our understanding of periprosthetic fractures. Bone Joint J 96-B:713–716
Lindahl H, Malchau H, Oden A, Garellick G (2006) Risk factors for failure after treatment of a periprosthetic fracture of the femur. J Bone Joint Surg 88-B:26–30
Yasen AT, Haddad FS (2015) The management of type B1 periprosthetic femoral fractures: when to fix and when to revise. Int Orthop 39(9):1873–1879
Bryant GK, Morshed S, Agel J, Henley MB, Barei DP, Taitsman LA, Nork SE (2009) Isolated locked compression plating for Vancouver Type B1 periprosthetic femoral fractures. Injury 40:1180–1186
Ruchholtz S, El-Zayat B, Kreslo D, Bücking B, Lewan U, Krüger A, Zettl R (2013) Less invasive polyaxial locking plate fixation in periprosthetic and peri-implant fractures of the femur—a prospective study of 41 patients. Injury 44:239–248
Moloney GB, Westrick ER, Siska PA, Tarkin IS (2014) Treatment of periprosthetic femur fractures around a well-fixed hip arthroplasty implant: span the whole bone. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg 134:9–14
Corten K, Vanrykel F, Bellemans J, Frederix PR, Simon JP, Broos PL (2009) An algorithm for the surgical treatment of periprosthetic fractures of the femur around a well fixed femoral component. J Bone Joint Surg (Br) 91:1424–1430
Beals RK, Tower SS, Periprosthetic fractures of the femur (1996) An analysis of 93 fractures. Clin Orthop Relat Res 327:238–246
Jukkala-Partio K, Partio EK, Solovieva S, Paavilainen T, Hirvensalo E, Alho A (1998) Treatment of periprosthetic fractures in association with total hip arthroplasty—a retrospective comparison between revision stem and plate fixation. Ann Chir Gynaecol 87:229–235
Harris WH (1969) Traumatic arthritis of the hip after dislocation and acetabular fractures: treatment by mold arthroplasty. An end-result study using a new method of result evaluation. J Bone Joint Surg Am 51:737–755
Buttaro MA, Farfalli G, Paredes Núñez M, Comba F, Piccaluga F (2007) Locking compression plate fixation of Vancouver type-B1 periprosthetic femoral fractures. J Bone Joint Surg Am 89:1964–1969
Emerson RH Jr, Malinin TI, Cuellar AD, Head WC, Peters PC (1992) Cortical strut allografts in the reconstruction of the femur in revision total hip arthroplasty. A basic science and clinical study. Clin Orthop Relat Res 285:35–44
Engh CA, Bobyn JD, Glassman AH (1987) Porous- coated hip replacement. The factors governing bone ingrowth, stress shielding, and clinical results. J Bone Joint Surg (Br) 69:45–55
Ricci WM, Bolhofner BR, Loftus T, Cox C, Mitchell S, Borrelli J Jr (2005) Indirect reduction and plate fixation, without grafting, for periprosthetic femoral shaft fractures about a stable intramedullary implant. J Bone Joint Surg Am 87:2240–2245
Chandler HP, King D, Limbird R, Hedley A, McCarthy J, Penenberg B, Danylchuk K (1993) The use of cortical allograft struts for fixation of fractures associated with well fixed total joint prostheses. Semin Arthroplast 4:99–107
Haddad FS, Duncan CP, Berry DJ, Lewallen DG, Gross AE, Chandler HP (2002) Periprosthetic femoral fractures around well-fixed implants: use of cortical onlay allografts with or without a plate. J Bone Joint Surg Am 84:945–950
Allan DG, Lavoie GJ, McDonald S, Oakeshott R, Gross AE (1991) Proximal femoral allografts in revision hip arthroplasty. J Bone Joint Surg (Br) 73:235–240
Gresham RB (1964) The freeze-dried cortical bone homograft: a roentgenographic and histologic evaluation. Clin Orthop Relat Res 37:194–201
Springfield DS (1987) Massive autogenous bone grafts. Orthop Clin N Am 18:249–256
Chen DW, Lin CL, Hu CC, Wu JW, Lee MS (2012) Finite element analysis of different repair methods of Vancouver B1 periprosthetic fractures after total hip arthroplasty. Injury 43:1061–1065
Demos HA, Briones MS, White PH, Hogan KA, Barfield WR (2012) A biomechanical comparison of periprosthetic femoral fracture fixation in normal and osteoporotic cadaveric bone. J Arthroplasty 27:783–788
Hoffmann MF, Burgers TA, Mason JJ, Williams BO, Sietsema DL, Jones CB (2014) Biomechanical evaluation of fracture fixation constructs using a variable-angle locked periprosthetic femur plate system. Injury 45:1035–1041
Gwinner C, Märdian S, Dröge T, Schulze M, Raschke MJ, Stange R (2015) Bicortical screw fixation provides superior biomechanical stability but devastating failure modes in periprosthetic femur fracture care using locking plates. Int Orthop 39:1749–1755
Konstantinidis L, Hauschild O, Beckmann NA, Hirschmüller A, Südkamp NP, Helwig P (2014) Treatment of periprosthetic femoral fractures with two different minimal invasive angle-stable plates: biomechanical comparison studies on cadaveric bones. Injury 41:1256–1261
Lenz M, Perren SM, Gueorguiev B, Richards RG, Hofmann GO, Fernandez dell’Oca A, Höntzsch D, Windolf M (2014) A biomechanical study on proximal plate fixation techniques in periprosthetic femur fractures. Injury 45(Suppl 1):S71–S75
Khashan M, Amar E, Drexler M, Chechik O, Cohen Z, Steinberg EL (2013) Superior outcome of strut allograft-augmented plate fixation for the treatment of periprosthetic fractures around a stable femoral stem. Injury 44:1556–1560
Sariyilmaz K, Dikici F, Dikmen G, Bozdag E, Sunbuloglu E, Bekler B, Yazicioglu O (2014) The effect of strut allograft and its position on Vancouver type B1 periprosthetic femoral fractures: a biomechanical study. J Arthroplasty 29:1485–1490
Wilson D, Frei H, Masri BA Oxland TR, Duncan CP (2005) A biomechanical study comparing cortical onlay allograft struts and plates in the treatment of periprosthetic femoral fractures. Clin Biomech (Bristol, Avon) 20:70–76
Müller FJ, Galler M, Füchtmeier B (2014) Clinical and radiological results of patients treated with orthogonal double plating for periprosthetic 340 femoral fractures. Int Orthop 341(38):2469–2472
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yeo, I., Rhyu, KH., Kim, SM. et al. High union rates of locking compression plating with cortical strut allograft for type B1 periprosthetic femoral fractures. International Orthopaedics (SICOT) 40, 2365–2371 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00264-015-3107-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00264-015-3107-x