Abstract
Purpose
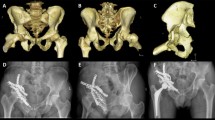
Periprosthetic acetabular fractures are rare and in the current literature largely underreported. The management is reported to be difficult. Treatment varies from non-operative to open reduction and internal fixation up to revision of the acetabular components.
Methods
A prospective consecutive case series in acetabular fractures was performed in a level 1 trauma centre. All patients with pre-existing total hip replacement were followed up for one year. Perioperative data, complications, radiological results, functional outcome and quality of life were measured.
Results
Eight (15 %) of 53 patients who were included in the study underwent total hip arthroplasty before and had stable implants at time of fracture. Mean age of the patients was 83 years. All of them were female. Mean operative time was 85 minutes. There were no soft tissue complications like infection or nerve damage in the post-operative course. No revision was needed. Two patients died in between the follow up. The Harris hip score was a mean of 77, with quality of life comparable to persons in the same age.
Conclusions
Minimally invasive reconstruction of the anterior column is a viable method to conserve stable acetabular components in this type of fracture. Short operation time and limited incisions are the most conclusive advantages.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ruchholtz S, El-Zayat B, Kreslo D, Bücking B, Lewan U, Krüger A, Zettl R (2013) Less invasive polyaxial locking plate fixation in periprostehtic and peri-implant fractures of the femur – A prospective study of 41 patients. Injury 44(2):239–248
Cochu G, Mabit C, Gougam T, Fiorenza F, Baertich C, Charissoux JL, Arnaud JP (2007) Total hip arthroplasty for treatment of acute acetabular fracture in elderly patients. Rev Chir Orthop Reparatrice Appar Mot 93(8):818–827
Peterson C, Lewallen D (1996) Periprosthetic fracture of the acetabulum after total hip arthroplasty. JBJS 78(8):1206–1213
Gelalis ID, Politis AN, Arnaoutoglou CM, Georgakopoulos N, Mitsiou D, Xenakis TA (2010) Traumatic periprosthetic acetabular fracture treated by acute one-stage revision arthroplasty. A case report and review of the literature. Injury 41:421–424
Hersovici D, Lindvall E, Bolhofner B, Scaduto J (2010) The combined hip procedure: Open reduction internal fixation combined with total hip arthroplasty for the management of acetabular fractures in the elderly. J Orthop Trauma 24:291–296
Carroll F, Hoad-Reddick D, Kerry R, Stockley I (2008) The survival of support rings in complex acetabular revision surgery. J Bone Joint Surg 90(5):574–578
Sporer S, O’Rourke M, Paprosky W (2005) The treatment of pelvic discontinuity during acetabular revision. J Arthoplasty 20(4 Suppl 2):79–84
Springer B, Berry D, Cabanela M, Hanssen A, Lewallen D (2005) Early postoperative transverse pelvic fracture: a new complication related to revision arthoplasty with an uncemented cup. J Bone Joint Surg 87(12):2626–2631
Ruchholtz S, Buecking B, Delschen A, Lewan U, Taeger G, Kuehne C, Zettl R (2013) The two-incision, minimally invasive approach in the treatment of acetabular fractures. J Orthop Trauma 27:248–255
Berry D, Lewallen D, Hanssen A, Cabanela M (1999) Pelvic discontinuity in revision total hip arthroplasty. J Bone Joint Surg 81(12):1692–1702
Beckmann N, Weiss S, Klotz M, Gondan M, Jaeger S, Bitsch R (2001) Loosening after acetabular revision: comparison of trabecular metal and reinforcement rings. A systematic review. J Arthoplasty 29:229–235
Weber M, Berry D, Harmsen W (1998) Total hip arthroplasty after operative treatment of an acetabular fracture. J Bone Joint Surg 80(9):1295–1305
Banerjee S, Issa K, Kapadia B, Pivec R, Khanuya H, Mont M (2014) Systematic review on outcomes of acetabular revisions with highly-porous metals. Int Orthop 38:689–702
Conflict of interest
All authors state that there are no competing interests in relation to this study including financial, consultant and other relationships that might lead to bias or a conflict of interest.
The study was not supported by external funding.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zettl, R., Eschbach, D. & Ruchholtz, S. Management of periprosthetic acetabular fractures in elderly patients—a minimally invasive approach. International Orthopaedics (SICOT) 39, 1845–1849 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00264-015-2936-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00264-015-2936-y