Abstract
Purpose
The aim of this study was to determine the biomechanical properties of four fixation options for periprosthetic supracondylar femoral fractures.
Methods
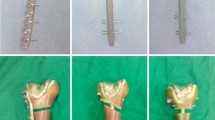
Fourth-generation composite femurs were implanted with a posterior-stabilizing femoral component of total knee arthroplasty. All femurs were osteotomized to produce a AO/OTA 33-A3 fracture pattern and four different constructs were tested: (1) non-locking plate; (2) polyaxial locking plate; (3) intramedullary fibular strut allograft with polyaxial locking plate; (4) retrograde intramedullary nail. The composite femurs underwent non-destructive tests to determine construct stiffness in axial and torsional cyclic loading. The final testing consisted of quasi-static axial loading until failure.
Results
Under cyclic torsional loading, the retrograde intramedullary nail was less stiff than non-locking plate, polyaxial locking plate and intramedullary fibular strut allograft with polyaxial locking plate (p = 0.046). No differences were detected in cyclic axial loading between the different constructs. During quasi-static axial loading to failure, the intramedullary nail achieved the highest axial stiffness while the non-locking plate showed the lowest (p = 0.036).
Conclusions
The intramedullary fibular strut allograft with polyaxial locking plate did not prove to be significantly better to the polyaxial locking plate only in a periprosthetic distal femur fracture model.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Kurtz SM, Ong KL, Lau E, Bozic KJ (2014) Impact of the economic downturn on total joint replacement demand in the United States: updated projections to 2021. J Bone Joint Surg Am 96:624–630
Della Rocca GJ, Leung KS, Pape HC (2011) Periprosthetic fractures: epidemiology and future projections. J Orthop Trauma 25(Suppl 2):S66–S70
Ricci WM, Borrelli J Jr (2007) Operative management of periprosthetic femur fractures in the elderly using biological fracture reduction and fixation techniques. Injury 38:S53–S58
Kancherla VK, Nwachuku CO (2014) The treatment of periprosthetic femur fractures after total knee arthroplasty. Orthop Clin North Am 45:457–467
Kim KI, Egol KA, Hozack WJ, Parvizi J (2006) Periprosthetic fractures after total knee arthroplasties. Clin Orthop Relat Res 446:167–175
Srinivasan K, Macdonald DA, Tzioupis CC, Giannoudis PV (2005) Role of long stem revision knee prosthesis in periprosthetic and complex distal femoral fractures: a review of eight patients. Injury 36:1094–1102
Saidi K, Ben-Lulu O, Tsuji M, Safir O, Gross AE, Backstein D (2014) Supracondylar periprosthetic fractures of the knee in the elderly patients: a comparison of treatment using allograft implant composites, standard revision components, distal femoral replacement prosthesis. J Arthroplasty 29:110–114
Jassim SS, McNamara I, Hopgood P (2014) Distal femoral replacement in periprosthetic fracture around total knee arthroplasty. Injury 45:550–553
Berkes MB, Little MT, Lazaro LE, Cymerman RM, Pardee NC, Helfet DL, Dines JS, Lorich DG (2014) Intramedullary allograft fibula as a reduction and fixation tool for treatment of complex proximal humerus fractures with diaphyseal extension. J Orthop Trauma 28:e56–e64
Ebraheim NA, Sabry FF, Elgafy H (2002) Intramedullary fibular allograft and nail for treatment of femoral shaft nonunion. Am J Orthop (Belle Mead NJ) 31:270–272
Elgafy H, Ebraheim NA, Bach HG (2011) Revision internal fixation and nonvascular fibular graft for femoral neck nonunion. J Trauma 70:169–173
Jagodzinski M, Krettek C (2007) Effect of mechanical stability on fracture healing–an update. Injury 38(Suppl 1):S3–S10
Kumar A, Chambers I, Maistrelli G, Wong P (2008) Management of periprosthetic fracture above total knee arthroplasty using intramedullary fibular allograft and plate fixation. J Arthroplasty 23:554–558
Chen SH, Chiang MC, Hung CH, Lin SC, Chang HW (2014) Finite element comparison of retrograde intramedullary nailing and locking plate fixation with/without an intramedullary allograft for distal femur fracture following total knee arthroplasty. Knee 21:224–231
Mathison C, Chaudhary R, Beaupre L, Reynolds M, Adeeb S, Bouliane M (2010) Biomechanical analysis of proximal humeral fixation using locking plate fixation with an intramedullary fibular allograft. Clin Biomech (Bristol, Avon) 25:642–646
Osterhoff G, Baumgartner D, Favre P, Wanner GA, Gerber H, Simmen HP, Werner CM (2011) Medial support by fibula bone graft in angular stable plate fixation of proximal humeral fractures: an in vitro study with synthetic bone. J Shoulder Elbow Surg 20:740–746
Zlowodzki M, Williamson S, Cole PA, Zardiackas LD, Kregor PJ (2004) Biomechanical evaluation of the less invasive stabilization system, angled blade plate, and retrograde intramedullary nail for the internal fixation of distal femur fractures. J Orthop Trauma 18:494–502
Pekmezci M, McDonald E, Buckley J, Kandemir U (2014) Retrograde intramedullary nails with distal screws locked to the nail have higher fatigue strength than locking plates in the treatment of supracondylar femoral fractures: A cadaver-based laboratory investigation. Bone Joint J 96-B:114–121
Ahmadi S, Shah S, Wunder JS, Schemitsch EH, Ferguson PC, Zdero R (2013) The biomechanics of three different fracture fixation implants for distal femur repair in the presence of a tumor-like defect. Proc Inst Mech Eng H 227:78–86
Salas C, Mercer D, DeCoster TA, Reda Taha MM (2011) Experimental and probabilistic analysis of distal femoral periprosthetic fracture: a comparison of locking plate and intramedullary nail fixation. Part A: experimental investigation. Comput Methods Biomech Biomed Engin 14:157–164
Hanschen M, Aschenbrenner IM, Fehske K, Kirchhoff S, Keil L, Holzapfel BM, Winkler S, Fuechtmeier B, Neugebauer R, Luehrs S, Liener U, Biberthaler P (2014) Mono- versus polyaxial locking plates in distal femur fractures: a prospective randomized multicentre clinical trial. Int Orthop 38:857–863
Tejwani NC, Park S, Iesaka K, Kummer F (2005) The effect of locked distal screws in retrograde nailing of osteoporotic distal femur fractures: a laboratory study using cadaver femurs. J Orthop Trauma 19:380–383
Herrera DA, Kregor PJ, Cole PA, Levy BA, Jönsson A, Zlowodzki M (2008) Treatment of acute distal femur fractures above a total knee arthroplasty: systematic review of 415 cases (1981–2006). Acta Orthop 79:22–27
Gliatis J, Megas P, Panagiotopoulos E, Lambiris E (2005) Midterm results of treatment with a retrograde nail for supracondylar periprosthetic fractures of the femur following total knee arthroplasty. J Orthop Trauma 19:164–170
Lehmann W, Rupprecht M, Nuechtern J, Melzner D, Sellenschloh K, Kolb J, Fensky F, Hoffmann M, Püschel K, Morlock M, Rueger JM (2012) What is the risk of stress risers for interprosthetic fractures of the femur? A biomechanical analysis. Int Orthop 36:2441–2446
Horneff JG 3rd, Scolaro JA, Jafari SM, Mirza A, Parvizi J, Mehta S (2013) Intramedullary nailing versus locked plate for treating supracondylar periprosthetic femur fractures. Orthopedics 36:e561–e566
Davison BL (2003) Varus collapse of comminuted distal femur fractures after open reduction and internal fixation with a lateral condylar buttress plate. Am J Orthop (Belle Mead NJ) 32:27–30
Acknowledgments
H. S. Dhotar, M. Woodside, T. L. Willett and P. R. T. Kuzyk have received funding from the Orthopaedic Research and Education Foundation Young Investigators Grant. All the implants used in this study were provided by Zimmer Inc.
Conflicts of interest
The authors state there are no conflicts of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mäkinen, T.J., Dhotar, H.S., Fichman, S.G. et al. Periprosthetic supracondylar femoral fractures following knee arthroplasty: a biomechanical comparison of four methods of fixation. International Orthopaedics (SICOT) 39, 1737–1742 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00264-015-2764-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00264-015-2764-0