Abstract
Purpose
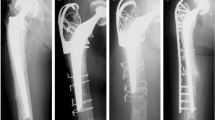
In case of stem loosening in periprosthetic femoral fractures (PPFF), revision arthroplasty should be performed. The first hypothesis of this study was that advanced patient age and female gender shows higher non-union rates. The second hypothesis was that primary cementless arthroplasty is associated with a higher non-union rate compared to cemented primary hip arthroplasty.
Methods
All PPFF occurring between January 2000 and June 2010 treated by revision arthroplasty were included. Multiple regression analysis was performed to identify independent variables leading to fracture non-union.
Results
Eighty one patients (78 % female) met the inclusion criteria. In 20/81 patients (24.7 %) no adequate fracture healing could be determined on radiographs 12 months after revision surgery. Although age and female gender showed a positive correlation with bony non-union after PPFF as expected, the p-values were not statistically significant. Multiple regression analysis revealed primary cementless prosthesis (p = 0.001) to be the only independent variable associated with non-union.
Conclusion
Non-cemented primary prosthesis might be a negative predicting factor for the development of non-union after long-stem revision arthroplasty in PPFF. We therefore recommend the thorough debridement of pannus tissue thus inducing bone healing before the implantation of revision prostheses.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Berry DJ (1999) Epidemiology: hip and knee. Orthop Clin N Am 30:183–190
Mont MA, Maar DC, Krackow KA, Hungerford DS (1992) Hoop-stress fractures of the proximal femur during hip arthroplasty. Management and results in 19 cases. J Bone Joint Surg Br Vol 74:257–260
Berry DJ (2002) Management of periprosthetic fractures: the hip. J Arthroplasty 17:11–13
Meek RMD, Norwood T, Smith R, Brenkel IJ, Howie CR (2011) The risk of peri-prosthetic fracture after primary and revision total hip and knee replacement. J Bone Joint Surg Br 93:96–101
Foster AP, Thompson NW, Wong J, Charlwood AP (2005) Periprosthetic femoral fractures–a comparison between cemented and uncemented hemiarthroplasties. Injury 36:424–429
Lindahl H, Malchau H, Herberts P, Garellick G (2005) Periprosthetic femoral fractures classification and demographics of 1049 periprosthetic femoral fractures from the Swedish National Hip Arthroplasty Register. J Arthroplasty 20:857–865
Tsiridis E, Haddad FS, Gie GA (2003) The management of periprosthetic femoral fractures around hip replacements. Injury 34:95–105
Beals RK, Tower SS (1996) Periprosthetic fractures of the femur. An analysis of 93 fractures. Clin Orthop Relat Res 327:238–246
Lindahl H, Malchau H, Odén A, Garellick G (2006) Risk factors for failure after treatment of a periprosthetic fracture of the femur. J Bone Joint Surg Br Vol 88:26–30
Zuurmond RG, van Wijhe W, van Raay JJAM, Bulstra SK (2010) High incidence of complications and poor clinical outcome in the operative treatment of periprosthetic femoral fractures: an analysis of 71 cases. Injury 41:629–633
O’Shea K, Quinlan JF, Kutty S, Mulcahy D, Brady OH (2005) The use of uncemented extensively porous-coated femoral components in the management of Vancouver B2 and B3 periprosthetic femoral fractures. J Bone Joint Surg Br 87:1617–1621
Holley K, Zelken J, Padgett D, Chimento G, Yun A, Buly R (2007) Periprosthetic fractures of the femur after hip arthroplasty: an analysis of 99 patients. HSS J 3:190–197
Duncan CP, Masri BA (1995) Fractures of the femur after hip replacement. Instr Course Lect 44:293–304
Lenz M, Perren SM, Richards RG, Mückley T, Hofmann GO, Gueorguiev B, Windolf M (2013) Biomechanical performance of different cable and wire cerclage configurations. Int Orthop 37(1):125–130. doi:10.1007/s00264-012-1702-7
Perren SM, Fernandez Dell’Oca A, Lenz M, Windolf M (2011) Cerclage, evolution and potential of a Cinderella technology. An overview with reference to periprosthetic fractures. Acta Chir Orthop Traumatol Cech 78(3):190–199
Klein GR, Parvizi J, Rapuri V, Wolf CF, Hozack WJ, Sharkey PF, Purtill JJ (2005) Proximal femoral replacement for the treatment of periprosthetic fractures. J Bone Joint Surg Br 87:1777–1781
Langenhan R, Trobisch P, Ricart P, Probst A (2012) Aggressive surgical treatment of periprosthetic femur fractures can reduce mortality: comparison of open reduction and internal fixation versus a modular prosthesis nail. J Orthop Trauma 26:80–85
Lindahl H, Garellick G, Regnér H, Herberts P, Malchau H (2006) Three hundred and twenty-one periprosthetic femoral fractures. J Bone Joint Surg Br 88:1215–1222
Mukundan C, Rayan F, Kheir E, Macdonald D (2010) Management of late periprosthetic femur fractures: a retrospective cohort of 72 patients. Int Orthop 34:485–489
Probst A, Schneider T, Hankemeier S, Brug E (2003) The prosthesis nail — a new stable fixation device for periprosthetic fractures and critical fractures of the proximal femur. Unfallchirurg 106:722–731
Kessler SB, Hallfeldt KK, Perren SM, Schweiberer L (1986) The effects of reaming and intramedullary nailing on fracture healing. Clin Orthop Relat Res 212:18–25
Webb LX, Winquist RA, Hansen ST (1986) Intramedullary nailing and reaming for delayed union or nonunion of the femoral shaft. A report of 105 consecutive cases. Clin Orthop Relat Res 212:133–141
Society COT (2003) Nonunion following intramedullary nailing of the femur with and without reaming. Results of a multicenter randomized clinical trial. J Bone Joint Surg Am 85-A(11):2093–2096
Duan X, Li T, Mohammed AQ, Xiang Z (2011) Reamed intramedullary nailing versus unreamed intramedullary nailing for shaft fracture of femur: a systematic literature review. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg 131(10):1445–1452. doi:10.1007/s00402-011-1311-8
Forster MC, Aster AS, Ahmed S (2005) Reaming during anterograde femoral nailing: is it worth it? Injury 36(3):445–449, Review
Bong MR, Kummer FJ, Koval KJ, Egol KA (2007) Intramedullary nailing of the lower extremity: biomechanics and biology. J Am Acad Orthop Surg 15(2):97–106, Review
Fitzgerald RH, Brindley GW, Kavanagh BF (1988) The uncemented total hip arthroplasty. Intraoperative femoral fractures. Clin Orthop Relat Res 235:61–66
Schwartz JT, Mayer JG, Engh CA (1989) Femoral fracture during non-cemented total hip arthroplasty. J Bone Joint Surg Br 71:1135–1142
Laurer HL, Wutzler S, Possner S, Geiger EV, El Saman A, Marzi I, Frank J (2011) Outcome after operative treatment of Vancouver type B1 and C periprosthetic femoral fractures: open reduction and internal fixation versus revision arthroplasty. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg 131:983–989
Müller M, Kääb M, Tohtz S, Haas NP, Perka C (2009) Periprosthetic femoral fractures: outcome after treatment with LISS internal fixation or stem replacement in 36 patients. Acta Orthop Belg 75:776–783
Pavlou G, Panteliadis P, Macdonald D, Timperley JA, Gie G, Bancroft G, Tsiridis E (2011) A review of 202 periprosthetic fractures—stem revision and allograft improves outcome for type B fractures. Hip Int 21:21–29
Rayan F, Konan S, Haddad FS (2010) Uncemented revision hip arthroplasty in B2 and B3 periprosthetic femoral fractures—A prospective analysis. Hip Int 20:38–42
Fink B, Grossmann A, Singer J (2012) Hip revision arthroplasty in periprosthetic fractures of Vancouver type B2 and B3. J Orthop Trauma 26:206–211
Manolagas SC, Parfitt AM (2010) What old means to bone. Trends Endocrinol Metab 21:369–374
van Wunnik BPW, Weijers PHE, van Helden SH, Brink PRG, Poeze M (2011) Osteoporosis is not a risk factor for the development of nonunion: A cohort nested case-control study. Injury 42:1491–1494
Pressmar J, Macholz F, Merkert W, Gebhard F, Liener UC (2010) Results and complications in the treatment of periprosthetic femur fractures with a locked plate system. Unfallchirurg 113:195–202
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Boesmueller, S., Michel, M., Hofbauer, M. et al. Primary cementless hip arthroplasty as a potential risk factor for non-union after long-stem revision arthroplasty in periprosthetic femoral fractures. International Orthopaedics (SICOT) 39, 617–622 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00264-014-2489-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00264-014-2489-5