Abstract
Purpose
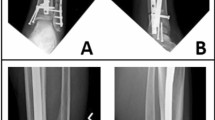
We evaluated radiographic fusion at follow-up and complication rates in patients who had either iliac crest (ICBG) or femoral reamer–irrigator–aspirator (RIA) bone graft for tibiotalar fusion.
Methods
We retrospectively reviewed charts and radiographs of all patients who had a tibiotalar fusion from August 2007 to February 2011. Records were analysed for patient demographics, complications, and clinical symptoms. Radiographs were reviewed in sequential order by two fellowship-trained foot and ankle surgeons and one orthopaedic surgeon who specialises in foot and ankle surgery to determine radiographic fusion at routine follow-up. Patients were contacted to determine current visual analog scores (VAS) at their graft site.
Results
Mean patient age was 49.4 ± 12.1 years in the RIA group and 49.3 ± 15.4 years in the ICBG group (p = .97). Pre-operative characteristics showed no significant differences between groups. The ICBG group had significantly more nonunions than the RIA group (six vs. one, p = 0.04). Two patients in the ICBG had chronic pain at their graft site based on their VAS score; there were none in the RIA group. Radiographic fusion at follow-up was similar between groups, with no significant difference (12.48 ± 3.85 weeks vs.12.21 ± 3.19 weeks, p = .80).
Conclusions
There was a significantly higher nonunion rate in the ICBG group, but both groups had a solid radiographic bony fusion at similar follow-up time points. Our results suggest RIA bone graft is a viable alternative to ICBG for tibiotalar fusion.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Gazdag AR, Lane JM, Glaser D, Forster RA (1995) Alternatives to autogenous bone graft: efficacy and indications. J Am Acad Orthop Surg 3:1–8
Grabowski G, Cornett CA (2013) Bone graft and bone graft substitutes in spine surgery: current concepts and controversies. J Am Acad Orthop Surg 21:51–60. doi:10.5435/JAAOS-21-01-51
Larsson S, Hannink G (2011) Injectable bone-graft substitutes: current products, their characteristics and indications, and new developments. Injury 42(Suppl 2):S30–S34. doi:10.1016/j.injury.2011.06.013
Mauffrey C, Seligson D, Lichte P, Pape HC, Al-Rayyan M (2011) Bone graft substitutes for articular support and metaphyseal comminution: what are the options? Injury 42(Suppl 2):S35–S39. doi:10.1016/j.injury.2011.06.012
Bauer TW, Muschler GF (2000) Bone graft materials. An overview of the basic science. Clin Orthop Relat Res 371:10–27
Belthur MV, Conway JD, Jindal G, Ranade A, Herzenberg JE (2008) Bone graft harvest using a new intramedullary system. Clin Orthop Relat Res 466:2973–2980. doi:10.1007/s11999-008-0538-3
Quintero AJ, Tarkin IS, Pape HC (2010) Technical tricks when using the reamer irrigator aspirator technique for autologous bone graft harvesting. J Orthop Trauma 24:42–45. doi:10.1097/BOT.0b013e3181b2b4eb
Kobbe P, Tarkin IS, Pape HC (2008) Use of the 'reamer irrigator aspirator' system for non-infected tibial non-union after failed iliac crest grafting. Injury 39:796–800. doi:10.1016/j.injury.2007.12.020
Ahlmann E, Patzakis M, Roidis N, Shepherd L, Holtom P (2002) Comparison of anterior and posterior iliac crest bone grafts in terms of harvest-site morbidity and functional outcomes. J Bone Joint Surg Am 84-A:716–720
Banwart JC, Asher MA, Hassanein RS (1995) Iliac crest bone graft harvest donor site morbidity. A statistical evaluation. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 20:1055–1060
Ebraheim NA, Elgafy H, Xu R (2001) Bone-graft harvesting from iliac and fibular donor sites: techniques and complications. J Am Acad Orthop Surg 9:210–218
Husebye EE, Lyberg T, Madsen JE, Eriksen M, Roise O (2006) The influence of a one-step reamer-irrigator-aspirator technique on the intramedullary pressure in the pig femur. Injury 37:935–940. doi:10.1016/j.injury.2006.06.119
Sagi HC, Young ML, Gerstenfeld L, Einhorn TA, Tornetta P (2012) Qualitative and quantitative differences between bone graft obtained from the medullary canal (with a Reamer/Irrigator/Aspirator) and the iliac crest of the same patient. J Bone Joint Surg Am 94:2128–2135. doi:10.2106/JBJS.L.00159
Porter RM, Liu F, Pilapil C, Betz OB, Vrahas MS, Harris MB, Evans CH (2009) Osteogenic potential of reamer irrigator aspirator (RIA) aspirate collected from patients undergoing hip arthroplasty. J Orthop Res 27:42–49. doi:10.1002/jor.20715
Lehman AA, Irgit KS, Cush GJ (2012) Harvest of autogenous bone graft using reamer-irrigator-aspirator in tibiotalocalcaneal arthrodesis: surgical technique and case series. Foot Ankle Int 33:1133–1138. doi:10.3113/FAI.2012.1133
Cox G, McGonagle D, Boxall SA, Buckley CT, Jones E, Giannoudis PV (2011) The use of the reamer-irrigator-aspirator to harvest mesenchymal stem cells. J Bone Joint Surg (Br) 93:517–524. doi:10.1302/0301-620X.93B4.25506
Kim DH, Rhim R, Li L, Martha J, Swaim BH, Banco RJ, Jenis LG, Tromanhauser SG (2009) Prospective study of iliac crest bone graft harvest site pain and morbidity. Spine J 9:886–892. doi:10.1016/j.spinee.2009.05.006
Dimitriou R, Mataliotakis GI, Angoules AG, Kanakaris NK, Giannoudis PV (2011) Complications following autologous bone graft harvesting from the iliac crest and using the RIA: a systematic review. Injury 42(Suppl 2):S3–S15. doi:10.1016/j.injury.2011.06.015
Moeckel BH, Patterson BM, Inglis AE, Sculco TP (1991) Ankle arthrodesis. A comparison of internal and external fixation. Clin Orthop Relat Res 268:78–83
Monroe MT, Beals TC, Manoli A 2nd (1999) Clinical outcome of arthrodesis of the ankle using rigid internal fixation with cancellous screws. Foot Ankle Int 20:227–231
Cheng H, Jiang W, Phillips FM, Haydon RC, Peng Y, Zhou L, Luu HH, An N, Breyer B, Vanichakarn P, Szatkowski JP, Park JY, He TC (2003) Osteogenic activity of the fourteen types of human bone morphogenetic proteins (BMPs). J Bone Joint Surg Am 85-A:1544–1552
Gerstenfeld LC, Cullinane DM, Barnes GL, Graves DT, Einhorn TA (2003) Fracture healing as a post-natal developmental process: molecular, spatial, and temporal aspects of its regulation. J Cell Biochem 88:873–884. doi:10.1002/jcb.10435
Owens WD, Felts JA, Spitznagel EL Jr (1978) ASA physical status classifications: a study of consistency of ratings. Anesthesiology 49:239–243
Loder RT (1988) The influence of diabetes mellitus on the healing of closed fractures. Clin Orthop Relat Res 232:210–216
Funk JR, Hale JE, Carmines D, Gooch HL, Hurwitz SR (2000) Biomechanical evaluation of early fracture healing in normal and diabetic rats. J Orthop Res 18:126–132. doi:10.1002/jor.1100180118
Castillo RC, Bosse MJ, MacKenzie EJ, Patterson BM (2005) Impact of smoking on fracture healing and risk of complications in limb-threatening open tibia fractures. J Orthop Trauma 19:151–157
Al-Hadithy N, Sewell MD, Bhavikatti M, Gikas PD (2012) The effect of smoking on fracture healing and on various orthopaedic procedures. Acta Orthop Belg 78:285–290
Qvick LM, Ritter CA, Mutty CE, Rohrbacher BJ, Buyea CM, Anders MJ (2013) Donor site morbidity with reamer-irrigator-aspirator (RIA) use for autogenous bone graft harvesting in a single centre 204 case series. Injury 44:1263–1269. doi:10.1016/j.injury.2013.06.008
Acknowledgments
We thank Dr. Rohrbacher and Dr. Gurske-dePerio for assistance with radiographic review and Cathy Buyea for assistance with statistical analysis.
Conflict of interest
None.
The authors received no financial support for the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nodzo, S.R., Kaplan, N.B., Hohman, D.W. et al. A radiographic and clinical comparison of reamer–irrigator–aspirator versus iliac crest bone graft in ankle arthrodesis. International Orthopaedics (SICOT) 38, 1199–1203 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00264-014-2348-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00264-014-2348-4