Abstract
Purpose
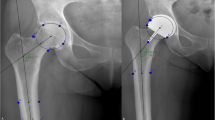
The aim of the study was to evaluate the effects of imageless computer-assisted surgery (CAS) on the accuracy of positioning of the femoral component and on the short-term clinical outcome in hip resurfacing (HR) using a randomised prospective design.
Methods
A total of 75 consecutive patients undergoing HR were randomly allocated to CAS and conventional implantation, respectively. Preoperatively and six months post-operatively standardised pelvic anteroposterior X-ray images, the total Western Ontario and McMaster Universities Osteoarthritis Index, the Harris Hip Score and the EQ-5D utility index were evaluated in a blinded manner. The primary end point of the study was a post-operative femoral component malpositioning in five degrees or more either varus or valgus absolute deviation from the planned stem shaft angle.
Results
Patient demographics and algofunctional scores did not differ between the CAS and conventional implantation samples. Using CAS fewer femoral components were positioned in five or more degrees absolute deviation (4/37 vs 12/38, Fisher’s exact p = 0.047; 95 % confidence interval for the primary end point’s incidence difference: +3 %; +39 %); the respective incidences of five or more degrees of varus deviation were 0/37 vs 5/38. One conversion to a stemmed prosthesis (CAS group) was performed for periprosthetic femoral neck fracture. Radiological signs of superolateral femoral neck/implant impingement were observed in two cases (one CAS-based and one conventional implantation).
Conclusions
The accuracy of femoral HR component positioning was significantly improved using CAS. However, one major complication necessitated early revision in the CAS group at six months of observation. Apart from that adverse event no inter-group differences were observed for the short-term clinical outcome. Future studies need to address the clinical long-term relevance of CAS in HR.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Prosser GH, Yates PJ, Wood DJ, Graves SE, de Steiger RN, Miller LN (2010) Outcome of primary resurfacing hip replacement: evaluation of risk factors for early revision. Acta Orthop 81(1):66–71
Corten K, MacDonald SJ (2010) Hip resurfacing data from national joint registries: what do they tell us? What do they not tell us? Clin Orthop Relat Res 468(2):351–357
Amstutz HC, Le Duff MJ, Campbell PA, Gruen TA, Wisk LE (2010) Clinical and radiographic results of metal-on-metal hip resurfacing with a minimum ten-year follow-up. J Bone Joint Surg Am 92(16):2663–2671
Amstutz HC, Campbell PA, Le Duff MJ (2004) Fracture of the neck of the femur after surface arthroplasty of the hip. J Bone Joint Surg Am 86-A(9):1874–1877
Kim PR, Beaulé PE, Laflamme GY, Dunbar M (2008) Causes of early failure in a multicenter clinical trial of hip resurfacing. J Arthroplasty 23(6 Suppl 1):44–49
Vail TP, Glisson RR, Dominguez DE, Kitaoka K, Ottaviano D (2008) Position of hip resurfacing component affects strain and resistance to fracture in the femoral neck. J Bone Joint Surg Am 90(9):1951–1960
Ganapathi M, Evans S, Roberts P (2008) Strain pattern following surface replacement of the hip. Proc Inst Mech Eng H 222(1):13–18
Shimmin AJ, Back D (2005) Femoral neck fractures following Birmingham hip resurfacing: a national review of 50 cases. J Bone Joint Surg Br 87(4):463–464
Freeman MA (1978) Some anatomical and mechanical considerations relevant to the surface replacement of the femoral head. Clin Orthop Relat Res (134):19–24
Beaulé PE, Lee JL, Le Duff MJ, Amstutz HC, Ebramzadeh E (2004) Orientation of the femoral component in surface arthroplasty of the hip. A biomechanical and clinical analysis. J Bone Joint Surg Am 86-A(9):2015–2021
Little CP, Ruiz AL, Harding IJ, McLardy-Smith P, Gundle R, Murray DW et al (2005) Osteonecrosis in retrieved femoral heads after failed resurfacing arthroplasty of the hip. J Bone Joint Surg Br 87(3):320–323
Langton DJ, Joyce TJ, Jameson SS, Lord J, Van Orsouw M, Holland JP et al (2011) Adverse reaction to metal debris following hip resurfacing: the influence of component type, orientation and volumetric wear. J Bone Joint Surg Br 93(2):164–171
Hart AJ, Skinner JA, Henckel J, Sampson B, Gordon F (2011) Insufficient acetabular version increases blood metal ion levels after metal-on-metal hip resurfacing. Clin Orthop Relat Res 469(9):2590–2597
Brin YS, Nikolaou VS, Joseph L, Zukor DJ, Antoniou J (2011) Imageless computer assisted versus conventional total knee replacement. A Bayesian meta-analysis of 23 comparative studies. Int Orthop 35(3):331–339
Leenders T, Vandevelde D, Mahieu G, Nuyts R (2002) Reduction in variability of acetabular cup abduction using computer assisted surgery: a prospective and randomized study. Comput Aided Surg 7(2):99–106
Ulrich SD, Bonutti PM, Seyler TM, Marker DR, Jones LC, Mont MA (2007) Outcomes-based evaluations supporting computer-assisted surgery and minimally invasive surgery for total hip arthroplasty. Expert Rev Med Devices 4(6):873–883
Ganapathi M, Vendittoli PA, Lavigne M, Günther KP (2009) Femoral component positioning in hip resurfacing with and without navigation. Clin Orthop Relat Res 467(5):1341–1347
Brooker AF, Bowerman JW, Robinson RA, Riley LH Jr (1973) Ectopic ossification following total hip replacement. Incidence and a method of classification. J Bone Joint Surg Am 55(8):1629–1632
Stucki G, Meier D, Stucki S, Michel BA, Tyndall AG, Dick W et al (1996) Evaluation of a German version of WOMAC (Western Ontario and McMaster Universities) Arthrosis Index. Z Rheumatol 55(1):40–49
Bellamy N, Buchanan WW, Goldsmith CH, Campbell J, Stitt LW (1988) Validation study of WOMAC: a health status instrument for measuring clinically important patient relevant outcomes to antirheumatic drug therapy in patients with osteoarthritis of the hip or knee. J Rheumatol 15(12):1833–1840
Beaton DE, Schemitsch E (2003) Measures of health-related quality of life and physical function. Clin Orthop Relat Res (413):90–105
Ethgen O, Bruyère O, Richy F, Dardennes C, Reginster JY (2004) Health-related quality of life in total hip and total knee arthroplasty. A qualitative and systematic review of the literature. J Bone Joint Surg Am 86-A(5):963–974
Sun Y, Stürmer T, Günther KP, Brenner H (1997) Reliability and validity of clinical outcome measurements of osteoarthritis of the hip and knee–a review of the literature. Clin Rheumatol 16(2):185–198
March L, Cross M, Tribe K, Lapsley H, Courtenay B, Brooks P (2002) Cost of joint replacement surgery for osteoarthritis: the patients’ perspective. J Rheumatol 29(5):1006–1014
Bachmeier CJ, March LM, Cross MJ, Lapsley HM, Tribe KL, Courtenay BG et al (2001) A comparison of outcomes in osteoarthritis patients undergoing total hip and knee replacement surgery. Osteoarthritis Cartilage 9(2):137–146
Harris WH (1969) Traumatic arthritis of the hip after dislocation and acetabular fractures: treatment by mold arthroplasty. An end-result study using a new method of result evaluation. J Bone Joint Surg Am 51(4):737–755
Saklad M (1941) Grading of patients for surgical procedures. Anesthesiology 2:281–284
Amstutz HC, Beaulé PE, Dorey FJ, Le Duff MJ, Campbell PA, Gruen TA (2004) Metal-on-metal hybrid surface arthroplasty: two to six-year follow-up study. J Bone Joint Surg Am 86-A(1):28–39
Beaulé PE, Dorey FJ, LeDuff M, Gruen T, Amstutz HC (2004) Risk factors affecting outcome of metal-on-metal surface arthroplasty of the hip. Clin Orthop Relat Res (418):87–93
Anglin C, Masri BA, Tonetti J, Hodgson AJ, Greidanus NV (2007) Hip resurfacing femoral neck fracture influenced by valgus placement. Clin Orthop Relat Res 465:71–79
Gautier E, Ganz K, Krügel N, Gill T, Ganz R (2000) Anatomy of the medial femoral circumflex artery and its surgical implications. J Bone Joint Surg Br 82(5):679–683
Beaulé PE, Campbell PA, Hoke R, Dorey F (2006) Notching of the femoral neck during resurfacing arthroplasty of the hip: a vascular study. J Bone Joint Surg Br 88(1):35–39
Beaulé PE, Amstutz HC (2005) Orientation of the femoral component in surface arthroplasty of the hip. J Bone Joint Surg Am 87(5):1162
McMinn D, Daniel J (2006) History and modern concepts in surface replacement. Proc Inst Mech Eng H 220(2):239–251
Davis ET, Olsen M, Zdero R, Waddell JP, Schemitsch EH (2008) Femoral neck fracture following hip resurfacing: the effect of alignment of the femoral component. J Bone Joint Surg Br 90(11):1522–1527
Seyler TM, Lai LP, Sprinkle DI, Ward WG, Jinnah RH (2008) Does computer-assisted surgery improve accuracy and decrease the learning curve in hip resurfacing? A radiographic analysis. J Bone Joint Surg Am 90(Suppl 3):71–80
Gallart X, Fernández-Valencia JA, Riba J, Bori G, García S, Carrillo S (2010) Alignment guided by computer navigation of the femoral component in hip resurfacing. Hip Int 20(Suppl 7 S7):43–47
Hart R, Sváb P, Filan P (2008) Intraoperative navigation in hip surface arthroplasty: a radiographic comparative analysis study. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg 128(4):429–434
Schnurr C, Nessler J, Koebke J, Michael JW, Eysel P, König DP (2010) Imageless computer navigation of hip resurfacing arthroplasty. Oper Orthop Traumatol 22(3):307–316
Krüger S, Zambelli PY, Leyvraz PF, Jolles BM (2009) Computer-assisted placement technique in hip resurfacing arthroplasty: improvement in accuracy? Int Orthop 33(1):27–33
Langton DJ, Jameson SS, Joyce TJ, Hallab NJ, Natu S, Nargol AV (2010) Early failure of metal-on-metal bearings in hip resurfacing and large-diameter total hip replacement: a consequence of excess wear. J Bone Joint Surg Br 92(1):38–46
Hartmann A, Lützner J, Kirschner S, Witzleb WC, Günther KP (2012) Do survival rate and serum ion concentrations 10 years after metal-on-metal hip resurfacing provide evidence for continued use? Clin Orthop Relat Res 470:3118–3126
Leslie IJ, Williams S, Isaac G, Ingham E, Fisher J (2009) High cup angle and microseparation increase the wear of hip surface replacements. Clin Orthop Relat Res 467(9):2259–2265
De Haan R, Pattyn C, Gill HS, Murray DW, Campbell PA, De Smet K (2008) Correlation between inclination of the acetabular component and metal ion levels in metal-on-metal hip resurfacing replacement. J Bone Joint Surg Br 90(10):1291–1297
Ybinger T, Kumpan W, Hoffart HE, Muschalik B, Bullmann W, Zweymüller K (2007) Accuracy of navigation-assisted acetabular component positioning studied by computed tomography measurements: methods and results. J Arthroplasty 22(6):812–817
Marker DR, Seyler TM, Jinnah RH, Delanois RE, Ulrich SD, Mont MA (2007) Femoral neck fractures after metal-on-metal total hip resurfacing: a prospective cohort study. J Arthroplasty 22(7 Suppl 3):66–71
Schnurr C, Michael JW, Eysel P, König DP (2009) Imageless navigation of hip resurfacing arthroplasty increases the implant accuracy. Int Orthop 33(2):365–372
Schnurr C, Münnich U, Eysel P, König DP (2010) Computer-assisted joint replacement surgery. Versicherungsmedizin 62(1):16–19
Olsen M, Schemitsch EH (2011) Avoiding short-term femoral neck fracture with imageless computer navigation for hip resurfacing. Clin Orthop Relat Res 469:1621–1626
Resubal JR, Morgan DA (2009) Computer-assisted vs conventional mechanical jig technique in hip resurfacing arthroplasty. J Arthroplasty 24(3):341–350
Acknowledgments
This study was partly supported by Zimmer GmbH, Winterthur, Switzerland; grants were provided for staff resources in data management and statistical evaluation. The authors declare no further conflicts of interest. We are grateful to Stephan Kirschner, M.D. for surgical contribution and critical interpretation of the results and to Heike Voigt and Brit Brethfeld for assistance in data management and in coordination of the study (all of them Department of Orthopaedics, University Hospital Dresden). We furthermore thank Katharina Schaper (Institute of Medical Biometry and Epidemiology, Witten/Herdecke) for assistance in data clearing and statistical analysis implementation.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Stiehler, M., Goronzy, J., Hartmann, A. et al. The First SICOT Oral Presentation Award 2011: Imageless computer-assisted femoral component positioning in hip resurfacing: a prospective randomised trial. International Orthopaedics (SICOT) 37, 569–581 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00264-012-1762-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00264-012-1762-8