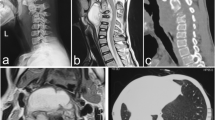
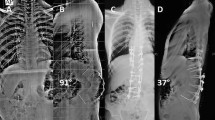
Abstract
Purpose
The outcomes of surgical treatment and related complications of post-tubercular kyphotic (PTK) deformity of the cervical spine or the cervico-thoracic spine were evaluated.
Methods
From January 2005 to October 2010, 12 cases with PTK (7 males, 5 females) with an average age of 30 years (range 21–43 years) formed the study group. There were ten patients with cervical deformities and two with cervico-thoracic kyphosis. Neurological function of all the patients was evaluated by the Japanese Orthopaedic Association (JOA) score and visual analogue scale (VAS) score. Two patients with severe cervico-thoracic deformity received modified skeleton traction pre-operatively. Ten patients underwent anterior debridement and reconstruction, using iliac crest or cages with autografts, while two patients with cervico-thoracic kyphosis received posterior instrumentation and fusion.
Results
The mean pre-operative focal kyphotic angle was 42.58° (range 30–67°), reducing to −8° (range −15–11°) postoperatively (at the last follow-up visit). The average operating time was 117.50 min (80–200 min) with an average blood loss of 110 ml (range 50–300 ml). Neurological assessment of all the patients, using the Japanese Orthopaedic Association (JOA) score and visual analogue scale (VAS) score, was improved significantly after surgery. All patients had solid fusion and no major complication was observed in the follow-up.
Conclusion
One-stage anterior debridement, instrumentation and fusion for cervical spinal TB and single posterior instrumentation for cervico-thoracic spinal TB followed by chemotherapy is practical to correct PTK. The procedure has the advantage of lower blood loss, effective kyphosis correction and minimal complications. To patients with severe deformity, skeletal traction seemed indispensible.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Jain A (2010) Tuberculosis of the spine: a fresh look at an old disease. J Bone Joint Surg Br 92:905–913
Ahmad S, Hussain T (2009) Anterior surgical interventions in spinal tuberculosis. JCPSP-J Coll Physici 19:500–505
Jain A, Dhammi I, Prashad B, Sinha S, Mishra P (2008) Simultaneous anterior decompression and posterior instrumentation of the tuberculous spine using an anterolateral extrapleural approach. J Bone Joint Surg Br 90:1477–1481
Yusof MI, Hassan E, Rahmat N, Yunus R (2009) Spinal tuberculosis: The association between pedicle involvement and anterior column damage and kyphotic deformity. Spine 34:713–717
Jain AK, Dhammi IK, Jain S, Kumar J (2010) Simultaneously anterior decompression and posterior instrumentation by extrapleural retroperitoneal approach in thoracolumbar lesions. Indian J Orthop 44:409–416
Avusoglu H, Kaya RA, Türkmenoğlu ON, Tuncer C, Colak I, Aydin Y (2008) A long-term follow-up study of anterior tibial allografting and instrumentation in the management of thoracolumbar tuberculous spondylitis. J Neurosurg 8:30–38
Rajasekaran S (2001) The natural history of post-tubercular kyphosis in children. Radiological signs which predict late increase in deformity. J Bone Joint Surg Br 83:954–962
Lee CK, Vessa P, Lee JK (1995) Chronic disabling low back pain syndrome caused by internal disc derangements: the results of disc excision and posterior lumbar interbody fusion. Spine 20:356–361
Rajasekaran S, Vijay K, Shetty AP (2010) Single-stage closing–opening wedge osteotomy of spine to correct severe post-tubercular kyphotic deformities of the spine: a 3-year follow-up of 17 patients. Eur Spine J 19:583–592
Kiran NAS, Vaishya S, Kale SS, Sharma BS, Mahapatra AK (2007) Surgical results in patients with tuberculosis of the spine and severe lower-extremity motor deficits: a retrospective study of 48 patients. J Neurosurg 6:320–326
Rajasekaran S, Soundarapandian S (1989) Progression of kyphosis in tuberculosis of the spine treated by anterior arthrodesis. J Bone Joint Surg Am 71:1314–1323
Nene A, Bhojraj S (2005) Results of nonsurgical treatment of thoracic spinal tuberculosis in adults. Spine J 5:79–84
Jain AK, Dhammi IK (2007) Tuberculosis of the spine: a review. Clin Orthop 460:39–49
Huang QS, Zheng C, Hu Y, Yin X, Xu H, Zhang G, Wang Q (2009) One-stage surgical management for children with spinal tuberculosis by anterior decompression and posterior instrumentation. Int Orthop 33:1385–1390
Hirakawa A, Miyamoto K, Masuda T, Fukuta S, Hosoe H, Iinuma N, Iwai C, Nishimoto H, Shimizu K (2010) Surgical outcome of 2-stage (posterior and anterior) surgical treatment using spinal instrumentation for tuberculous spondylitis. J Spinal Disord 23:133–138
Louw J (1990) Spinal tuberculosis with neurological deficit. Treatment with anterior vascularised rib grafts, posterior osteotomies and fusion. J Bone Joint Surg Br 72:686–693
Halpern EM, Bacon SA, Kitagawa T, Lewis SJ (2010) Posterior transdiscal three-column shortening in the surgical treatment of vertebral discitis/osteomyelitis with collapse. Spine 35:1316–1322
Moon MS, Moon JL, Kim SS, Moon YW (2007) Treatment of tuberculosis of the cervical spine: operative versus nonoperative. Clin Orthop 460:67–77
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Yuanyuan Chen contributed equally to the article.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, Y., Chen, Y., Yang, L. et al. The surgical treatment and related management for post-tubercular kyphotic deformity of the cervical spine or the cervico-thoracic spine. International Orthopaedics (SICOT) 36, 367–372 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00264-011-1438-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00264-011-1438-9