Abstract
Purpose
Here we introduce a two-stage procedure protocol for minimally invasive plate osteosynthesis (MIPO) to treat complex pilon fractures and evaluate surgical wound healing and infection rates after this method was applied in clinical practice.
Method
This is a retrospective study design. The protocol consisted of immediate (within eight to 24 hours) open reduction and internal fixation of the fibula, using a fibular plate or one third tubular plate and application of an external fixator spanning the ankle joint. Patients were discharged after initial stabilisation and revaluated approximately ten to 14 days after discharge. Formal open reconstruction of the articular surface using MIPO depended on whether soft tissue swelling had lessened. Artificial bone was then injected into the defect rather than open surgery. Objective evaluation criteria were wound infection rates. Objective criteria (amount of post-traumatic arthritis, range of ankle movement, number of arthrodeses) and subjective criteria (pain, swelling, restriction of work or leisure activities) were identified via chart and radiograph reviews, patient interviews and physical examination.
Results
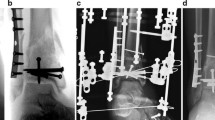
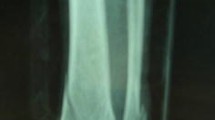
Twenty-nine patients, each with one pilon fracture were included. First-stage operations were performed from eight hours to seven days after injury, depending on whether the fracture was open or not. Average time from external fixation to open reduction and revision was one month (range 24–38 days); average time for the second-stage operation was 58 (range 45–110) minutes; average amount of haemorrhage was 400 (range 150–560) ml; average time of follow-up was 24 months and average time of healing was 6.7 (range five to 11.5) months after the second stage. There was no superficial or deep infection or wound-healing problem. All patients had normal functioning ankle joints.
Conclusion
Application of the two-stage procedure protocol with MIPO seems to play a key role in reducing infection rates associated with open reduction and internal fixation of pilon fractures. Its effectiveness in closed and open fractures will be further tested by a late randomised controlled study.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Barbieri R, Schenk R, Koval K, Aurori B, Aurori K (1996) Hybrid external fixation in the treatment of tibial plafond fractures. Clin Orthop 332:16–22
Barei DP, Nork SE, Mills WJ, Henley MB, Benirschke SK (2004) Complications associated with internal fixation of high-energy bicondylar tibial plateau fractures utilizing a two-incision technique. J Orthop Trauma 18:649–657
BhandariM ZM, Tornetta P III, SchmidtA TDC (2005) Intramedullary nailing following external fixation in femoral and tibial shaft fractures. J Orthop Trauma 19:140–144
Bonar SK, Marsh JL (1993) Unilateral external fixation for severe pilon fractures. Foot Ankle 14:57–64
Bone LB, Stegemann P, McNamara K, Seibel R (1993) External fixation of severely comminuted and open tibia pilon fractures. Clin Orthop 292:101–107
Carmack DB, Kaylor KL, Yaszemski MJ (2001) Structural stiffness and reducibility of external fixators placed in malalignment and malrotation. J Orthop Trauma 15:247–253
Clasper JC, Phillips SL (2005) Early failure of external fixation in the management of war injuries. J R Army Med Corps 151:81–86
Dickson KF, Montgomery S, Field J (2001) High energy plafond fractures treated by a spanning external fixator initially and followed by a second stage open reduction internal fixation of the articular surface: Preliminary report. Injury 32(suppl 4):SD92–SD98
Dougherty PJ, Vickaryous B, Conley E, Hickerson K (2003) A comparison of two military temporary femoral external fixators. Clin Orthop Relat Res 412:176–183
Egol KA, Tejwani NC, Capla EL, Wolinsky PL, Koval KJ (2005) Staged management of high-energy roximal tibia fractures (OTA types 41): The results of a prospective, standardized protocol. J Orthop Trauma 19:448–455
Nowotarski PJ, Turen CH, Brumback RJ, Scarboro JM (2000) Conversion of external fixation to intramedullary nailing for fractures of the shaft of the femur in multiply injured patients. J Bone Joint Surg Am 82:781–788
Holmes SM, Bomback D, Baumgaertner MR. J Orthop Trauma (2004) May-Jun;18(5):316–9
Sirkin M, Sanders R, DiPasquale T, Herscovici D Jr (2004) A staged protocol for soft tissue management in the treatment of complex pilon fractures. J Orthop Trauma 18(8 suppl):S32–S38
Tejwani NC, Achan P (2004) Staged management of high-energy proximal tibia fractures. Bull Hosp Jt Dis 62:62–66
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Tong, D., Ji, F., Zhang, H. et al. Two-stage procedure protocol for minimally invasive plate osteosynthesis technique in the treatment of the complex pilon fracture. International Orthopaedics (SICOT) 36, 833–837 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00264-011-1434-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00264-011-1434-0