Abstract
Purpose
The purpose of this study was to reach conclusions about the diagnosis and treatment of a series of patients with spondylodiscitis under haemodialysis treatment.
Methods
We collected and studied 23 patients included in a prospective database from two neighbouring hospitals. Descriptive statistical analysis was performed.
Results
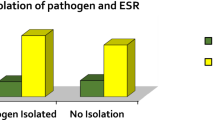
The diagnosis was frequently made very late and early negative cultures were not uncommon; magnetic resonance images allowed for an early diagnosis with accurate anatomical information. Empirical antibiotic treatment with prompt surgery produced good results in patients under risk of, or having neurological problems. Surgical approaches did not differ from pyogenic or tuberculous spondylodiscitis. Age in our series was not a predictive issue.
Conclusions
Whenever a patient under haemodialysis has symptoms of spinal disease, particularly back pain with fever, they should undergo an MRI. If diagnosis of spondylodiscitis is made prompt empirical antibiotherapy should be instituted. Blood cultures should be performed and tissue samples taken for cultures; however, culture outcome must not delay therapy. Early surgical decompression leads to good results.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Almirall J, Gonzales J, Rello J, Campistol JM, Montoliu J, De la Bellasca JP, Revert L, Gatell JM (1989) Infection of hemodialysis catheters: Incidence and mechanisms. Am J Nephrol 9:454–459
Carrage EJ (1997) Pyogenic vertebral osteomyelitis. J Bone Joint Surg Am 79:874–880
Carragee EJ (1997) The clinical use of magnetic resonance imaging in pyogenic vertebral osteomyelitis. Spine 22:780–785
Colmenero JD, Jimenez-Mejias ME, Sanchez-Lora FJ, Reguera JM, Palomino-Nicas J, Martos F, García de las Heras J, Pachon J (1997) Pyogenic tuberculous and brucellar vertebral osteomyelitis: a descriptive and comparative study of 219 cases. Ann Rheum Dis 56:709–715
Corrah TW, Enoch DA, Aliyu SH, Lever AM (2011) Bacteraemia and subsequent vertebral osteomyelitis: a retrospective review of 125 patients. Q J Med 104:201–207
Danner RL, Hartman BJ (1987) Update of spinal epidural abscess. 35 cases and review of literature. Rev Infect Dis 9:265–274
Dobdin JF, Miller MH, Steigbigel NH (1978) Septicemia in patients on chronic hemodialysis. Ann Intern Med 88:28–33
Grados F, Lescure FX, Senneville E, Flippo RM, Schmit JL, Fardellone P (2007) Suggestions for managing pyogenic (non-tuberculous) discitis in adults. Joint Bone Spine 74:133–139
Helewa R, Embil JM (2008) Risk factors for infectious spondylodiscitis in patients receiving hemodialysis. Infect Control Hosp Epidemiol 29:566–571
Helewa RM, Embil JM, Boughen CG, Cheang M, Goytan M, Zacharias JM, Trepman E (2008) Risk factors for infectious spondylodiscitis in patients receiving hemodialysis. Infec Control Hosp Epidemiol 29:567–571
Hoen B, Paul-Dauphin A, Hestin D (1988) EPIBACDIAL: A multicenter prospective study of risk factors for bacteriemia in chronic hemodialysis patients. J Am Soc Nephrol 9:869–876
Hoen B, Paul-Dauphin A, Hestin D, Mayeux D (1995) Risk factors for bacterial infections in chronic haemodialysis adult patients: A multicenter prospective survey. Nephrol Dial Transplant 10:377–381
Kessler M, Hoen B, Mayeux D, Hestin D, Fontenaille C (1993) Bacteriemia in patients on chronic haemodialysis. Nephron 64:95–100
Legrand E, Flipo RM, Guggengbuhl P, Masson C, Maillefert JF, Soubrier M et al, The Rheumatology Network Organization (2001) Management of nontuberculous infectious discitis. Treatments used in 110 patients admitted to 12 teaching hospitals in France. Joint Bone Spine 68:504–509
Malawski Sk, Lukawski S (1991) Pyogenic infection of the spine. Clin Orthop Relat Res 272:58–66
McHenry MC, Easley KA, Locker GA (2002) Vertebral osteomyelitis: long-term outcome for 253 patients from 7 Cleveland-area hospitals. Clin Infect Dis 34:1342–1350
Meyers SP, Wiener SN (1991) Diagnosis of hematogenous pyogenic vertebral osteomyelitis by using magnetic resonance imaging. Arch Intern Med 151:683–687
Modic MT, Feiglin DH, Piraino DW, Boumphrey F, Weinstein MA, Duchesneau PM, Rehm S (1985) Vertebral osteomyelitis assessment using MR. Radiology 157:157–166
Mylona E, Samarkos M, Kakalou E, Fanourgiakis P, Skoutelis A (2009) Pyogenic vertebral osteomyelitis: a systematic review of clinical characteristics. Semin Arthritis Rheum 39:10–17
Philipneri M, Al Aly Z (2003) Routine replacement of tunneled, cuffed, hemodialysis catheters eliminates paraspinal/vertebral infections in patients with catheter-associated bacteremia. Am J Nephrol 23:202–207
Punnaiah CM, Saquib H (2007) Report of 2 cases of vertebral osteomyelitis/discitis caused by Enterococcus faecalis in dialysis patients. Infect Dis Clin Pract 15:199–200
Roblot F, Beisnier JM, Juhel L, Vidal C, Ragot S, Bastides F, Le Moal G, Godet C, Mulleman D, Azaïs I, Becq-Giraudon B, Choutet P (2007) Optimal duration of antibiotic therapy in vertebral osteomyelitis. Semin Arthritis Rheum 36:269–277
Tsuchiya K, Yamaoka K (2004) Bacterial spondylodiscitis in the patients with hemodialysis. Spine (Phila Pa 1976) 29:2533–2537
Valero R, Castañeda O (2004) Clinical suspect about vertebral osteomielitis: back pain in patients with hemodyalisis by catheter related infection. Nefrologia 24:583–588
Yoon SH, Chung SK, Kim KJ, Kim HJ, Jin YJ, Kim HB (2010) Pyogenic vertebral osteomyelitis: identification of microorganism and laboratory markers used to predict clinical outcome. Eur Spine J 19:575–582
Conflicts of interest
The authors do not have conflicts of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cervan, A.M., Colmenero, J.D., Del Arco, A. et al. Spondylodiscitis in patients under haemodyalisis. International Orthopaedics (SICOT) 36, 421–426 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00264-011-1433-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00264-011-1433-1