Abstract
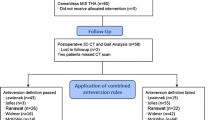
The purpose of this study was to perform an objective clinical and radiological assessment of the thrust plate prosthesis (TPP). Fifty-three prostheses were evaluated clinically using the Harris hip score (HHS), visual analog scale (VAS), and radiographically before surgery, at the time of discharge, and postoperatively after on average of 8.09 (range 4.61–9.93) years. The average HHS significantly (p ≤ 0.05) improved from 48 (range 18–77) points to 95 (range 46–100) points. The VAS revealed significant (p ≤ 0.05) reduction of pain at rest and under load. Radiographic analysis showed a considerable potential for osteolysis under the thrust plate. Sixteen prostheses revealed signs of radiolucent zones. In general, there was a good clinical outcome with no major limitations in function. Radiographic changes under the thrust plate indicate an adaptation processes resulting from changed biomechanics. This study suggests that the TPP could be a good alternative in total hip replacement in younger patients.
Résumé
Le propos de cette étude est d’évaluer cliniquement et radiologiquement une prothèse plaque (TPP). 53 prothèses plaques ont été évaluées cliniquement grâce au score de Harris et à l’échelle visuelle analogique et radiographiquement avant l’intervention, après la sortie de l’établissement, en post-opératoire avec une moyenne de 8,09 ans (de 4,61 à 9,93 ans). le score de Harris a augmenté de façon significative (p = 0.05) passant de 48 (18–77) à 95 (46–100) points. L’évaluation de la douleur par échelle visuelle analogique (p = 005) a montré une réduction de celle-ci. L’analyse radiographique a montré par contre un potentiel important de liserés sous la prothèse. 16 prothèses montrent des signes radiologiques d’appréciation difficile. ces prothèses démontrent qu’une bonne évolution clinique est possible avec peu de limitations fonctionnelles. La radiographie montre par contre des processus d’adaptation et de modifications osseuses secondaires aux sollicitations biomécaniques. Cette étude permet de penser que la prothèse TPP est une bonne alternative au remplacement de la hanche chez les sujets les plus jeunes.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alt F, Walker N (1999) Klinische und radiologische Resultate der Druckscheibenprothese im Vergleich zur ESKA-Schenkelhalsprothese. Orthop Praxis 35:419–427
Amstutz HC, Beaule PE, Dorey FJ et al (2004) Metal-on-metal hybrid surface arthroplasty: two to six-year follow-up study. J Bone Joint Surg Am 86:28–39
Brooker AF, Bowermann JW, Robinson RA, Riley LH (1973) Ectopic ossification following total hip replacement. Incidence and a method of classification. J Bone Joint Surg (Am) 55:1629–1632
Burgi M, Schenk R (1997) Finite element investigations of the proximal femur after implantation of the thrust plate prosthesis compared with findings in a post-mortem histological specimen in radiological follow-up examinations. In: Huggler AH, Jacob HAC (eds) The thrust plate hip prosthesis. Springer, Berlin, pp 48–62
Dunai FJ, Menge M (1996) Die Druckscheibenprothese - Erfahrungen der ersten 5 Jahre. Orthop Praxis 32:673–678
Engh CA, Bobyn JD, Glassman AH (1987) Porous-coated hip replacement. The factors governing bone ingrowth, stress shielding, and clinical results. J Bone Joint Surg (Br) 69(1):45–55
Faraj AA, Yousuf M (2005) Anterior thigh pain after cementless total hip arthroplasty. Int Orthop 29(3):149–151
Fink B, Ruther W (2000) Partial and total joint replacement in femur head necrosis. Orthopade 29(5):449–456
Fink B, Siegmuller C, Schneider T, Conrad S, Schmielau G, Ruther W (2000) Short- and medium-term results of the thrust plate prosthesis in patients with polyarthritis. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg 120(5–6):294–298
Fink B, Schneider T, Conrad S, Jaeger M, Protzen M, Ruther W (2002) The thrust plate prosthesis in patients with aseptic osteonecrosis of the femoral head. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg 122(9–10):499–505
Fink B, Wessel S, Deuretzbacher G, Protzen M, Ruther W (2007) Midterm results of ‘thrust plate’ prosthesis. J Arthroplasty 22(5):703–710
Goetz DD, Smith EJ, Harris WH (1994) The prevalence of femoral osteolysis associated with components inserted with or without cement in total hip replacements. A retrospective matched-pair series. J Bone Joint Surg (Am) 76(8):1121–1129
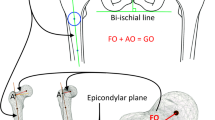
Gruber G, Wricke J, Sturz H (1997) Recommendations for standardized radiologic follow-up of thrust plate endoprosthesis. Aktuelle Radiologie 7(6):312–316
Huggler AH, Jacob HAC (1997) The thrust plate prosthesis: a new experience in hip surgery. In: Huggler AH, Jacob HAC (eds) The thrust plate hip prosthesis. Springer, Berlin, pp 1–24
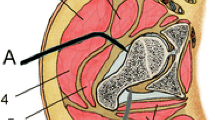
Huggler AH, Jacob HAC (1997) Biomechanical principles and design details of the thrust plate prosthesis. In: Huggler AH, Jacob HAC (eds) The thrust plate hip prosthesis. Springer, Berlin, pp 25–47
Huggler AH, Jacob HA, Bereiter H, Haferkorn M, Ryf C, Schenk R (1993) Long-term results with the uncemented thrust plate prosthesis (TPP). Acta Orthop Belg 59(Suppl 1):215–223
Ishaque BA, Wienbeck S, Basad E, Stürz H (2005) Clinical and radiological results of the thrust plate prosthesis in patients with aseptic necrosis of the femoral head. Z Orthop 143(6):622–630
Ishaque BA, Wienbeck S, Stürz H (2004) Midterm results and revisions of the thrust plate prosthesis (TPP). Z Orthop 142(1):25–32
Ishaque BA, Wienbeck S, Basad E, Stürz H (2004) Radiological analysis of the thrust plate prosthesis (TPP). Z Orthop 142(1):15–24
Karatosun V, Gunal I, Unver B, Gultekin A (2006) Thrust plate prosthesis for osteonecrosis of the femoral head: short-term results of 15 patients followed 2–6 years. J Orthop Sci 11(5):450–453
Karatosun V, Gunal I, Unver B (2005) Medium-term results of thrust plate prostheses for osteoarthritis of the hip. Bull Hosp Joint Dis 63(1–2):28–30
Krappel F, Harland U (1998) Die Druckscheibenprothese als neuartiges Konzept in der Behandlung von Dysplasiecoxarthrosen. Orthop Praxis 34:78–82
Lindgren JU, Svensson O, Mathieson EB (1996) Remodelling and pain after uncemented total hip replacement. Int Orthop 20(1):7–11
Menge M (2000) Acht Jahre Druckscheibenprothese - eine mittelfristige Bewertung. Orthop Praxis 36:143–151
Pellicci PM, Bostrom M, Poss R (1998) Posterior approach to total hip replacement using enhanced posterior soft tissue repair. Clin Orthop Relat Res 355:224–228
Steens W, Rosenbaum D, Goetze C, Gosheger G, van den Daele R, Steinbeck J (2003) Clinical and functional outcome of the thrust plate prosthesis: short an medium-term results. Clin Biomech 18(7):647–654
Suezawa Y (1983) Erste klinische Ergebnisse der neuen Druckscheiben-Hüfttotalendoprothese. Orthop Praxis 19:264–267
Witzleb WC, Arnold M et al (2008) Birmingham hip resurfacing arthroplasty: short term clinical and radiographic outcome. Eur J Med Res 13(1):39–46
Zelle BA, Gerich TG, Bastian L, Shuler FD, Pape HC, Krettek C (2004) Total hip arthroplasty in young patients using the thrust plate prosthesis: clinical and radiological results. Arch Orthop Trauma Surg 124(5):310–316
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Steens, W., v.d. Daele, R., Simon, U. et al. Clinical and radiological mid-term results of the thrust plate prosthesis. International Orthopaedics (SICOT) 33, 1519–1524 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00264-008-0714-9
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00264-008-0714-9