Abstract
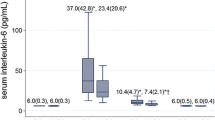
In this study, interleukin-6 (IL-6), C-reactive protein (CRP), and haemoglobin levels were evaluated to compare the degree of surgical invasion between mini and standard incisions in total hip arthroplasty (THA). Sixty-two patients admitted for primary cementless THA were enrolled in this randomised study. The patients were allocated to have surgery through either a mini incision of <10 cm or a standard incision of 15 cm. In each group, inflammatory responses were evaluated by IL-6, CRP, and haemoglobin levels before operation and one day after operation. Significant differences were not found in IL-6, CRP, and haemoglobin levels between both groups. At six months after surgery, there were no significant differences in postoperative Harris hip scores or radiographic evaluations between both groups. In conclusion, a 5.0 cm difference in the skin incision to the hip joint seemed to have no influence on the degree of surgical invasion during THA.
Résumé
Afin de mesurer l’importance de l’agression chirurgicale tissulaire dans les prothèses totales de hanche, incision standard, versus mini-invasifs, les niveaux d’Interleukin 6 (IL-6) de protéine C-réactive (CRP) et d’hémoglobine doivent être appréciés. 62 patients devant bénéficier d’une prothèse totale de hanche primaire sans ciment ont été enrôlés dans cette étude randomisée. Ces patients devaient bénéficier soit d’une mini-incision inférieure à 10 cm, soit d’une incision standard supérieure à 15 cm. Chaque groupe a été évalué avec ces différents facteurs biologiques avant l’intervention et un jour après intervention. Il n’a été trouvé aucune différence significative dans les deux groupes avec ces différents marqueurs Inteleukin, CRP et hémoglobine. Six mois après la chirurgie pas de différence significative non plus au niveau des scores de Harris ou au niveau de l’évaluation radiographique. En conclusion, la différence d’incision cutanée de 5 cm ne semble pas avoir d’influence sur l’importance des lésions des parties molles au cours d’une prothèse totale de hanche.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Baumann H, Gauldie J (1990) Regulation of hepatic acute phase plasma protein genes by hepatocyte stimulating factors and other mediators of inflammation. Mol Biol Med 7:147–159
Bilgen O, Atici T, Durak K, Karaeminogullari O, Bilgen MS (2001) C-reactive protein and erythrocyte sedimentation rates after total hip and total knee arthroplasty. J Int Med Res 29:7–12
Brady OH, Garbuz DS, Masri BA, Duncan CP (2000) The reliability and validity of the Vancouver classification of femoral fractures after hip replacement. J Arthroplasty 15:59–62
Delgado S, Lacy AM, Filella X, Castells A, Garcia-Valdecasas JC, Pique JM, Momblan D, Visa J (2001) Acute phase response in laparoscopic and open colectomy in colon cancer: randomized study. Dis Colon Rectum 44:638–646
Di Cesare PE, Chang E, Preston CF, Liu CJ (2005) Serum interleukin-6 as a marker of periprosthetic infection following total hip and knee arthroplasty. J Bone Joint Surg [Am] 87:1921–1927
DiGioia AM 3rd, Plakseychuk AY, Levision TJ, Jaramaz B (2003) Mini-incision technique for total hip arthroplasty with navigation. J Arthroplasty 18:123–128
Frndak PA, Mallory TH, Lombardi AV Jr (1993) Translateral surgical approach to the hip. The abductor muscle “split”. Clin Orthop 295:135–141
Fukushima R, Kawamura YJ, Saito H, Saito Y, Hashiguchi Y, Sawada T, Muto T (1996) Interleukin-6 and stress hormone responses after uncomplicated gasless laparoscopic-assisted and open sigmoid colectomy. Dis Colon Rectum 39:S29–S34
Goldstein WM, Branson JJ, Berland KA, Gordon AC (2003) Minimal-incision total hip arthroplasty. J Bone Joint Surg [Am] 85:33–38
Kehlet H (1999) Surgical stress response: does endoscopic surgery confer an advantage? World J Surg 23:801–807
Kennon RE, Keggi JM, Wetmore RS, Zatorski LE, Huo MH, Keggi KJ (2003) Total hip arthroplasty through a minimally invasive anterior surgical approach. J Bone Joint Surg [Am] 85:39–48
Kishimoto T (1989) The biology of interleukin-6. Blood 74:1–10
Ogonda L, Wilson R, Archbold P, Lawlor M, Humphreys P, O’Brien S, Beverland D (2005) A minimal-incision technique in total hip arthroplasty dose not improve early postoperative outcomes. J Bone Joint Surg [Am] 87:701–710
Ohzato H, Yoshizaki K, Nishimoto N, Ogata A, Tagoh H, Monden M, Gotoh M, Kishimoto T, Mori T (1992) Interleukin-6 as a new indicator of inflammatory status: detection of serum levels of interleukin-6 and C-reactive protein after surgery. Surgery 111:201–209
Sculco TP, Jordan LC, Walter WL (2004) Minimally invasive total hip arthroplasty: the Hospital for Special Surgery experience. Orthop Clin North Am 35:137–142
Suzuki K, Kawachi S, Sakai H, Nanke H, Morita S (2004) Mini-incision total hip arthroplasty: a quantitative assessment of laboratory data and clinical outcomes. J Orthop Sci 9:571–575
Targarona EM, Gracia E, Garriga J, Martinez-Bru C, Cortes M, Boluda R, Lerma L, Trias M (2002) Prospective randomized trial comparing conventional laparoscopic colectomy with hand-assisted laparoscopic colectomy: applicability, immediate clinical outcome, inflammatory response, and cost. Surg Endosc 16:234–239
Waldman BJ (2003) Advancements in minimally invasive total hip arthroplasty. Orthopedics 26:833–836
Wentz JF, Gurkan I, Jibodh SR (2002) Mini-incision total hip arthroplasty: a comparative assessment of perioperative outcomes. Orthopedics 25:1031–1043
White J, Kelly M, Dunsmuir R (1998) C-reactive protein level after total hip and total knee replacement. J Bone Joint Surg [Br] 85:909–911
Wirtz DC, Heller KD, Miltner O, Zilkens KW, Wolff JM (2000) Interleukin-6: a potential inflammatory marker after total joint replacement. Int Orthop 24:194–196
Woolson ST, Mow CS, Syquia JF, Lannin JV, Schurman DJ (2004) Comparison of primary total hip replacements performed with a standard incision or a mini-incision. J Bone Joint Surg [Am] 86:1353–1358
Wright JM, Crockett HC, Sculco TP (2001) Mini-incision for total hip arthroplasty. Orthopedics 7:18–20
Yamaguchi T, Naito M, Asayama I, Kambe T, Fujisawa M, Ishiko T (2003) The effect of posterolateral reconstruction on range of motion and muscle strength in total hip arthroplasty. J Arthroplasty 18:347–351
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shitama, T., Kiyama, T., Naito, M. et al. Which is more invasive—mini versus standard incisions in total hip arthroplasty?. International Orthopaedics (SICOT) 33, 1543–1547 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00264-008-0708-7
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00264-008-0708-7