Abstract
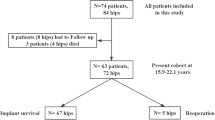
This study examined the long-term results of a metal-on-metal total hip replacement with a Metasul-lined cup. Twenty-nine total hip arthroplasties were performed in 27 young patients (mean age 49 years). Twenty-two patients (23 hips) were available for clinical and radiographic analysis after a mean duration of 99 months. Mean preoperative Harris hip score of 60 improved to 93 at most recent follow-up. One patient required revision of his cup for periacetabular osteolysis. Radiographic analysis showed osteolysis in another four hips. The high rate of osteolysis found in this series has not previously been reported with this type of implant. The length of follow-up in this series is greater than other reports in the literature and may explain this difference.
Résumé
Cette étude permet d’examiner les résultats à long terme des prothèses totales de hanche métal/métal de type Métasul. 29 prothèses totales de hanche ont été réalisées chez 27 patients relativement jeunes (âge moyen 49 ans). 22 patients (23 hanches) ont des résultats utilisables avec revue radiographique après un temps moyen post-opératoire de 99 mois. Le score moyen de Harris pré-opératoire a été amélioré de 60 à 93 au dernier suivi. Un patient a nécessité une révision de la cupule du fait d’une ostéolyse acétabulaire. L’analyse radiographique a montré une ostéolyse dans 4 autres hanches. Le taux important d’ostéolyse dans cette série n’a jamais été rapporté avec ce type d’implants. Le temps de surveillance de cette série est plus important que dans les autres séries de la littérature et peut expliquer cette différence.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Cozzolino FMM, Costa L, Scognamiglio D, Cozzolino A, Marino D, Milano C (2002) A comparative study on medium-term results of cementless acetabular components with metal-on-metal and metal-on-polyethylene articulations. J Orthopaed Traumatol 2(3):129–133
Delaunay CP (2004) Metal-on-metal bearings in cementless primary total hip arthroplasty. J Arthroplasty 19(Suppl 3):8
DeLee JG, Charnley J (1976) Radiological demarcation of cemented sockets in total hip replacement. Clin Orthop Relat Res 121:20–32
Dorr LD, Hilton KR, Wan Z, Markovich GD, Bloebaum R (1996) Modern metal on metal articulation for total hip replacements. Clin Orthop Relat Res 333:108–117
Dorr LD, Wan Z, Longjohn DB, Dubois B, Murken R (2000) Total hip arthroplasty with use of the Metasul metal-on-metal articulation. Four to seven-year results. J Bone Joint Surg Am 82:6
Harris WH (1969) Traumatic arthritis of the hip after dislocation and acetabular fractures: treatment by mold arthroplasty. An end-result study using a new method of result evaluation. J Bone Joint Surg Am 51:4
Heisel C, Silva M, Skipor AK, Jacobs JJ, Schmalzried TP (2005) The relationship between activity and ions in patients with metal-on-metal bearing hip prostheses. J Bone Joint Surg Am 87:4
Jacobs JJ, Hallab NJ (2006) Loosening and osteolysis associated with metal-on-metal bearings: a local effect of metal hypersensitivity? J Bone Joint Surg Am 88:6
Johnston RC, Fitzgerald RH Jr., Harris WH, Poss R, Muller ME, Sledge CB (1990) Clinical and radiographic evaluation of total hip replacement. A standard system of terminology for reporting results. J Bone Joint Surg Am 72:2
Kim SY, Kyung HS, Ihn JC, Cho MR, Koo KH, Kim CY (2004) Cementless Metasul metal-on-metal total hip arthroplasty in patients less than fifty years old. J Bone Joint Surg Am 86:11
Kitamura N, Naudie DD, Leung SB, Hopper RH Jr., Engh CA Sr. (2005) Diagnostic features of pelvic osteolysis on computed tomography: the importance of communication pathways. J Bone Joint Surg Am 87:7
Klapperich C, Graham J, Pruitt L, Ries MD (1999) Failure of a metal-on-metal total hip arthroplasty from progressive osteolysis. J Arthroplasty 14:7
Lazennec JL, Boyer PJ, Rousseau MA, Laude F, Catonne Y, Saillant G (2007) Poor eight year survival of second generation metal-on-metal cemented total hip arthroplasty. Presented at the annual meeting of the American Academy of Orthopaedic Surgeons, San Diego, CA
Migaud H, Jobin A, Chantelot C, Giraud F, Laffargue P, Duquennoy A (2004) Cementless metal-on-metal hip arthroplasty in patients less than 50 years of age: comparison with a matched control group using ceramic-on-polyethylene after a minimum 5-year follow-up. J Arthroplasty 19(Suppl 3):8
Milosev I, Trebse R, Kovac S, Cor A, Pisot V (2006) Survivorship and retrieval analysis of Sikomet metal-on-metal total hip replacements at a mean of seven years. J Bone Joint Surg Am 88:6
Prakash U, Mulgrew S, Espley AJ (1999) Effect of activity levels on polyethylene wear in Charnley low-friction arthroplasty. J R Coll Surg Edinb 44:3
Szuszczewicz ES, Schmalzried TP, Petersen TD (1997) Progressive bilateral pelvic osteolysis in a patient with McKee-Farrar metal-metal total hip prostheses. J Arthroplasty 12:7
Wagner M, Wagner H (2000) Medium-term results of a modern metal-on-metal system in total hip replacement. Clin Orthop Relat Res 379:123–133
Walter WL, Clabeaux J, Wright TM, Walsh W, Walter WK, Sculco TP (2005) Mechanisms for pumping fluid through cementless acetabular components with holes. J Arthroplasty 20:8
Walter WL, Walter WK, O’Sullivan M (2004) The pumping of fluid in cementless cups with holes. J Arthroplasty 19:2
Wasielewski RC, Jacobs JJ, Arthurs B, Rubash HE (2005) The acetabular insert-metal backing interface: an additional source of polyethylene wear debris. J Arthroplasty 20:7
Weber BG (1996) Experience with the Metasul total hip bearing system. Clin Orthop Relat Res 329(Suppl):69–77
Willert HG, Bertram H, Buchhorn GH (1990) Osteolysis in alloarthroplasty of the hip. The role of ultra-high molecular weight polyethylene wear particles. Clin Orthop Relat Res 258:108–121
Willert HG, Buchhorn GH, Fayyazi A, Flury R, Windler M, Koster G, Lohmann CH (2005) Metal-on-metal bearings and hypersensitivity in patients with artificial hip joints. A clinical and histomorphological study. J Bone Joint Surg Am 87:1
Young AM, Sychterz CJ, Hopper RH Jr., Engh CA (2002) Effect of acetabular modularity on polyethylene wear and osteolysis in total hip arthroplasty. J Bone Joint Surg Am 84:1
Zicat B, Engh CA, Gokcen E (1995) Patterns of osteolysis around total hip components inserted with and without cement. J Bone Joint Surg Am 77:3
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Holloway, I., Walter, W.L., Zicat, B. et al. Osteolysis with a cementless second generation metal-on-metal cup in total hip replacement. International Orthopaedics (SICOT) 33, 1537–1542 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00264-008-0679-8
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00264-008-0679-8