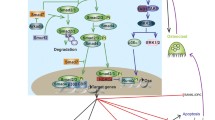
Abstract
We have recently shown that human recombinant BMP-6 (rhBMP-6), given systematically, can restore bone in animal models of osteoporosis. To further elucidate the underlying mechanisms of new bone formation following systemic application of BMPs, we conducted gene expression profiling experiments using bone samples of oophrectomised mice treated with BMP-6. Gene set enrichment analysis revealed enrichment of insulin-like growth factor-I and epidermal growth factor related pathways in animals treated with BMP-6. Significant upregulation of IGF-I and EGF expression in bones of BMP-6 treated mice was confirmed by quantitative PCR. To develop an in vitro model for evaluation of the effects of BMP-6 on cells of human origin, we cultured primary human osteoblasts. Treatment with rhBMP-6 accelerated cell differentiation as indicated by the formation of mineralised nodules by day 18 of culture versus 28–30 days in vehicle treated cultures. In addition, alkaline phosphatase gene expression and activity were dramatically increased upon BMP-6 treatment. Expression of IGF-I and EGF was upregulated in human osteoblast cells treated with BMP-6. These results collectively indicate that BMP-6 exerts its osteoinductive effect, at least in part, through IGF-I and EGF pathways, which can be observed both in a murine model of osteopenia and in human osteoblasts.
Résumé
Nous avons récemment pu mettre en évidence que la BMP-6 (rhBMP-6), administrée de façon systématique, pouvait améliorer la restauration du capital osseux de modèles animaux avec ostéoporose. Nous avons conduit une expérimentation utilisant des souris ovarieactomisées traitées par BMP-6. L’analyse a montré qu’il y avait un apport d’insulin like growth factor et d’épidermal growth factor chez les animaux traités par BMP-6. Pour développer un modèle in vitro nous avons étudié l’effet de la BMP-6 sur les cellules de type ostéoplasties d’origine humaine. Le traitement par BMP-6 accélère la différenciation cellulaire au 18ème jour alors que normalement cette différence est notée aux alentours du 28ème et 30ème jour. De plus, l’expression du gène de la phosphatase alkaline et l’activité sont augmentées par le traitement par la BMP-6, de même en ce qui concerne l’IGF-1 et l’EGF. Ces résultats nous permettent de penser que le BMP-6 a un effet ostéo conducteur notamment pour les pathologies intéressant IGF-1 et EGF. Nous avons observé ces effets dans un modèle animal avec ostéoplastie et sur les ostéoblastes humains.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bagi C, van der Meulen M, Brommage R, Rosen D, Sommer A (1995) The effect of systemically administered rhIGF-I/IGFBP-3 complex on cortical bone strength and structure in ovariectomized rats. Bone 16:559–565
Baylink DJ, Finkelman RD, Mohan S (1993) Growth factors to stimulate bone formation. J Bone Miner Res 2:S565–S572
Bilic R, Simic P, Jelic M, Stern-Padovan R, Dodig D, van Meerdervoort HP, Martinovic S, Ivankovic D, Pecina M, Vukicevic S (2006) Osteogenic protein-1 (BMP-7) accelerates healing of scaphoid non-union with proximal pole sclerosis. Int Orthop 30:128–134
Franceschi RT, Iyer BS, Cui Y (1994) Effects of ascorbic acid on collagen matrix formation and osteoblast differentiation in murine MC3T3-E1 cells. J Bone Miner Res 9:843–854
Jelic M, Pecina M, Haspl M, Kos J, Taylor K, Maticic D, McCartney J, Yin S, Rueger D, Vukicevic S (2001) Regeneration of articular cartilage chondral defects by osteogenic protein-1 (bone morphogenetic protein-7) in sheep. Growth Factors 19:101–113
Jones WK, Richmond EA, White K, Sasak H, Kusmik W, Smart J, Oppermann H, Rueger DC, Tucker RF (1994) Osteogenic protein-1 (OP-1) expression and processing in Chinese hamster ovary cells: isolation of a soluble complex containing the mature and pro-domains of OP-1. Growth Factors 11:215–225
Knutsen R, Honda Y, Strong DD, Sampath TK, Baylink DJ, Mohan S (1995) Regulation of insulin-like growth factor system components by osteogenic protein-1 in human bone cells. Endocrinology 136:857–865
Koch H, Jadlowiec JA, Campbell PG (2005) Insulin-like growth factor-I induces early osteoblast gene expression in human mesenchymal stem cells. Stem Cells Dev 14:621–631
Kratchmarova I, Blagoev B, Haack-Sorensen M, Kassem M, Mann M (2005) Mechanism of divergent growth factor effects in mesenchymal stem cell differentiation. Science 308:1472–1477
Livak KJ, Schmittgen TD (2001) Analysis of relative gene expression data using real-time quantitative PCR and the 2(-Delta Delta C(T)) method. Methods 25:402–408
Martinovic S, Simic P, Borovecki F, Vukicevic S (2004) Biology of bone morphogenetic proteins. In: Vukicevic S, Sampath K (eds) Bone morphogenetic proteins: from laboratory to clinical practice. Birkhäuser, Basel, pp 45–72
McCarthy TL, Centrella M, Canalis E (1989) Insulin-like growth factor (IGF) and bone. Connect Tissue Res 20:277–282
Mohan S (1993) Insulin-like growth factor binding proteins in bone cell regulation. Growth Reg 3:67–70
National Academy of Sciences, Institute of Laboratory Animal Resources Commission on Life Sciences (1996) Guide for the care and use of laboratory animals. National Academy Press, Washington, DC
Pecina M, Giltaij LR, Vukicevic S (2001) Orthopaedic applications of osteogenic protein-1 (BMP-7). Int Orthop 25:203–208
Pecina M, Haspl M, Jelic M, Vukicevic S (2003) Repair of a resistant tibial non-union with a recombinant bone morphogenetic protein-7 (rh-BMP-7). Int Orthop 27:320–321
Pecina M, Jelic M, Martinovic S, Haspl M, Vukicevic S (2002) Articular cartilage repair: the role of bone morphogenetic proteins. Int Orthop 26:131–136
Reddi AH (1997) Bone morphogenetic proteins: an unconventional approach to isolation of first mammalian morphogens. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev 8:11–20
Simic P, Buljan-Culej J, Orlic I, Borovecki F, Vukicevic S (2005) BMP-6 restores bone in osteoporotic aged rats and, unlike estradiol and PTH, restores trabecular bone in ovariectomized BMP-6 knockout mice. J Bone Miner Res 20:S8
Simic P, Culej JB, Orlic I, Grgurevic L, Draca N, Spaventi R, Vukicevic S (2006) Systemically administered bone morphogenetic protein-6 restores bone in aged ovariectomized rats by increasing bone formation and suppressing bone resorption. J Biol Chem 281:25509–25521
Subramanian A, Tamayo P, Mootha VK, Mukherjee S, Ebert BL, Gillette MA, Paulovich A, Pomeroy SL, Golub TR, Lander ES, Mesirov JP (2005) Gene set enrichment analysis: a knowledge-based approach for interpreting genome-wide expression profiles. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 102:15545–15550
van der Horst G, van Bezooijen RL, Deckers MM, Hoogendam J, Visser A, Lowik CW, Karperien M (2002) Differentiation of murine preosteoblastic KS483 cells depends on autocrine bone morphogenetic protein signaling during all phases of osteoblast formation. Bone 31:661–669
Vukicevic S, Luyten FP, Reddi AH (1989) Stimulation of the expression of osteogenic and chondrogenic phenotypes in vitro by osteogenin. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 86:8793–8797
Wozney JM (1992) The bone morphogenetic protein family and osteogenesis. Mol Reprod Dev 32:160–167
Xian CJ (2007) Roles of epidermal growth factor family in the regulation of postnatal somatic growth. Endocr Rev 28:284–296
Acknowledgments
The authors acknowledge the great help of Djurdjica Car and Mirjana Palcic for performing animal studies.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
W.A. Grasser and I. Orlic equally contributed to the results of this manuscript.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Grasser, W.A., Orlic, I., Borovecki, F. et al. BMP-6 exerts its osteoinductive effect through activation of IGF-I and EGF pathways. International Orthopaedics (SICO 31, 759–765 (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00264-007-0407-9
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00264-007-0407-9