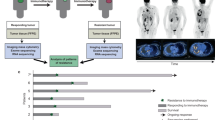
Abstract
Background
Immune checkpoint inhibitor (ICI) has an emerging role in several types of cancer. However, the mechanisms of acquired resistance (AR) to ICI have not been elucidated yet. To identify these mechanisms, we analyzed the pre- and post-ICI paired tumor samples in patients with AR.
Methods
Six patients with renal cell carcinoma, urothelial cell carcinoma, or head and neck cancer, who showed an initial response to ICI followed by progression and had available paired tissue samples, were retrospectively analyzed. Whole exome sequencing, RNA sequencing, and multiplex immunohistochemistry were performed on pre-treatment and resistant tumor samples.
Results
The median time to AR was 370 days (range, 210 to 739). Increased expression of alternative immune checkpoints including TIM3, LAG3, and PD-1 as well as increased CD8+ tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes were observed in post-treatment tumor than in pre-treatment tumor of a renal cell carcinoma patient. In contrast, CD8+ T cells and immunosuppressive markers were all decreased at AR in another patient with human papillomavirus-positive head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. This patient had an evident APOBEC-associated signature, and the tumor mutation burden increased at AR. Resistant tumor tissue of this patient harbored a missense mutation (E542K) in PIK3CA. No significant aberrations of antigen-presenting machinery or IFN-γ pathway were detected in any patient.
Conclusions
Our study findings suggest that the observed increase in immunosuppressive markers after ICI might contribute to AR. Moreover, APOBEC-mediated PIK3CA mutagenesis might be an AR mechanism. To validate these mechanisms of AR, further studies with enough sample size are required.






Similar content being viewed by others
Availability of data and materials
The dataset used and/or analyzed during the current study is provided in the supplemental materials and additional materials are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
Abbreviations
- ICI:
-
Immune checkpoint inhibitor
- AR:
-
Acquired resistance
- PD-L1:
-
Programmed death-ligand 1
- TMB:
-
Tumor mutational burden
- PD-1:
-
Programmed cell death protein 1
- FFPE:
-
Formalin-fixed and paraffin-embedded
- LAG3:
-
Lymphocyte-activation gene 3
- TIM3:
-
T cell immunoglobulin and mucin-domain containing-3
- HLA:
-
Human Leukocyte Antigen
- DAPI:
-
4′,6-diamidino-2-phenylindole
- WES:
-
Whole Exome Sequencing
- RNA-seq:
-
RNA sequencing
- FPKM:
-
Fragments per kilobase million
- DEG:
-
Differentially expressed genes
- HNSCC:
-
Head and neck squamous cell carcinoma
- TIL:
-
Tumor-infiltrating lymphocyte
- APOBEC:
-
Apolipoprotein B mRNA editing catalytic polypeptide-like
- HPV:
-
Human papillomavirus
References
Hugo W, Zaretsky JM, Sun L, Song C, Moreno BH, Hu-Lieskovan S, Berent-Maoz B, Pang J, Chmielowski B, Cherry G, Seja E, Lomeli S, Kong X, Kelley MC, Sosman JA, Johnson DB, Ribas A, Lo RS (2016) Genomic and transcriptomic features of response to Anti-PD-1 therapy in metastatic melanoma. Cell 165(1):35–44. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2016.02.065
Peng W, Chen JQ, Liu C, Malu S, Creasy C, Tetzlaff MT, Xu C, McKenzie JA, Zhang C, Liang X, Williams LJ, Deng W, Chen G, Mbofung R, Lazar AJ, Torres-Cabala CA, Cooper ZA, Chen PL, Tieu TN, Spranger S, Yu X, Bernatchez C, Forget MA, Haymaker C, Amaria R, McQuade JL, Glitza IC, Cascone T, Li HS, Kwong LN, Heffernan TP, Hu J, Bassett RL Jr, Bosenberg MW, Woodman SE, Overwijk WW, Lizee G, Roszik J, Gajewski TF, Wargo JA, Gershenwald JE, Radvanyi L, Davies MA, Hwu P (2016) Loss of PTEN promotes resistance to t cell-mediated immunotherapy. Cancer Discov 6(2):202–216. https://doi.org/10.1158/2159-8290.CD-15-0283
Gide TN, Wilmott JS, Scolyer RA, Long GV (2018) Primary and acquired resistance to immune checkpoint inhibitors in metastatic melanoma. Clin Cancer Res 24(6):1260–1270. https://doi.org/10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-17-2267
Zaretsky JM, Garcia-Diaz A, Shin DS, Escuin-Ordinas H, Hugo W, Hu-Lieskovan S, Torrejon DY, Abril-Rodriguez G, Sandoval S, Barthly L, Saco J, Homet Moreno B, Mezzadra R, Chmielowski B, Ruchalski K, Shintaku IP, Sanchez PJ, Puig-Saus C, Cherry G, Seja E, Kong X, Pang J, Berent-Maoz B, Comin-Anduix B, Graeber TG, Tumeh PC, Schumacher TN, Lo RS, Ribas A (2016) Mutations associated with acquired resistance to pd-1 blockade in melanoma. N Engl J Med 375(9):819–829. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMoa1604958
Gettinger S, Choi J, Hastings K, Truini A, Datar I, Sowell R, Wurtz A, Dong W, Cai G, Melnick MA, Du VY, Schlessinger J, Goldberg SB, Chiang A, Sanmamed MF, Melero I, Agorreta J, Montuenga LM, Lifton R, Ferrone S, Kavathas P, Rimm DL, Kaech SM, Schalper K, Herbst RS, Politi K (2017) Impaired HLA class i antigen processing and presentation as a mechanism of acquired resistance to immune checkpoint inhibitors in lung cancer. Cancer Discov 7(12):1420–1435. https://doi.org/10.1158/2159-8290.CD-17-0593
Tran E, Robbins PF, Lu YC, Prickett TD, Gartner JJ, Jia L, Pasetto A, Zheng Z, Ray S, Groh EM, Kriley IR, Rosenberg SA (2016) T-Cell transfer therapy targeting mutant kras in cancer. N Engl J Med 375(23):2255–2262. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJMoa1609279
Anagnostou V, Smith KN, Forde PM, Niknafs N, Bhattacharya R, White J, Zhang T, Adleff V, Phallen J, Wali N, Hruban C, Guthrie VB, Rodgers K, Naidoo J, Kang H, Sharfman W, Georgiades C, Verde F, Illei P, Li QK, Gabrielson E, Brock MV, Zahnow CA, Baylin SB, Scharpf RB, Brahmer JR, Karchin R, Pardoll DM, Velculescu VE (2017) Evolution of neoantigen landscape during immune checkpoint blockade in non-small cell lung cancer. Cancer Discov 7(3):264–276. https://doi.org/10.1158/2159-8290.CD-16-0828
Efremova M, Rieder D, Klepsch V, Charoentong P, Finotello F, Hackl H, Hermann-Kleiter N, Lower M, Baier G, Krogsdam A, Trajanoski Z (2018) Targeting immune checkpoints potentiates immunoediting and changes the dynamics of tumor evolution. Nat Commun 9(1):32. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-017-02424-0
Koyama S, Akbay EA, Li YY, Herter-Sprie GS, Buczkowski KA, Richards WG, Gandhi L, Redig AJ, Rodig SJ, Asahina H, Jones RE, Kulkarni MM, Kuraguchi M, Palakurthi S, Fecci PE, Johnson BE, Janne PA, Engelman JA, Gangadharan SP, Costa DB, Freeman GJ, Bueno R, Hodi FS, Dranoff G, Wong KK, Hammerman PS (2016) Adaptive resistance to therapeutic PD-1 blockade is associated with upregulation of alternative immune checkpoints. Nat Commun 7:10501. https://doi.org/10.1038/ncomms10501
Syn NL, Teng MWL, Mok TSK, Soo RA (2017) De-novo and acquired resistance to immune checkpoint targeting. Lancet Oncol 18(12):e731–e741. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1470-2045(17)30607-1
Eisenhauer EA, Therasse P, Bogaerts J, Schwartz LH, Sargent D, Ford R, Dancey J, Arbuck S, Gwyther S, Mooney M, Rubinstein L, Shankar L, Dodd L, Kaplan R, Lacombe D, Verweij J (2009) New response evaluation criteria in solid tumours: revised RECIST guideline (version 11). Eur J Cancer 45(2):228–247. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejca.2008.10.026
Kim S, Jang JY, Koh J, Kwon D, Kim YA, Paeng JC, Ock CY, Keam B, Kim M, Kim TM, Heo DS, Chung DH, Jeon YK (2019) Programmed cell death ligand-1-mediated enhancement of hexokinase 2 expression is inversely related to T-cell effector gene expression in non-small-cell lung cancer. J Exp Clin Cancer Res 38(1):462. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13046-019-1407-5
Li H, Durbin R (2010) Fast and accurate long-read alignment with Burrows-Wheeler transform. Bioinformatics 26(5):589–595. https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/btp698
McKenna A, Hanna M, Banks E, Sivachenko A, Cibulskis K, Kernytsky A, Garimella K, Altshuler D, Gabriel S, Daly M, DePristo MA (2010) The Genome Analysis Toolkit: a MapReduce framework for analyzing next-generation DNA sequencing data. Genome Res 20(9):1297–1303. https://doi.org/10.1101/gr.107524.110
Wang K, Li M, Hakonarson H (2010) ANNOVAR: functional annotation of genetic variants from high-throughput sequencing data. Nucleic Acids Res 38(16):e164. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkq603
Chalmers ZR, Connelly CF, Fabrizio D, Gay L, Ali SM, Ennis R, Schrock A, Campbell B, Shlien A, Chmielecki J, Huang F, He Y, Sun J, Tabori U, Kennedy M, Lieber DS, Roels S, White J, Otto GA, Ross JS, Garraway L, Miller VA, Stephens PJ, Frampton GM (2017) Analysis of 100,000 human cancer genomes reveals the landscape of tumor mutational burden. Genome Med 9(1):34. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13073-017-0424-2
Rosenthal R, McGranahan N, Herrero J, Taylor BS, Swanton C (2016) DeconstructSigs: delineating mutational processes in single tumors distinguishes DNA repair deficiencies and patterns of carcinoma evolution. Genome Biol 17:31. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13059-016-0893-4
Gao J, Aksoy BA, Dogrusoz U, Dresdner G, Gross B, Sumer SO, Sun Y, Jacobsen A, Sinha R, Larsson E, Cerami E, Sander C, Schultz N (2013) Integrative analysis of complex cancer genomics and clinical profiles using the cBioPortal. Sci Signal 6(269):pl1. https://doi.org/10.1126/scisignal.2004088
Cerami E, Gao J, Dogrusoz U, Gross BE, Sumer SO, Aksoy BA, Jacobsen A, Byrne CJ, Heuer ML, Larsson E, Antipin Y, Reva B, Goldberg AP, Sander C, Schultz N (2012) The cBio cancer genomics portal: an open platform for exploring multidimensional cancer genomics data. Cancer Discov 2(5):401–404. https://doi.org/10.1158/2159-8290.CD-12-0095
D’Aurizio R, Pippucci T, Tattini L, Giusti B, Pellegrini M, Magi A (2016) Enhanced copy number variants detection from whole-exome sequencing data using EXCAVATOR2. Nucleic Acids Res 44(20):e154. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkw695
Talevich E, Shain AH, Botton T, Bastian BC (2016) CNVkit: genome-wide copy number detection and visualization from targeted DNA sequencing. PLoS Comput Biol 12(4):e1004873. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pcbi.1004873
Dobin A, Davis CA, Schlesinger F, Drenkow J, Zaleski C, Jha S, Batut P, Chaisson M, Gingeras TR (2013) STAR: ultrafast universal RNA-seq aligner. Bioinformatics 29(1):15–21. https://doi.org/10.1093/bioinformatics/bts635
Li B, Dewey CN (2011) RSEM: accurate transcript quantification from RNA-Seq data with or without a reference genome. BMC Bioinformatics 12:323. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2105-12-323
Yoshihara K, Shahmoradgoli M, Martinez E, Vegesna R, Kim H, Torres-Garcia W, Trevino V, Shen H, Laird PW, Levine DA, Carter SL, Getz G, Stemke-Hale K, Mills GB, Verhaak RG (2013) Inferring tumour purity and stromal and immune cell admixture from expression data. Nat Commun 4:2612. https://doi.org/10.1038/ncomms3612
Newman AM, Liu CL, Green MR, Gentles AJ, Feng W, Xu Y, Hoang CD, Diehn M, Alizadeh AA (2015) Robust enumeration of cell subsets from tissue expression profiles. Nat Methods 12(5):453–457. https://doi.org/10.1038/nmeth.3337
da Huang W, Sherman BT, Lempicki RA (2009) Systematic and integrative analysis of large gene lists using DAVID bioinformatics resources. Nat Protoc 4(1):44–57. https://doi.org/10.1038/nprot.2008.211
Tate JG, Bamford S, Jubb HC, Sondka Z, Beare DM, Bindal N, Boutselakis H, Cole CG, Creatore C, Dawson E, Fish P, Harsha B, Hathaway C, Jupe SC, Kok CY, Noble K, Ponting L, Ramshaw CC, Rye CE, Speedy HE, Stefancsik R, Thompson SL, Wang S, Ward S, Campbell PJ, Forbes SA (2019) COSMIC: the Catalogue Of Somatic Mutations In Cancer. Nucleic Acids Res 47(D1):D941–D947. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gky1015
Landrum MJ, Lee JM, Benson M, Brown G, Chao C, Chitipiralla S, Gu B, Hart J, Hoffman D, Hoover J, Jang W, Katz K, Ovetsky M, Riley G, Sethi A, Tully R, Villamarin-Salomon R, Rubinstein W, Maglott DR (2016) ClinVar: public archive of interpretations of clinically relevant variants. Nucleic Acids Res 44(D1):D862–868. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkv1222
Chakravarty D, Gao J, Phillips SM, Kundra R, Zhang H, Wang J, Rudolph JE, Yaeger R, Soumerai T, Nissan MH, Chang MT, Chandarlapaty S, Traina TA, Paik PK, Ho AL, Hantash FM, Grupe A, Baxi SS, Callahan MK, Snyder A, Chi P, Danila D, Gounder M, Harding JJ, Hellmann MD, Iyer G, Janjigian Y, Kaley T, Levine DA, Lowery M, Omuro A, Postow MA, Rathkopf D, Shoushtari AN, Shukla N, Voss M, Paraiso E, Zehir A, Berger MF, Taylor BS, Saltz LB, Riely GJ, Ladanyi M, Hyman DM, Baselga J, Sabbatini P, Solit DB, Schultz N (2017) OncoKB: a precision oncology knowledge base. JCO Precis Oncol. https://doi.org/10.1200/PO.17.00011
Liu Y, He M, Wang D, Diao L, Liu J, Tang L, Guo S, He F, Li D (2017) HisgAtlas 1.0: a human immunosuppression gene database. Database (Oxford). https://doi.org/10.1093/database/bax094
Rooney MS, Shukla SA, Wu CJ, Getz G, Hacohen N (2015) Molecular and genetic properties of tumors associated with local immune cytolytic activity. Cell 160(1–2):48–61. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2014.12.033
Kanehisa M, Goto S (2000) KEGG: kyoto encyclopedia of genes and genomes. Nucleic Acids Res 28(1):27–30. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/28.1.27
Gao J, Shi LZ, Zhao H, Chen J, Xiong L, He Q, Chen T, Roszik J, Bernatchez C, Woodman SE, Chen PL, Hwu P, Allison JP, Futreal A, Wargo JA, Sharma P (2016) Loss of IFN-gamma pathway genes in tumor cells as a mechanism of resistance to anti-CTLA-4 therapy. Cell 167(2):397–404. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2016.08.069
Ayers M, Lunceford J, Nebozhyn M, Murphy E, Loboda A, Kaufman DR, Albright A, Cheng JD, Kang SP, Shankaran V, Piha-Paul SA, Yearley J, Seiwert TY, Ribas A, McClanahan TK (2017) IFN-gamma-related mRNA profile predicts clinical response to PD-1 blockade. J Clin Invest 127(8):2930–2940. https://doi.org/10.1172/JCI91190
Alexandrov LB, Nik-Zainal S, Wedge DC, Aparicio SA, Behjati S, Biankin AV, Bignell GR, Bolli N, Borg A, Borresen-Dale AL, Boyault S, Burkhardt B, Butler AP, Caldas C, Davies HR, Desmedt C, Eils R, Eyfjord JE, Foekens JA, Greaves M, Hosoda F, Hutter B, Ilicic T, Imbeaud S, Imielinski M, Jager N, Jones DT, Jones D, Knappskog S, Kool M, Lakhani SR, Lopez-Otin C, Martin S, Munshi NC, Nakamura H, Northcott PA, Pajic M, Papaemmanuil E, Paradiso A, Pearson JV, Puente XS, Raine K, Ramakrishna M, Richardson AL, Richter J, Rosenstiel P, Schlesner M, Schumacher TN, Span PN, Teague JW, Totoki Y, Tutt AN, Valdes-Mas R, van Buuren MM, van’t Veer L, Vincent-Salomon A, Waddell N, Yates LR, Australian Pancreatic Cancer Genome I, Consortium IBC, Consortium IM-S, PedBrain I, Zucman-Rossi J, Futreal PA, McDermott U, Lichter P, Meyerson M, Grimmond SM, Siebert R, Campo E, Shibata T, Pfister SM, Campbell PJ, Stratton MR (2013) Signatures of mutational processes in human cancer. Nature 500(7463):415–421. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature12477
Arce Vargas F, Furness AJS, Solomon I, Joshi K, Mekkaoui L, Lesko MH, Miranda Rota E, Dahan R, Georgiou A, Sledzinska A, Ben Aissa A, Franz D, Werner Sunderland M, Wong YNS, Henry JY, O’Brien T, Nicol D, Challacombe B, Beers SA, Melanoma TC, Renal TC, Lung TC, Turajlic S, Gore M, Larkin J, Swanton C, Chester KA, Pule M, Ravetch JV, Marafioti T, Peggs KS, Quezada SA (2017) Fc-optimized anti-CD25 depletes tumor-infiltrating regulatory t cells and synergizes with PD-1 blockade to eradicate established tumors. Immunity 46(4):577–586. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.immuni.2017.03.013
Roberts SA, Lawrence MS, Klimczak LJ, Grimm SA, Fargo D, Stojanov P, Kiezun A, Kryukov GV, Carter SL, Saksena G, Harris S, Shah RR, Resnick MA, Getz G, Gordenin DA (2013) An APOBEC cytidine deaminase mutagenesis pattern is widespread in human cancers. Nat Genet 45(9):970–976. https://doi.org/10.1038/ng.2702
Nik-Zainal S, Alexandrov LB, Wedge DC, Van Loo P, Greenman CD, Raine K, Jones D, Hinton J, Marshall J, Stebbings LA, Menzies A, Martin S, Leung K, Chen L, Leroy C, Ramakrishna M, Rance R, Lau KW, Mudie LJ, Varela I, McBride DJ, Bignell GR, Cooke SL, Shlien A, Gamble J, Whitmore I, Maddison M, Tarpey PS, Davies HR, Papaemmanuil E, Stephens PJ, McLaren S, Butler AP, Teague JW, Jonsson G, Garber JE, Silver D, Miron P, Fatima A, Boyault S, Langerod A, Tutt A, Martens JW, Aparicio SA, Borg A, Salomon AV, Thomas G, Borresen-Dale AL, Richardson AL, Neuberger MS, Futreal PA, Campbell PJ, Stratton MR, Breast Cancer Working Group of the International Cancer Genome C (2012) Mutational processes molding the genomes of 21 breast cancers. Cell 149(5):979–993. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2012.04.024
Henderson S, Chakravarthy A, Su X, Boshoff C, Fenton TR (2014) APOBEC-mediated cytosine deamination links PIK3CA helical domain mutations to human papillomavirus-driven tumor development. Cell Rep 7(6):1833–1841. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.celrep.2014.05.012
Paulson KG, Voillet V, McAfee MS, Hunter DS, Wagener FD, Perdicchio M, Valente WJ, Koelle SJ, Church CD, Vandeven N, Thomas H, Colunga AG, Iyer JG, Yee C, Kulikauskas R, Koelle DM, Pierce RH, Bielas JH, Greenberg PD, Bhatia S, Gottardo R, Nghiem P, Chapuis AG (2018) Acquired cancer resistance to combination immunotherapy from transcriptional loss of class I HLA. Nat Commun 9(1):3868. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-018-06300-3
Benci JL, Xu B, Qiu Y, Wu TJ, Dada H, Twyman-Saint Victor C, Cucolo L, Lee DSM, Pauken KE, Huang AC, Gangadhar TC, Amaravadi RK, Schuchter LM, Feldman MD, Ishwaran H, Vonderheide RH, Maity A, Wherry EJ, Minn AJ (2016) Tumor interferon signaling regulates a multigenic resistance program to immune checkpoint blockade. Cell 167(6):1540–1554. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2016.11.022
Sharma P, Hu-Lieskovan S, Wargo JA, Ribas A (2017) Primary, adaptive, and acquired resistance to cancer immunotherapy. Cell 168(4):707–723. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2017.01.017
Taube JM, Young GD, McMiller TL, Chen S, Salas JT, Pritchard TS, Xu H, Meeker AK, Fan J, Cheadle C, Berger AE, Pardoll DM, Topalian SL (2015) Differential expression of immune-regulatory genes associated with PD-L1 display in melanoma: implications for PD-1 pathway blockade. Clin Cancer Res 21(17):3969–3976. https://doi.org/10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-15-0244
Smith NJ, Fenton TR (2019) The APOBEC3 genes and their role in cancer: insights from human papillomavirus. J Mol Endocrinol. https://doi.org/10.1530/JME-19-0011
Alexandrov LB, Nik-Zainal S, Wedge DC, Campbell PJ, Stratton MR (2013) Deciphering signatures of mutational processes operative in human cancer. Cell Rep 3(1):246–259. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.celrep.2012.12.008
Lui VW, Hedberg ML, Li H, Vangara BS, Pendleton K, Zeng Y, Lu Y, Zhang Q, Du Y, Gilbert BR, Freilino M, Sauerwein S, Peyser ND, Xiao D, Diergaarde B, Wang L, Chiosea S, Seethala R, Johnson JT, Kim S, Duvvuri U, Ferris RL, Romkes M, Nukui T, Kwok-Shing Ng P, Garraway LA, Hammerman PS, Mills GB, Grandis JR (2013) Frequent mutation of the PI3K pathway in head and neck cancer defines predictive biomarkers. Cancer Discov 3(7):761–769. https://doi.org/10.1158/2159-8290.CD-13-0103
Lechner M, Frampton GM, Fenton T, Feber A, Palmer G, Jay A, Pillay N, Forster M, Cronin MT, Lipson D, Miller VA, Brennan TA, Henderson S, Vaz F, O’Flynn P, Kalavrezos N, Yelensky R, Beck S, Stephens PJ, Boshoff C (2013) Targeted next-generation sequencing of head and neck squamous cell carcinoma identifies novel genetic alterations in HPV + and HPV- tumors. Genome Med 5(5):49. https://doi.org/10.1186/gm453
Boichard A, Pham TV, Yeerna H, Goodman A, Tamayo P, Lippman S, Frampton GM, Tsigelny IF, Kurzrock R (2019) APOBEC-related mutagenesis and neo-peptide hydrophobicity: implications for response to immunotherapy. Oncoimmunology 8(3):1550341. https://doi.org/10.1080/2162402X.2018.1550341
Wang S, Jia M, He Z, Liu XS (2018) APOBEC3B and APOBEC mutational signature as potential predictive markers for immunotherapy response in non-small cell lung cancer. Oncogene 37(29):3924–3936. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41388-018-0245-9
Camacho M, Leon X, Fernandez-Figueras MT, Quer M, Vila L (2008) Prostaglandin E(2) pathway in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. Head Neck 30(9):1175–1181. https://doi.org/10.1002/hed.20850
Whiteside TL, Jackson EK (2013) Adenosine and prostaglandin e2 production by human inducible regulatory T cells in health and disease. Front Immunol 4:212. https://doi.org/10.3389/fimmu.2013.00212
Acknowledgements
This study was supported by a grant of the Korea Health Technology R&D Project “Strategic Center of Cell and Bio Therapy for Heart, Diabetes & Cancer” through the Korea Health Industry Development Institute (KHIDI), funded by the Ministry of Health & Welfare (MHW), Republic of Korea (grant number : HI17C2085). This study was also supported by Seoul National University Hospital Research Fund (No. 03-2015-0380).
Funding
This study was supported by a grant of the Korea Health Technology R&D Project “Strategic Center of Cell and Bio Therapy for Heart, Diabetes & Cancer” through the Korea Health Industry Development Institute (KHIDI), funded by the Ministry of Health & Welfare (MHW), Republic of Korea (Grant Number: HI17C2085). This study was also supported by Seoul National University Hospital Research Fund (No. 03-2015-0380).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Conception and design: SHY, BK, CYO; Development of methodology: SHY, JY, BK, CYO, JIK; Acquisition of data: BK, MK, TMK, DWK, DSH; Analysis and interpretation of data: SHY, JY, SPH, BK, CYO, JK, SK; Administrative, technical, or material support: BK, YKJ, KCJ, JIK; Study supervision: BK, DSH; All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Competing interest
The authors report no conflict of interest.
Ethics approval and consent to participate
The study protocol was reviewed and approved by the Institutional Review Board of Seoul National University Hospital (no. H-1809-144-978 and H-1506-092-681). We conducted the study in accordance with the Principles of the Declaration of Helsinki. Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study.
Consent for publication
Patients signed informed consent regarding publishing their data and photographs.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yoo, S.H., Yun, J., Keam, B. et al. Discovery of acquired molecular signature on immune checkpoint inhibitors in paired tumor tissues. Cancer Immunol Immunother 70, 1755–1769 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00262-020-02799-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00262-020-02799-y