Abstract
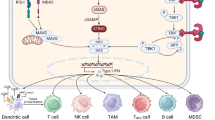
The clinical success of immune checkpoint blockade against diverse human cancers highlights the critical importance of insightful understanding into mechanisms underlying PD-L1 regulation. IFN-γ released by intratumoral lymphocytes regulates PD-L1 expression in tumor cells through JAK-STAT-IRF1 pathway, while the molecular events prime IRF1 to translocate into nucleus are still obscure. Here we identified STXBP6, previously recognized involving in SNARE complex assembly, negatively regulates PD-L1 transcription via retention of IRF1 in cytoplasm. IFN-γ exposure stimulates accumulation of cytosolic IRF1, which eventually saturates STXBP6 and triggers nuclear translocation of IRF1. Nuclear IRF1 in turn inhibits STXBP6 expression and thereby liberates more IRF1 to migrate to nucleus. Therefore, we identified a novel positive feedback loop between STXBP6 and IRF1 in regulation of PD-L1 expression in cancer. Furthermore, we demonstrate STXBP6 overexpression significantly inhibits T cell activation both in vitro and in vivo. These findings offer new insight into the complexity of PD-L1 expression in cancer and suggest a valuable measure to predict the response to PD-1/PD-L1-based immunotherapy.






Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
All data generated or analyzed during this study are included in this published article.
Abbreviations
- ATCC:
-
American Tissue Culture Collection
- ATRA:
-
All-trans retinoic acid
- BSA:
-
Bovine serum albumin
- ChIP:
-
Chromatin immunoprecipitation
- DAB:
-
Diaminobenzidine
- DAPI:
-
4′,6-Diamidino-2-phenylindole
- DMEM:
-
Dulbecco’s modified Eagle medium
- DTT:
-
Dithiothreitol
- ECL:
-
Enhanced chemiluminescence
- ELISA:
-
Enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay
- EMSA:
-
Electrophoretic mobility shift assay
- FBS:
-
Fetal bovine serum
- GAPDH:
-
Glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate dehydrogenase
- HBSS:
-
Hank's Balanced Salt Solution
- IHC:
-
Immunohistochemistry
- IL-2:
-
Interleukin-2
- PBS:
-
Phosphate-buffered saline
- PCR:
-
Polymerase chain reaction
- PFA:
-
Paraformaldehyde
- PVDF:
-
Polyvinylidene fluoride
- RIPA:
-
Radioimmunoprecipitation assay
- TLRs:
-
Toll-like receptors
- SD:
-
Standard deviation
- SLE:
-
Systemic lupus erythematosus
- STR:
-
Short tandem repeat
- SV:
-
Structural variation
References
Sharma P, Allison JP (2015) The future of immune checkpoint therapy. Science 348:56–61. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.aaa8172
Ribas A, Wolchok JD (2018) Cancer immunotherapy using checkpoint blockade. Science 359:1350–1355. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.aar4060
Gibney GT, Weiner LM, Atkins MB (2016) Predictive biomarkers for checkpoint inhibitor-based immunotherapy. Lancet Oncol 17:e542–e551. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1470-2045(16)30406-5
Pitt JM, Vetizou M, Daillere R et al (2016) Resistance mechanisms to immune-checkpoint blockade in cancer: tumor-intrinsic and -extrinsic factors. Immunity 44:1255–1269. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.immuni.2016.06.001
Havel JJ, Chowell D, Chan TA (2019) The evolving landscape of biomarkers for checkpoint inhibitor immunotherapy. Nat Rev Cancer 19:133–150. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41568-019-0116-x
Topalian SL, Taube JM, Anders RA, Pardoll DM (2016) Mechanism-driven biomarkers to guide immune checkpoint blockade in cancer therapy. Nat Rev Cancer 16:275–287. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrc.2016.36
Green MR, Monti S, Rodig SJ et al (2010) Integrative analysis reveals selective 9p24.1 amplification, increased PD-1 ligand expression, and further induction via JAK2 in nodular sclerosing Hodgkin lymphoma and primary mediastinal large B-cell lymphoma. Blood 116:3268–3277. https://doi.org/10.1182/blood-2010-05-282780
Goodman AM, Piccioni D, Kato S et al (2018) Prevalence of PDL1 amplification and preliminary response to immune checkpoint blockade in solid tumors. JAMA Oncol 4:1237–1244. https://doi.org/10.1001/jamaoncol.2018.1701
Casey SC, Tong L, Li Y et al (2016) MYC regulates the antitumor immune response through CD47 and PD-L1. Science 352:227–231. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.aac9935
Barsoum IB, Smallwood CA, Siemens DR, Graham CH (2014) A mechanism of hypoxia-mediated escape from adaptive immunity in cancer cells. Cancer Res 74:665–674. https://doi.org/10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-13-0992
Noman MZ, Desantis G, Janji B, Hasmim M, Karray S, Dessen P, Bronte V, Chouaib S (2014) PD-L1 is a novel direct target of HIF-1alpha, and its blockade under hypoxia enhanced MDSC-mediated T cell activation. J Exp Med 211:781–790. https://doi.org/10.1084/jem.20131916
Huang G, Wen Q, Zhao Y, Gao Q, Bai Y (2013) NF-kappaB plays a key role in inducing CD274 expression in human monocytes after lipopolysaccharide treatment. PLoS ONE 8:e61602. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0061602
Gowrishankar K, Gunatilake D, Gallagher SJ, Tiffen J, Rizos H, Hersey P (2015) Inducible but not constitutive expression of PD-L1 in human melanoma cells is dependent on activation of NF-kappaB. PLoS ONE 10:e0123410. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0123410
Chen L, Gibbons DL, Goswami S et al (2014) Metastasis is regulated via microRNA-200/ZEB1 axis control of tumour cell PD-L1 expression and intratumoral immunosuppression. Nat Commun 5:5241. https://doi.org/10.1038/ncomms6241
Pyzer AR, Stroopinsky D, Rosenblatt J et al (2017) MUC1 inhibition leads to decrease in PD-L1 levels via upregulation of miRNAs. Leukemia 31:2780–2790. https://doi.org/10.1038/leu.2017.163
Kataoka K, Shiraishi Y, Takeda Y et al (2016) Aberrant PD-L1 expression through 3'-UTR disruption in multiple cancers. Nature 534:402–406. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature18294
Burr ML, Sparbier CE, Chan YC et al (2017) CMTM6 maintains the expression of PD-L1 and regulates anti-tumour immunity. Nature 549:101–105. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature23643
Mezzadra R, Sun C, Jae LT et al (2017) Identification of CMTM6 and CMTM4 as PD-L1 protein regulators. Nature 549:106–110. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature23669
Zhang J, Bu X, Wang H et al (2018) Cyclin D-CDK4 kinase destabilizes PD-L1 via cullin 3-SPOP to control cancer immune surveillance. Nature 553:91–95. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature25015
Sun C, Mezzadra R, Schumacher TN (2018) Regulation and function of the PD-L1 Checkpoint. Immunity 48:434–452. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.immuni.2018.03.014
Zhang J, Dang F, Ren J, Wei W (2018) Biochemical aspects of PD-L1 regulation in cancer immunotherapy. Trends Biochem Sci 43:1014–1032. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tibs.2018.09.004
Lee SJ, Jang BC, Lee SW et al (2006) Interferon regulatory factor-1 is prerequisite to the constitutive expression and IFN-gamma-induced upregulation of B7–H1 (CD274). FEBS Lett 580:755–762. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.febslet.2005.12.093
Mimura K, Teh JL, Okayama H et al (2018) PD-L1 expression is mainly regulated by interferon gamma associated with JAK-STAT pathway in gastric cancer. Cancer Sci 109:43–53. https://doi.org/10.1111/cas.13424
Garcia-Diaz A, Shin DS, Moreno BH et al (2017) Interferon receptor signaling pathways regulating PD-L1 and PD-L2 Expression. Cell Rep 19:1189–1201. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.celrep.2017.04.031
Shao L, Hou W, Scharping NE et al (2019) IRF1 Inhibits antitumor immunity through the upregulation of PD-L1 in the tumor cell. Cancer Immunol Res 7:1258–1266. https://doi.org/10.1158/2326-6066.CIR-18-0711
Scales SJ, Hesser BA, Masuda ES, Scheller RH (2002) Amisyn, a novel syntaxin-binding protein that may regulate SNARE complex assembly. J Biol Chem 277:28271–28279. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M204929200
Constable JR, Graham ME, Morgan A, Burgoyne RD (2005) Amisyn regulates exocytosis and fusion pore stability by both syntaxin-dependent and syntaxin-independent mechanisms. J Biol Chem 280:31615–31623. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M505858200
Spolski R, Li P, Leonard WJ (2018) Biology and regulation of IL-2: from molecular mechanisms to human therapy. Nat Rev Immunol 18:648–659. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41577-018-0046-y
Fornes O, Castro-Mondragon JA, Khan A et al (2019) JASPAR 2020: update of the open-access database of transcription factor binding profiles. Nucleic Acids Res. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkz1001
Pizzoferrato E, Liu Y, Gambotto A et al (2004) Ectopic expression of interferon regulatory factor-1 promotes human breast cancer cell death and results in reduced expression of survivin. Cancer Res 64:8381–8388. https://doi.org/10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-04-2223
Xie RL, Gupta S, Miele A, Shiffman D, Stein JL, Stein GS, van Wijnen AJ (2003) The tumor suppressor interferon regulatory factor 1 interferes with SP1 activation to repress the human CDK2 promoter. J Biol Chem 278:26589–26596. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M301491200
Fragale A, Gabriele L, Stellacci E et al (2008) IFN regulatory factor-1 negatively regulates CD4+ CD25+ regulatory T cell differentiation by repressing Foxp3 expression. J Immunol 181:1673–1682. https://doi.org/10.4049/jimmunol.181.3.1673
Ramsauer K, Farlik M, Zupkovitz G, Seiser C, Kroger A, Hauser H, Decker T (2007) Distinct modes of action applied by transcription factors STAT1 and IRF1 to initiate transcription of the IFN-gamma-inducible gbp2 gene. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 104:2849–2854. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0610944104
Gao J, Senthil M, Ren B, Yan J, Xing Q, Yu J, Zhang L, Yim JH (2010) IRF-1 transcriptionally upregulates PUMA, which mediates the mitochondrial apoptotic pathway in IRF-1-induced apoptosis in cancer cells. Cell Death Differ 17:699–709. https://doi.org/10.1038/cdd.2009.156
Lin JR, Hu J (2013) SeqNLS: nuclear localization signal prediction based on frequent pattern mining and linear motif scoring. PLoS ONE 8:e76864. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0076864
Schaper F, Kirchhoff S, Posern G, Koster M, Oumard A, Sharf R, Levi BZ, Hauser H (1998) Functional domains of interferon regulatory factor I (IRF-1). Biochem J 335(Pt 1):147–157. https://doi.org/10.1042/bj3350147
Negishi H, Fujita Y, Yanai H et al (2006) Evidence for licensing of IFN-gamma-induced IFN regulatory factor 1 transcription factor by MyD88 in Toll-like receptor-dependent gene induction program. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 103:15136–15141. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0607181103
Luo XM, Ross AC (2006) Retinoic acid exerts dual regulatory actions on the expression and nuclear localization of interferon regulatory factor-1. Exp Biol Med (Maywood) 231:619–631. https://doi.org/10.1177/153537020623100517
Lessard CJ, Adrianto I, Ice JA et al (2012) Identification of IRF8, TMEM39A, and IKZF3-ZPBP2 as susceptibility loci for systemic lupus erythematosus in a large-scale multiracial replication study. Am J Hum Genet 90:648–660. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ajhg.2012.02.023
Leung YT, Shi L, Maurer K, Song L, Zhang Z, Petri M, Sullivan KE (2015) Interferon regulatory factor 1 and histone H4 acetylation in systemic lupus erythematosus. Epigenetics 10:191–199. https://doi.org/10.1080/15592294.2015.1009764
Zhang Z, Shi L, Song L, Ephrem E, Petri M, Sullivan KE (2015) Interferon regulatory factor 1 marks activated genes and can induce target gene expression in systemic lupus erythematosus. Arthritis Rheumatol 67:785–796. https://doi.org/10.1002/art.38964
Liu J, Berthier CC, Kahlenberg JM (2017) Enhanced inflammasome activity in systemic lupus erythematosus is mediated via type I interferon-induced up-regulation of interferon regulatory factor 1. Arthritis Rheumatol 69:1840–1849. https://doi.org/10.1002/art.40166
Liu M, Liu J, Hao S, Wu P, Zhang X, Xiao Y, Jiang G, Huang X (2018) Higher activation of the interferon-gamma signaling pathway in systemic lupus erythematosus patients with a high type I IFN score: relation to disease activity. Clin Rheumatol 37:2675–2684. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10067-018-4138-7
Fernandez SV, Snider KE, Wu YZ, Russo IH, Plass C, Russo J (2010) DNA methylation changes in a human cell model of breast cancer progression. Mutat Res 688:28–35. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mrfmmm.2010.02.007
Lenka G, Tsai MH, Lin HC et al (2017) Identification of methylation-driven, differentially expressed STXBP6 as a novel biomarker in lung adenocarcinoma. Sci Rep 7:42573. https://doi.org/10.1038/srep42573
Wang J, Duan Y, Meng QH, Gong R, Guo C, Zhao Y, Zhang Y (2018) Integrated analysis of DNA methylation profiling and gene expression profiling identifies novel markers in lung cancer in Xuanwei. China PLoS One 13:e0203155. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0203155
Funding
This work was supported by National Natural Science Foundation of China, No. 81672796 to Y.B.L. and No. 81171947 to H.H.W.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Y.B.L. conceived this project and interpreted data. Y.B.L. and H.H.W. wrote the manuscript. Y.B.L., Z.C.H., Y.L.W., M.M.Z. and X.Z.L. performed experiments and analyzed data. Y.B.L., H.H.W. and S.L.Y. supervised the whole study.
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Competing interests
All other authors have no conflicts of interest to disclose.
Ethical approval
This study was approved by the Sun Yat-sen University Institutional Review Board.
Consent for publication
All authors are aware and agree to the content of the paper and their authorships.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.







Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, Y., Huang, Z., Wei, Y. et al. Identification of STXBP6-IRF1 positive feedback loop in regulation of PD-L1 in cancer. Cancer Immunol Immunother 70, 275–287 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00262-020-02678-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00262-020-02678-6