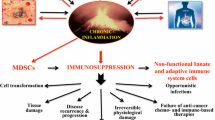
Abstract
Chronic inflammation typical to various chronic diseases is associated with immunosuppression, mediated primarily by immature myeloid-derived suppressor cells (MDSCs). A variety of factors induce MDSC differentiation arrest, thus manipulating the host’s immune function and suppressing the innate and adaptive immune systems, as reflected by their impaired status associated with down-regulated expression of the CD247 molecule. Such chronic inflammation-induced immunosuppressive features are also found in many tumors, generating tumor micro- and macro-environments that act as critical barriers to effective anti-tumor responses and therapies. This knowledge offers new and novel candidate immune targets for therapeutic interventions, in combination with more conventional approaches as chemotherapy, radiotherapy, and cancer cell targeted therapy. Therapeutic manipulation of chronic inflammation during cancer development is likely to enhance efficacy of treatments such as vaccinations, and adoptive T cell transfer, thus switching the chronic pro-cancer inflammatory environments into an anti-cancer milieu. Based on the functional relevance of immune networking in tumors, it is advantageous to merge monitoring immune biomarkers into the traditional patient’s categorization and treatment regiments, which will provide new prognostic and/or predictive tools to clinical practice. A better identification of environmental and tumor-specific inflammatory mechanisms will allow directing the clinical management of cancer toward a more personalized medicine.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Baniyash M (2004) TCR zeta-chain downregulation: curtailing an excessive inflammatory immune response. Nat Rev Immunol 4(9):675–687. doi:10.1038/nri1434
Ciszak L, Pawlak E, Kosmaczewska A, Potoczek S, Frydecka I (2007) Alterations in the expression of signal-transducing CD3 zeta chain in T cells from patients with chronic inflammatory/autoimmune diseases. Arch Immunol Ther Exp (Warsz) 55(6):373–386. doi:10.1007/s00005-007-0042-6
Vaknin I, Blinder L, Wang L, Gazit R, Shapira E, Genina O, Pines M, Pikarsky E, Baniyash M (2008) A common pathway mediated through Toll-like receptors leads to T- and natural killer-cell immunosuppression. Blood 111(3):1437–1447. doi:10.1182/blood-2007-07-100404
Bronstein-Sitton N, Cohen-Daniel L, Vaknin I, Ezernitchi AV, Leshem B, Halabi A, Houri-Hadad Y, Greenbaum E, Zakay-Rones Z, Shapira L, Baniyash M (2003) Sustained exposure to bacterial antigen induces interferon-gamma-dependent T cell receptor zeta down-regulation and impaired T cell function. Nat Immunol 4(10):957–964. doi:10.1038/ni975
Gabrilovich DI, Nagaraj S (2009) Myeloid-derived suppressor cells as regulators of the immune system. Nat Rev Immunol 9(3):162–174. doi:10.1038/nri2506
Bunt SK, Clements VK, Hanson EM, Sinha P, Ostrand-Rosenberg S (2009) Inflammation enhances myeloid-derived suppressor cell cross-talk by signaling through Toll-like receptor 4. J Leukoc Biol 85(6):996–1004. doi:10.1189/jlb.0708446
Sade-Feldman M, Kanterman J, Ish-Shalom E, Elnekave M, Horwitz E, Baniyash M (2013) Tumor necrosis factor-alpha blocks differentiation and enhances suppressive activity of immature myeloid cells during chronic inflammation. Immunity 38(3):541–554. doi:10.1016/j.immuni.2013.02.007
Bunt SK, Sinha P, Clements VK, Leips J, Ostrand-Rosenberg S (2006) Inflammation induces myeloid-derived suppressor cells that facilitate tumor progression. J Immunol 176(1):284–290. doi:10.1189/jlb.0708446
Serafini P, Carbley R, Noonan KA, Tan G, Bronte V, Borrello I (2004) High-dose granulocyte-macrophage colony-stimulating factor-producing vaccines impair the immune response through the recruitment of myeloid suppressor cells. Cancer Res 64(17):6337–6343. doi:10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-04-0757
Yang L, Huang J, Ren X, Gorska AE, Chytil A, Aakre M, Carbone DP, Matrisian LM, Richmond A, Lin PC, Moses HL (2008) Abrogation of TGF beta signaling in mammary carcinomas recruits Gr-1+CD11b+ myeloid cells that promote metastasis. Cancer Cell 13(1):23–35. doi:10.1016/j.ccr.2007.12.004
Zhao X, Rong L, Li X, Liu X, Deng J, Wu H, Xu X, Erben U, Wu P, Syrbe U, Sieper J, Qin Z (2012) TNF signaling drives myeloid-derived suppressor cell accumulation. J Clin Investig 122(11):4094–4104. doi:10.1172/JCI64115
Srivastava MK, Andersson A, Zhu L, Harris-White M, Lee JM, Dubinett S, Sharma S (2012) Myeloid suppressor cells and immune modulation in lung cancer. Immunotherapy 4(3):291–304. doi:10.2217/imt.11.178
Carswell EA, Old LJ, Kassel RL, Green S, Fiore N, Williamson B (1975) An endotoxin-induced serum factor that causes necrosis of tumors. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 72(9):3666–3670
Balkwill F (2009) Tumour necrosis factor and cancer. Nat Rev Cancer 9(5):361–371. doi:10.1038/nrc2628
Thompson AE, Rieder SW, Pope JE (2011) Tumor necrosis factor therapy and the risk of serious infection and malignancy in patients with early rheumatoid arthritis: a meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Arthritis Rheum 63(6):1479–1485. doi:10.1002/art.30310
Kopylov U, Ben-Horin S, Zmora O, Eliakim R, Katz LH (2012) Anti-tumor necrosis factor and postoperative complications in Crohn’s disease: systematic review and meta-analysis. Inflamm Bowel Dis 18(12):2404–2413. doi:10.1002/ibd.22954
Meyer C, Sevko A, Ramacher M, Bazhin AV, Falk CS, Osen W, Borrello I, Kato M, Schadendorf D, Baniyash M, Umansky V (2011) Chronic inflammation promotes myeloid-derived suppressor cell activation blocking antitumor immunity in transgenic mouse melanoma model. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 108(41):17111–17116. doi:10.1073/pnas.1108121108
Talmadge JE (2007) Pathways mediating the expansion and immunosuppressive activity of myeloid-derived suppressor cells and their relevance to cancer therapy. Clin Cancer Res 13(18 Pt 1):5243–5248. doi:10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-07-0182
Marigo I, Dolcetti L, Serafini P, Zanovello P, Bronte V (2008) Tumor-induced tolerance and immune suppression by myeloid derived suppressor cells. Immunol Rev 222:162–179. doi:10.1111/j.1600-065X.2008.00602.x
Martin F, Apetoh L, Ghiringhelli F (2012) Role of myeloid-derived suppressor cells in tumor immunotherapy. Immunotherapy 4(1):43–57. doi:10.2217/imt.11.154
Kanterman J, Sade-Feldman M, Baniyash M (2012) New insights into chronic inflammation-induced immunosuppression. Semin Cancer Biol 22(4):307–318. doi:10.1016/j.semcancer.2012.02.008
Fujimura T, Mahnke K, Enk AH (2010) Myeloid derived suppressor cells and their role in tolerance induction in cancer. J Dermatol Sci 59(1):1–6. doi:10.1016/j.jdermsci.2010.05.001
Apetoh L, Vegran F, Ladoire S, Ghiringhelli F (2011) Restoration of antitumor immunity through selective inhibition of myeloid derived suppressor cells by anticancer therapies. Curr Mol Med 11(5):365–372. doi:10.1016/j.molmed.2008.02.002
Kodumudi KN, Weber A, Sarnaik AA, Pilon-Thomas S (2012) Blockade of myeloid-derived suppressor cells after induction of lymphopenia improves adoptive T cell therapy in a murine model of melanoma. J Immunol 189(11):5147–5154. doi:10.4049/jimmunol.1200274
Zitvogel L, Apetoh L, Ghiringhelli F, Andre F, Tesniere A, Kroemer G (2008) The anticancer immune response: indispensable for therapeutic success? J Clin Investig 118(6):1991–2001. doi:10.1172/JCI35180
Srivastava MK, Zhu L, Harris-White M, Kar UK, Huang M, Johnson MF, Lee JM, Elashoff D, Strieter R, Dubinett S, Sharma S (2012) Myeloid suppressor cell depletion augments antitumor activity in lung cancer. PLoS One 7(7):e40677. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0040677
Najjar YG, Finke JH (2013) Clinical perspectives on targeting of myeloid derived suppressor cells in the treatment of cancer. Front Oncol 3:49. doi:10.3389/fonc.2013.00049
Youn JI, Gabrilovich DI (2010) The biology of myeloid-derived suppressor cells: the blessing and the curse of morphological and functional heterogeneity. Eur J Immunol 40(11):2969–2975. doi:10.1002/eji.201040895
Wang L, Chang EW, Wong SC, Ong SM, Chong DQ, Ling KL (2013) Increased myeloid-derived suppressor cells in gastric cancer correlate with cancer stage and plasma S100A8/A9 proinflammatory proteins. J Immunol 190(2):794–804. doi:10.4049/jimmunol.1202088
van Cruijsen H, van der Veldt AA, Vroling L, Oosterhoff D, Broxterman HJ, Scheper RJ, Giaccone G, Haanen JB, van den Eertwegh AJ, Boven E, Hoekman K, de Gruijl TD (2008) Sunitinib-induced myeloid lineage redistribution in renal cell cancer patients: CD1c+ dendritic cell frequency predicts progression-free survival. Clin Cancer Res 14(18):5884–5892. doi:10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-08-0656
Ko JS, Zea AH, Rini BI, Ireland JL, Elson P, Cohen P, Golshayan A, Rayman PA, Wood L, Garcia J, Dreicer R, Bukowski R, Finke JH (2009) Sunitinib mediates reversal of myeloid-derived suppressor cell accumulation in renal cell carcinoma patients. Clin Cancer Res 15(6):2148–2157. doi:10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-08-1332
Bose A, Lowe DB, Rao A, Storkus WJ (2012) Combined vaccine + axitinib therapy yields superior antitumor efficacy in a murine melanoma model. Melanoma Res 22(3):236–243. doi:10.1097/CMR.0b013e3283538293
Vincent J, Mignot G, Chalmin F, Ladoire S, Bruchard M, Chevriaux A, Martin F, Apetoh L, Rebe C, Ghiringhelli F (2010) 5-Fluorouracil selectively kills tumor-associated myeloid-derived suppressor cells resulting in enhanced T cell-dependent antitumor immunity. Cancer Res 70(8):3052–3061. doi:10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-09-3690
Suzuki E, Kapoor V, Jassar AS, Kaiser LR, Albelda SM (2005) Gemcitabine selectively eliminates splenic Gr-1+/CD11b+ myeloid suppressor cells in tumor-bearing animals and enhances antitumor immune activity. Clin Cancer Res 11(18):6713–6721. doi:10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-05-0883
Le HK, Graham L, Cha E, Morales JK, Manjili MH, Bear HD (2009) Gemcitabine directly inhibits myeloid derived suppressor cells in BALB/c mice bearing 4T1 mammary carcinoma and augments expansion of T cells from tumor-bearing mice. Int Immunopharmacol 9(7–8):900–909. doi:10.1016/j.intimp.2009.03.015
Bruchard M, Mignot G, Derangere V, Chalmin F, Chevriaux A, Vegran F, Boireau W, Simon B, Ryffel B, Connat JL, Kanellopoulos J, Martin F, Rebe C, Apetoh L, Ghiringhelli F (2013) Chemotherapy-triggered cathepsin B release in myeloid-derived suppressor cells activates the Nlrp3 inflammasome and promotes tumor growth. Nat Med 19(1):57–64. doi:10.1038/nm.2999
Lutsiak ME, Semnani RT, De Pascalis R, Kashmiri SV, Schlom J, Sabzevari H (2005) Inhibition of CD4(+)25+ T regulatory cell function implicated in enhanced immune response by low-dose cyclophosphamide. Blood 105(7):2862–2868. doi:10.1182/blood-2004-06-2410
Sevko A, Sade-Feldman M, Kanterman J, Michels T, Falk CS, Umansky L, Ramacher M, Kato M, Schadendorf D, Baniyash M, Umansky V (2013) Cyclophosphamide promotes chronic inflammation-dependent immunosuppression and prevents antitumor response in melanoma. J Investig Dermatol 133(6):1610–1619. doi:10.1038/jid.2012.444
Liu Y, Kosaka A, Ikeura M, Kohanbash G, Fellows-Mayle W, Snyder LA, Okada H (2013) Premetastatic soil and prevention of breast cancer brain metastasis. Neuro Oncol 15(7):891–903. doi:10.1093/neuonc/not031
Ma C, Kapanadze T, Gamrekelashvili J, Manns MP, Korangy F, Greten TF (2012) Anti-Gr-1 antibody depletion fails to eliminate hepatic myeloid-derived suppressor cells in tumor-bearing mice. J Leukoc Biol 92(6):1199–1206. doi:10.1189/jlb.0212059
Veltman JD, Lambers ME, van Nimwegen M, Hendriks RW, Hoogsteden HC, Aerts JG, Hegmans JP (2010) COX-2 inhibition improves immunotherapy and is associated with decreased numbers of myeloid-derived suppressor cells in mesothelioma. Celecoxib influences MDSC function. BMC Cancer 10:464. doi:10.1186/1471-2407-10-464
Serafini P, Meckel K, Kelso M, Noonan K, Califano J, Koch W, Dolcetti L, Bronte V, Borrello I (2006) Phosphodiesterase-5 inhibition augments endogenous antitumor immunity by reducing myeloid-derived suppressor cell function. J Exp Med 203(12):2691–2702. doi:10.1084/jem.20061104
Zhou J, Wu J, Chen X, Fortenbery N, Eksioglu E, Kodumudi KN, Pk EB, Dong J, Djeu JY, Wei S (2011) Icariin and its derivative, ICT, exert anti-inflammatory, anti-tumor effects, and modulate myeloid derived suppressive cells (MDSCs) functions. Int Immunopharmacol 11(7):890–898. doi:10.1016/j.intimp.2011.01.007
Chen SR, Xu XZ, Wang YH, Chen JW, Xu SW, Gu LQ, Liu PQ (2010) Icariin derivative inhibits inflammation through suppression of p38 mitogen-activated protein kinase and nuclear factor-kappaB pathways. Biol Pharm Bull 33(8):1307–1313. doi:10.1242/dev.089052
Schilling B, Sucker A, Griewank K, Zhao F, Weide B, Gorgens A, Giebel B, Schadendorf D, Paschen A (2013) Vemurafenib reverses immunosuppression by myeloid derived suppressor cells. Int J Cancer 133:1653–1664. doi:10.1002/ijc.28168
Diaz-Montero CM, Salem ML, Nishimura MI, Garrett-Mayer E, Cole DJ, Montero AJ (2009) Increased circulating myeloid-derived suppressor cells correlate with clinical cancer stage, metastatic tumor burden, and doxorubicin-cyclophosphamide chemotherapy. Cancer Immunol Immunother 58(1):49–59. doi:10.1007/s00262-008-0523-4
Mirza N, Fishman M, Fricke I, Dunn M, Neuger AM, Frost TJ, Lush RM, Antonia S, Gabrilovich DI (2006) All-trans-retinoic acid improves differentiation of myeloid cells and immune response in cancer patients. Cancer Res 66(18):9299–9307. doi:10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-06-1690
Michels T, Shurin GV, Naiditch H, Sevko A, Umansky V, Shurin MR (2012) Paclitaxel promotes differentiation of myeloid-derived suppressor cells into dendritic cells in vitro in a TLR4-independent manner. J Immunotoxicol 9(3):292–300. doi:10.3109/1547691X.2011.642418
Kodumudi KN, Woan K, Gilvary DL, Sahakian E, Wei S, Djeu JY (2010) A novel chemoimmunomodulating property of docetaxel: suppression of myeloid-derived suppressor cells in tumor bearers. Clin Cancer Res 16(18):4583–4594. doi:10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-10-0733
Djeu J, Wei S (2012) Chemoimmunomodulation of MDSCs as a novel strategy for cancer therapy. Oncoimmunology 1(1):121–122. doi:10.4161/onci.1.1.18074
Acknowledgments
We gratefully acknowledge the support of the Society of Research Associates of the Lautenberg Center, the Concern Foundation of Los Angeles, and the Harold B. Abramson Chair in Immunology. This study was supported by the Israel Science foundation (ISF), the Israeli Ministry of Health, the Joint German-Israeli Research Program (DKFZ-MOST), the Israel Cancer Research Fund (ICRF), and the United States-Israel Binational Science Foundation (BSF) and by the Joseph and Matilda Melnick Funds. We thank Dr. Lynn Wang for reading and commenting on the manuscript.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Moshe Sade-Feldman and Julia Kanterman contributed equally to this review.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Baniyash, M., Sade-Feldman, M. & Kanterman, J. Chronic inflammation and cancer: suppressing the suppressors. Cancer Immunol Immunother 63, 11–20 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00262-013-1468-9
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00262-013-1468-9