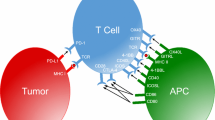
Abstract
Combinatory strategies are becoming of increasing interest in cancer immunotherapy. Costimulation by individual members of the immunoglobulin-like (Ig)- and TNF superfamily have already shown promising antitumor potential, thus prompting the exploration of their synergistic abilities in combinatorial approaches. Here, we pursued a targeted strategy with antibody-fusion proteins composed of a tumor-directed antibody and the extracellular domain of the costimulatory ligand B7.1, 4-1BBL, OX40L, GITRL or LIGHT, respectively. Costimulatory activity was assessed in an experimental setting where initial T cell activation was induced by a bispecific antibody (tumor-related antigen × CD3). Advantage of combined targeted costimulation was shown for either B7.1 or 4-1BBL with OX40L, GITRL, LIGHT and 4-1BBL in terms of T cell proliferation and IFN-γ release. Since encouraging results were obtained by the combination of B7.1 and 4-1BBL, we adapted the model system for a time-shift setting. Here, enhanced proliferation and granzyme B expression as well as reduced PD-1 expression on the T cell population demonstrated the benefit of costimulation-assisted restimulation. Finally, the antitumor potential of this combinatorial setting was confirmed in vivo in a lung metastasis mouse model. Thus, combinatorial approaches with costimulatory antibody–ligand fusion proteins seem a promising strategy to be further investigated for cancer immunotherapy.





Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- GITRL:
-
Glucocorticoid-induced TNF receptor ligand
- LIGHT:
-
Homologous to lymphotoxins, shows inducible expression and competes with herpes simplex virus glycoprotein D for herpesvirus entry mediator (HVEM), a receptor expressed by T lymphocytes
- TNFSF:
-
Tumor necrosis factor superfamily
- mAb:
-
Monoclonal antibody
- FAP:
-
Fibroblast activation protein
References
Pardoll D, Drake C (2012) Immunotherapy earns its spot in the ranks of cancer therapy. J Exp Med 209(2):201–209. doi:10.1084/jem.20112275
Schaer DA, Murphy JT, Wolchok JD (2012) Modulation of GITR for cancer immunotherapy. Curr Opin Immunol 24(2):217–224. doi:10.1016/j.coi.2011.12.011
Melero I, Martinez-Forero I, Dubrot J, Suarez N, Palazón A, Chen L (2009) Palettes of vaccines and immunostimulatory monoclonal antibodies for combination. Clin Cancer Res 15(5):1507–1509. doi:10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-08-2931
Takeda K, Kojima Y, Uno T, Hayakawa Y, Teng MW, Yoshizawa H, Yagita H, Gejyo F, Okumura K, Smyth MJ (2010) Combination therapy of established tumors by antibodies targeting immune activating and suppressing molecules. J Immunol 184(10):5493–5501. doi:10.4049/jimmunol.0903033
Serghides L, Bukczynski J, Wen T, Wang C, Routy JP, Boulassel MR, Sekaly RP, Ostrowski M, Bernard NF, Watts TH (2005) Evaluation of OX40 ligand as a costimulator of human antiviral memory CD8 T cell responses: comparison with B7.1 and 4–1BBL. J Immunol 175(10):6368–6377
Pan PY, Zang Y, Weber K, Meseck ML, Chen SH (2002) OX40 ligation enhances primary and memory cytotoxic T lymphocyte responses in an immunotherapy for hepatic colon metastases. Mol Ther 6(4):528–536
Uno T, Takeda K, Kojima Y, Yoshizawa H, Akiba H, Mittler RS, Gejyo F, Okumura K, Yagita H, Smyth MJ (2006) Eradication of established tumors in mice by a combination antibody-based therapy. Nat Med 12(6):693–698
Kocak E, Lute K, Chang X, May KF Jr, Exten KR, Zhang H, Abdessalam SF, Lehman AM, Jarjoura D, Zheng P, Liu Y (2006) Combination therapy with anti-CTL antigen-4 and anti-4-1BB antibodies enhances cancer immunity and reduces autoimmunity. Cancer Res 66(14):7276–7284
Curran MA, Kim M, Montalvo W, Al-Shamkhani A, Allison JP (2011) Combination CTLA-4 blockade and 4–1BB activation enhances tumor rejection by increasing T-cell infiltration, proliferation, and cytokine production. PLoS ONE 6(4):e19499. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0019499
Hirano F, Kaneko K, Tamura H, Dong H, Wang S, Ichikawa M, Rietz C, Flies DB, Lau JS, Zhu G, Tamada K, Chen L (2005) Blockade of B7–H1 and PD-1 by monoclonal antibodies potentiates cancer therapeutic immunity. Cancer Res 65(3):1089–1096
Driessens G, Kline J, Gajewski TF (2009) Costimulatory and coinhibitory receptors in anti-tumor immunity. Immunol Rev 229(1):126–144. doi:10.1111/j.1600-065X.2009.00771.x
Melero I, Hervas-Stubbs S, Glennie M, Pardoll DM, Chen L (2007) Immunostimulatory monoclonal antibodies for cancer therapy. Nat Rev Cancer 7(2):95–106
Murphy KA, Lechner MG, Popescu FE, Bedi J, Decker SA, Hu P, Erickson JR, O’Sullivan MG, Swier L, Salazar AM, Olin MR, Epstein AL, Ohlfest JR (2012) An in vivo immunotherapy screen of costimulatory molecules identifies Fc-OX40L as a potent reagent for the treatment of established murine gliomas. Clin Cancer Res 18(17):4657–4668. doi:10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-12-0990
Lechner MG, Russell SM, Bass RS, Epstein AL (2011) Chemokines, costimulatory molecules and fusion proteins for the immunotherapy of solid tumors. Immunotherapy 3(11):1317–1340. doi:10.2217/imt.11.115
Kanagavelu SK, Snarsky V, Termini JM, Gupta S, Barzee S, Wright JA, Khan WN, Kornbluth RS, Stone GW (2012) Vaccine. 30(4):691–702. doi:10.1016/j.vaccine.2011.11.088
Sharma RK, Schabowsky RH, Srivastava AK, Elpek KG, Madireddi S, Zhao H, Zhong Z, Miller RW, Macleod KJ, Yolcu ES, Shirwan H (2010) 4–1BB ligand as an effective multifunctional immunomodulator and antigen delivery vehicle for the development of therapeutic cancer vaccines. Cancer Res 70(10):3945–3954. doi:10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-09-4480
Wyzgol A, Müller N, Fick A, Munkel S, Grigoleit GU, Pfizenmaier K, Wajant H (2009) Trimer stabilization, oligomerization, and antibody-mediated cell surface immobilization improve the activity of soluble trimers of CD27L, CD40L, 41BBL, and glucocorticoid-induced TNF receptor ligand. J Immunol 183(3):1851–1861. doi:10.4049/jimmunol.0802597
Ascierto PA, Simeone E, Sznol M, Fu YX, Melero I (2010) Clinical experiences with anti-CD137 and anti-PD1 therapeutic antibodies. Semin Oncol 37(5):508–516. doi:10.1053/j.seminoncol.2010.09.008
Liu A, Hu P, Khawli LA, Epstein AL (2006) B7.1/NHS76: a new costimulator fusion protein for the immunotherapy of solid tumors. J Immunother 29(4):425–435
Liu R, Jiang W, Yang M, Guo H, Zhang Y, Wang J, Zhu H, Shi R, Fan D, Yang C, Zhu Z, Xie Y, Xiong D (2010) Efficient inhibition of human B-cell lymphoma in SCID mice by synergistic antitumor effect of human 4–1BB ligand/anti-CD20 fusion proteins and anti-CD3/anti-CD20 diabodies. J Immunother 33(5):500–509. doi:10.1097/CJI.0b013e3181d75c20
Burckhart T, Thiel M, Nishikawa H, Wüest T, Müller D, Zippelius A, Ritter G, Old L, Shiku H, Renner C (2010) Tumor-specific crosslinking of GITR as costimulation for immunotherapy. J Immunother 33(9):925–934. doi:10.1097/CJI.0b013e3181f3cc87
Hornig N, Kermer V, Frey K, Diebolder P, Kontermann RE, Müller D (2012) Combination of a bispecific antibody and costimulatory antibody-ligand fusion proteins for targeted cancer immunotherapy. J Immunother 35(5):418–429. doi:10.1097/CJI.0b013e3182594387
Zhang N, Sadun RE, Arias RS, Flanagan ML, Sachsman SM, Nien YC, Khawli LA, Hu P, Epstein AL (2007) Targeted and untargeted CD137L fusion proteins for the immunotherapy of experimental solid tumors. Clin Cancer Res 13(9):2758–2767
Müller D, Trunk G, Sichelstiel A, Zettlitz K, Quintanilla M, Kontermann RE (2008) Murine endoglin-specific single-chain Fv fragments for the analysis of vascular targeting strategies in mice. J Immunol Methods 339(1):90–98. doi:10.1016/j.jim.2008.08.008
Völkel T, Müller R, Kontermann RE (2004) Isolation of endothelial cell-specific human antibodies from a novel fully synthetic scFv library. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 317(2):515–521
Gerspach J, Muller D, Munkel S, Selchow O, Nemeth J, Noack M, Petrul H, Menrad A, Wajant H, Pfizenmaier K (2006) Restoration of membrane TNF-like activity by cell surface targeting and matrix metalloproteinase-mediated processing of a TNF prodrug. Cell Death Differ 13(2):273–284
Liao KW, Lo YC, Roffler SR (2000) Activation of lymphocytes by anti-CD3 single-chain antibody dimers expressed on the plasma membrane of tumor cells. Gene Ther 7(4):339–347
Cochran WG, Cox GM (1992) Experimental designs, 2nd edn. Wiley, Oxford
Croft M (2003) Co-stimulatory members of the TNFR family: keys to effective T-cell immunity? Nat Rev Immunol 3(8):609–620
Bodmer JL, Schneider P, Tschopp J (2002) The molecular architecture of the TNF superfamily. Trends Biochem Sci 27(1):19–26
Bremer E, de Bruyn M, Wajant H, Helfrich W (2009) Targeted cancer immunotherapy using ligands of the tumor necrosis factor super-family. Curr Drug Targets 10(2):94–103
Wajant H, Gerspach J, Pfizenmaier K (2005) Tumor therapeutics by design: targeting and activation of death receptors. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev 16(1):55–76
Müller N, Wyzgol A, Münkel S, Pfizenmaier K, Wajant H (2008) Activity of soluble OX40 ligand is enhanced by oligomerization and cell surface immobilization. FEBS J 275(9):2296–2304. doi:10.1111/j.1742-4658.2008.06382.x
Chattopadhyay K, Lazar-Molnar E, Yan Q, Rubinstein R, Zhan C, Vigdorovich V, Ramagopal UA, Bonanno J, Nathenson SG, Almo SC (2009) Sequence, structure, function, immunity: structural genomics of costimulation. Immunol Rev 229(1):356–386. doi:10.1111/j.1600-065X.2009.00778.x
Kober J, Leitner J, Klauser C, Woitek R, Majdic O, Stöckl J, Herndler-Brandstetter D, Grubeck-Loebenstein B, Reipert BM, Pickl WF, Pfistershammer K, Steinberger P (2008) The capacity of the TNF family members 4–1BBL, OX40L, CD70, GITRL, CD30L and LIGHT to costimulate human T cells. Eur J Immunol 38(10):2678–2688. doi:10.1002/eji.200838250
Yu P, Lee Y, Liu W, Chin RK, Wang J, Wang Y, Schietinger A, Philip M, Schreiber H, Fu YX (2004) Priming of naive T cells inside tumors leads to eradication of established tumors. Nat Immunol 5(2):141–149
Melero I, Bach N, Hellström KE, Aruffo A, Mittler RS, Chen L (1998) Amplification of tumor immunity by gene transfer of the co-stimulatory 4–1BB ligand: synergy with the CD28 co-stimulatory pathway. Eur J Immunol 28(3):1116–1121
Li G, Wu X, Zhang F, Li X, Sun B, Yu Y, Yin A, Deng L, Yin J, Wang X (2010) Triple expression of B7–1, B7–2 and 4–1BBL enhanced antitumor immune response against mouse H22 hepatocellular carcinoma. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol 137(4):695–703. doi:10.1007/s00432-010-0905-9
Habib-Agahi M, Jaberipour M, Searle PF (2009) 4–1BBL costimulation retrieves CD28 expression in activated T cells. Cell Immunol 256(1–2):39–46. doi:10.1016/j.cellimm.2009.01.003
Ronchetti S, Nocentini G, Bianchini R, Krausz LT, Migliorati G, Riccardi C (2007) Glucocorticoid-induced TNFR-related protein lowers the threshold of CD28 costimulation in CD8 + T cells. J Immunol 179(9):5916–5926
Tamada K, Shimozaki K, Chapoval AI, Zhu G, Sica G, Flies D, Boone T, Hsu H, Fu YX, Nagata S, Ni J, Chen L (2000) Modulation of T-cell-mediated immunity in tumor and graft-versus-host disease models through the LIGHT co-stimulatory pathway. Nat Med 6(3):283–289
Fife BT, Bluestone JA (2008) Control of peripheral T-cell tolerance and autoimmunity via the CTLA-4 and PD-1 pathways. Immunol Rev 224:166–182. doi:10.1111/j.1600-065X.2008.00662.x
Dong H, Strome SE, Salomao DR, Tamura H, Hirano F, Flies DB, Roche PC, Lu J, Zhu G, Tamada K, Lennon VA, Celis E, Chen L (2002) Tumor-associated B7–H1 promotes T-cell apoptosis: a potential mechanism of immune evasion. Nat Med 8(8):793–800
Topalian SL, Drake CG, Pardoll DM (2012) Targeting the PD-1/B7-H1(PD-L1) pathway to activate anti-tumor immunity. Curr Opin Immunol 24(2):207–212. doi:10.1016/j.coi.2011.12.009
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by a Grant from the Deutsche Krebshilfe (108743). We would like to thank Robert Lindner for technical support on the high‐performance liquid chromatography analysis.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hornig, N., Reinhardt, K., Kermer, V. et al. Evaluating combinations of costimulatory antibody–ligand fusion proteins for targeted cancer immunotherapy. Cancer Immunol Immunother 62, 1369–1380 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00262-013-1441-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00262-013-1441-7