Abstract
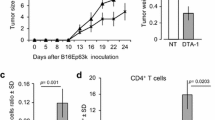
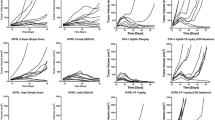
The systemic administration of an agonist antibody against glucocorticoid-induced tumor necrosis factor receptor related (GITR) protein has been shown to be effective in overcoming immune tolerance and promoting tumor rejection in a variety of murine tumor models. However, little is known regarding the functional consequence of ligation of GITR with its natural ligand (GITR-L) in the context of regulatory T cell (Treg) suppression in vivo. To determine the mechanism of GITR-L action in vivo, we generated a panel of tumor cell clones that express varying levels of GITR-L. The ectopic expression of GITR-L on the tumor cell surface was sufficient to enhance anti-tumor immunity and delay tumor growth in syngeneic BALB/c mice. Within the range examined, the extent of anti-tumor activity in vivo did not correlate with the level of GITR-L expression, as all clones tested exhibited a similar delay in tumor growth. The localized expression of GITR-L on tumor cells led to a significant increase in CD8+ T cell infiltration compared to the levels seen in control tumors. The increased proportion of CD8+ T cells was only observed locally at the tumor site and was not seen in the tumor draining lymph node. Depletion studies showed that CD8+ T cells, but not CD4+ T cells, were required for GITR-L mediated protection against tumor growth. These studies demonstrate that signaling between GITR-L and GITR in the tumor microenvironment promotes the infiltration of CD8+ T cells, which are essential for controlling tumor growth.







Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- GITR:
-
Glucocorticoid-induced TNF receptor related
- GITR-L:
-
GITR ligand
- Tregs:
-
Regulatory T cells
- ECD:
-
Extracellular domain
References
Baltz KM, Krusch M, Bringmann A, Brossart P, Mayer F, Kloss M, Baessler T, Kumbier I, Peterfi A, Kupka S, Kroeber S, Menzel D, Radsak MP, Rammensee HG, Salih HR (2007) Cancer immunoediting by GITR (glucocorticoid-induced TNF-related protein) ligand in humans: NK cell/tumor cell interactions. FASEB J 21(10):2442–2454
Calmels B, Paul S, Futin N, Ledoux C, Stoeckel F, Acres B (2005) Bypassing tumor-associated immune suppression with recombinant adenovirus constructs expressing membrane bound or secreted GITR-L. Cancer Gene Ther 12(2):198–205
Cohen AD, Diab A, Perales MA, Wolchok JD, Rizzuto G, Merghoub T, Huggins D, Liu C, Turk MJ, Restifo NP, Sakaguchi S, Houghton AN (2006) Agonist anti-GITR antibody enhances vaccine-induced CD8(+) T-cell responses and tumor immunity. Cancer Res 66(9):4904–4912
Curiel TJ, Coukos G, Zou L, Alvarez X, Cheng P, Mottram P, Evdemon-Hogan M, Conejo-Garcia JR, Zhang L, Burow M, Zhu Y, Wei S, Kryczek I, Daniel B, Gordon A, Myers L, Lackner A, Disis ML, Knutson KL, Chen L, Zou W (2004) Specific recruitment of regulatory T cells in ovarian carcinoma fosters immune privilege and predicts reduced survival. Nat Med 10(9):942–949
Fearon ER, Itaya T, Hunt B, Vogelstein B, Frost P (1988) Induction in a murine tumor of immunogenic tumor variants by transfection with a foreign gene. Cancer Res 48(11):2975–2980
Foulds KE, Zenewicz LA, Shedlock DJ, Jiang J, Troy AE, Shen H (2002) Cutting edge: CD4 and CD8 T cells are intrinsically different in their proliferative responses. J Immunol 168(4):1528–1532
Golgher D, Jones E, Powrie F, Elliott T, Gallimore A (2002) Depletion of CD25+ regulatory cells uncovers immune responses to shared murine tumor rejection antigens. Eur J Immunol 32(11):3267–3275
Grohmann U, Volpi C, Fallarino F, Bozza S, Bianchi R, Vacca C, Orabona C, Belladonna ML, Ayroldi E, Nocentini G, Boon L, Bistoni F, Fioretti MC, Romani L, Riccardi C, Puccetti P (2007) Reverse signaling through GITR ligand enables dexamethasone to activate IDO in allergy. Nat Med 13(5):579–586
Hanabuchi S, Watanabe N, Wang YH, Wang YH, Ito T, Shaw J, Cao W, Qin FX, Liu YJ (2006) Human plasmacytoid predendritic cells activate NK cells through glucocorticoid-induced tumor necrosis factor receptor-ligand (GITRL). Blood 107(9):3617–3623
Hartman ZC, Appledorn DM, Amalfitano A (2008) Adenovirus vector induced innate immune responses: Impact upon efficacy and toxicity in gene therapy and vaccine applications. Virus Res 132:1–14
Ichihara F, Kono K, Takahashi A, Kawaida H, Sugai H, Fujii H (2003) Increased populations of regulatory T cells in peripheral blood and tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes in patients with gastric and esophageal cancers. Clin Cancer Res 9(12):4404–4408
Ji HB, Liao G, Faubion WA, Abadia-Molina AC, Cozzo C, Laroux FS, Caton A, Terhorst C (2004) Cutting edge: the natural ligand for glucocorticoid-induced TNF receptor-related protein abrogates regulatory T cell suppression. J Immunol 172(10):5823–5827
Kim JD, Choi BK, Bae JS, Lee UH, Han IS, Lee HW, Youn BS, Vinay DS, Kwon BS (2003) Cloning and characterization of GITR ligand. Genes Immun 4(8):564–569
Ko K, Yamazaki S, Nakamura K, Nishioka T, Hirota K, Yamaguchi T, Shimizu J, Nomura T, Chiba T, Sakaguchi S (2005) Treatment of advanced tumors with agonistic anti-GITR mAb and its effects on tumor-infiltrating Foxp3 + CD25 + CD4 + regulatory T cells. J Exp Med 202(7):885–891
Kohm AP, Williams JS, Miller SD (2004) Cutting edge: ligation of the glucocorticoid-induced TNF receptor enhances autoreactive CD4 + T cell activation and experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis. J Immunol 172(8):4686–4690
Levings MK, Sangregorio R, Sartirana C, Moschin AL, Battaglia M, Orban PC, Roncarolo MG (2002) Human CD25 + CD4 + T suppressor cell clones produce transforming growth factor beta, but not interleukin 10, and are distinct from type 1 T regulatory cells. J Exp Med 196(10):1335–1346
Li Z, Mahesh SP, Kim BJ, Buggage RR, Nussenblatt RB (2003) Expression of glucocorticoid induced TNF receptor family related protein (GITR) on peripheral T cells from normal human donors and patients with non-infectious uveitis. J Autoimmun 21(1):83–92
Liyanage UK, Moore TT, Joo HG, Tanaka Y, Herrmann V, Doherty G, Drebin JA, Strasberg SM, Eberlein TJ, Goedegebuure PS, Linehan DC (2002) Prevalence of regulatory T cells is increased in peripheral blood and tumor microenvironment of patients with pancreas or breast adenocarcinoma. J Immunol 169(5):2756–2761
Muriglan SJ, Ramirez-Montagut T, Alpdogan O, Van Huystee TW, Eng JM, Hubbard VM, Kochman AA, Tjoe KH, Riccardi C, Pandolfi PP, Sakaguchi S, Houghton AN, Van Den Brink MR (2004) GITR activation induces an opposite effect on alloreactive CD4(+) and CD8(+) T cells in graft-versus-host disease. J Exp Med 200(2):149–157
Nocentini G, Giunchi L, Ronchetti S, Krausz LT, Bartoli A, Moraca R, Migliorati G, Riccardi C (1997) A new member of the tumor necrosis factor/nerve growth factor receptor family inhibits T cell receptor-induced apoptosis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 94(12):6216–6221
Onizuka S, Tawara I, Shimizu J, Sakaguchi S, Fujita T, Nakayama E (1999) Tumor rejection by in vivo administration of anti-CD25 (interleukin-2 receptor alpha) monoclonal antibody. Cancer Res 59(13):3128–3133
Ronchetti S, Zollo O, Bruscoli S, Agostini M, Bianchini R, Nocentini G, Ayroldi E, Riccardi C (2004) GITR, a member of the TNF receptor superfamily, is costimulatory to mouse T lymphocyte subpopulations. Eur J Immunol 34(3):613–622
Sakaguchi S (2004) Naturally arising CD4 + regulatory t cells for immunologic self-tolerance and negative control of immune responses. Annu Rev Immunol 22:531–562
Sakaguchi S, Fukuma K, Kuribayashi K, Masuda T (1985) Organ-specific autoimmune diseases induced in mice by elimination of T cell subset. I. Evidence for the active participation of T cells in natural self-tolerance; deficit of a T cell subset as a possible cause of autoimmune disease. J Exp Med 16(1):72–87
Sasada T, Kimura M, Yoshida Y, Kanai M, Takabayashi A (2003) CD4 + CD25 + regulatory T cells in patients with gastrointestinal malignancies: possible involvement of regulatory T cells in disease progression. Cancer 98(5):1089–1099
Sato E, Olson SH, Ahn J, Bundy B, Nishikawa H, Qian F, Jungbluth AA, Frosina D, Gnjatic S, Ambrosone C, Kepner J, Odunsi T, Ritter G, Lele S, Chen YT, Ohtani H, Old LJ, Odunsi K (2005) Intraepithelial CD8 + tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes and a high CD8 +/regulatory T cell ratio are associated with favorable prognosis in ovarian cancer. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 102(51):18538–18543
Shimizu J, Yamazaki S, Sakaguchi S (1999) Induction of tumor immunity by removing CD25+ CD4+ T cells: a common basis between tumor immunity and autoimmunity. J Immunol 163(10):5211–5218
Shimizu J, Yamazaki S, Takahashi T, Ishida Y, Sakaguchi S (2002) Stimulation of CD25(+)CD4(+) regulatory T cells through GITR breaks immunological self-tolerance. Nat Immunol 3(2):135–142
Shin HH, Lee MH, Kim SG, Lee YH, Kwon BS, Choi HS (2002) Recombinant glucocorticoid induced tumor necrosis factor receptor (rGITR) induces NOS in murine macrophage. FEBS Lett 514(2–3):275–280
Stephens GL, McHugh RS, Whitters MJ, Young DA, Luxenberg D, Carreno BM, Collins M, Shevach EM (2004) Engagement of glucocorticoid-induced TNFR family-related receptor on effector T cells by its ligand mediates resistance to suppression by CD4 + CD25 + T cells. J Immunol 173(8):5008–5020
Suri A, Shimizu J, Katz JD, Sakaguchi S, Unanue ER, Kanagawa O (2004) Regulation of autoimmune diabetes by non-islet-specific T cells—a role for the glucocorticoid-induced TNF receptor. Eur J Immunol 34(2):447–454
Sutmuller RP, van Duivenvoorde LM, van Elsas A, Schumacher TN, Wildenberg ME, Allison JP, Toes RE, Offringa R, Melief CJ (2001) Synergism of cytotoxic T lymphocyte-associated antigen 4 blockade and depletion of CD25(+) regulatory T cells in antitumor therapy reveals alternative pathways for suppression of autoreactive cytotoxic T lymphocyte responses. J Exp Med 194(6):823–832
Tone M, Tone Y, Adams E, Yates SF, Frewin MR, Cobbold SP, Waldmann H (2003) Mouse glucocorticoid-induced tumor necrosis factor receptor ligand is costimulatory for T cells. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 100(25):15059–15064
Tuyaerts S, Van Meirvenne S, Bonehill A, Heirman C, Corthals J, Waldmann H, Breckpot K, Thielemans K, Aerts JL (2007) Expression of human GITRL on myeloid dendritic cells enhances their immunostimulatory function but does not abrogate the suppressive effect of CD4+ CD25+ regulatory T cells. J Leukoc Biol 82(1):93–105
Uraushihara K, Kanai T, Ko K, Totsuka T, Makita S, Iiyama R, Nakamura T, Watanabe M (2003) Regulation of murine inflammatory bowel disease by CD25+ and CD25− CD4+ glucocorticoid-induced TNF receptor family-related gene + regulatory T cells. J Immunol 171(2):708–716
Wolf AM, Wolf D, Steurer M, Gastl G, Gunsilius E, Grubeck-Loebenstein B (2003) Increase of regulatory T cells in the peripheral blood of cancer patients. Clin Cancer Res 9(2):606–612
Woo EY, Chu CS, Goletz TJ, Schlienger K, Yeh H, Coukos G, Rubin SC, Kaiser LR, June CH (2001) Regulatory CD4(+)CD25(+) T cells in tumors from patients with early-stage non-small cell lung cancer and late-stage ovarian cancer. Cancer Res 61(12):4766–4772
Yu P, Lee Y, Liu W, Krausz T, Chong A, Schreiber H, Fu YX (2005) Intratumor depletion of CD4+ cells unmasks tumor immunogenicity leading to the rejection of late-stage tumors. J Exp Med 201(5):779–791
Zhou P, L’Italien L, Hodges D, Schebye XM (2007) Pivotal roles of CD4+ effector T cells in mediating agonistic anti-GITR mAb-induced-immune activation and tumor immunity in CT26 tumors. J Immunol 179(11):7365–7375
Acknowledgments
We thank Dr. Koteswara R. Chintalacharuvu, Caiyun Xuan, and Sepideh Afshar for critically reading the manuscript. We are also grateful to Letitia Wims for help with protein purification and Dr. B. S. Kwon for generously providing the cDNA of GITR-L. Flow cytometry was performed in the UCLA Jonsson Comprehensive Cancer Center (JCCC) and Center for AIDS Research Flow Cytometry Core Facility that is supported by National Institutes of Health awards CA-16042 and AI-28697, and by the JCCC, the UCLA AIDS Institute, the David Geffen School of Medicine at UCLA, and the UCLA Chancellor’s Office. J. S. Cho was supported in part by NIH Tumor Immunology training grant 5 T32 CA009120: 32.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cho, J.S., Hsu, J.V. & Morrison, S.L. Localized expression of GITR-L in the tumor microenvironment promotes CD8+ T cell dependent anti-tumor immunity. Cancer Immunol Immunother 58, 1057–1069 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00262-008-0622-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00262-008-0622-2