Abstract
Introduction
Amino-bisphosphonates are potent activators of human γδ T cells. The aim of our study was to evaluate the immunomodulating properties of a single-dose of zoledronic acid (ZA) on γδ T cells in a select group of disease-free breast cancer patients with osteopenia.
Materials and methods
Blood samples were obtained, from 23 patients, before and 7, 28, 56, 90 and 180 days after a single-dose (4 mg) of ZA and analyzed by flow cyometry.
Results
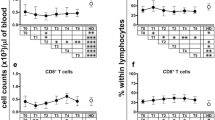
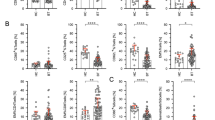
A significant decrease of the different γδ T cell subsets was observed: Naïve (CD3+/Vdelta2+/CD45RA+/CD27+) after 180 days (P < 0.01); Central Memory (CD3+/Vdelta2+/CD45RA-CD27+) after 28 (P < 0.05), 90 (P < 0.01) and 180 days (P < 0.01); and Effector Memory (CD3+/Vdelta2+/CD45RA-/CD27-) after 56 (P < 0.01) and 90 (P < 0.05) days. Based on the observed γδ T cells kinetics patients could be divided in two groups: “responders” that showed a significant decrease in total numbers of γδ T cells and “non-responders” that showed no significant change. However, in vitro phosphoantigen stimulation of patients cells did not show significant differences in terms of IFN-γ response by Vδ2 T cells.
Conclusion
We describe for the first time a long-lasting activation of effector subsets of γδ T cells in disease-free breast cancer patients after a single-dose of ZA. Our results highlight the need to further investigate the clinical significance of the immunomodulating properties of N-BPs.




Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- N-BPs:
-
Amino-bisphosphonates
- BPs:
-
Bisphosphonates
- ZA:
-
Zoledronic acid
- γ/δ T Ly:
-
γ/δ T lymphocytes
- IPP:
-
Isopentenyl-diphosphate
- CM:
-
Central memory
- EM:
-
Effector memory
- TE:
-
Terminal effectors
References
Green JR, Muller K, Jaeggi KA (1994) Preclinical pharmacology of CGP 42′446, a new, potent, heterocyclic bisphosphonate compound. J Bone Miner Res 9:745–751
Sietsema WK, Ebetino FH, Salvagno AM, Bevan JA (1989) Antiresorptive dose–response relationship across three generations of bisphosphonates. Drugs Exp Clin Res 15:389–396
Hillner BE, Ingle JN, Chlebowski RT, Gralow J, Yee GC, Janjan NA, Cauley JA et al (2004) American Society of Clinical Oncology 2003 update on the role of bisphosphonates and bone health issues in women with breast cancer. J Clin Oncol 22:1351
Saad F, Gleason D, Murray R et al (2003) Zoledronic acid is well tolerated for up to 24 months and significantly reduces skeletal complications in patients with advanced prostate cancer metastatic to bone. J Urol 169(suppl):394
Rosen LS, Gordon D, Tchekmedyian NS, Yanagihara R, Hirsh V, Krzakowski M, Pawlicki M et al (2004) Long-term efficacy and safety of zoledronic acid in the treatment of skeletal metastases in patients with non small cell lung carcinoma and other solid tumors: a randomized, phase III, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. Cancer 100:2613–2621
Van Beek E, Pieterman E, Cohen L, Lowick C, Papapoulous S (1999) Farnesyl pyrophosphate synthase is the molecular target of nitrogen-containing bisphosphonates. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 264:108–111
Zhang FL, Casey PJ (1996) Protein prenylation: molecular mechanisms and functional consequences. Annu Rev Biochem 65:241–269
Santini D, Vespasiani Gentilucci U, Vincenzi B, Picardi A, Vasaturo F, LaCesa A, Onori N et al (2003) The antineoplastic role of bisphosphonates: from basic research to clinical evidence. Ann Oncol 14:1468–1476
Kabelitz D, Marischen L, Oberg HH, Holtmeier W, Wesch D (2005) Epithelial defence by γ/δ T cells. Int Arch Allergy Immunol 137:73–81
Hiraga T, Williams PJ, Ueda A, Tamura D, Yoneda D (2004) Zoledronic acid inhibits visceral metastasis in the 4T1/luc mouse breast cancer model. Clin Cancer Res 10:4554–4567
Caccamo N, Meraviglia S, Ferlazzo V, Angelini D, Borsellino G, Poccia F, Battistini L et al (2005) Differential requirements for antigen or homeostatic cytokines for proliferation and differentiation of human Vgamma9Vdelta2 naïve, memory and effector T cell subsets. Eur J Immunol 35:1764–1772
Zocchi MR, Ferrarini M, Rugarli C (1990) Selective lysis of the autologous tumor by delta TCS1+ gamma/delta+ tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes from human lung carcinomas. Eur J Immunol 20:2685–2689
Choudhary A, Davodeau F, Moreau A, Peyrat MA, Bonneville M, Jotereau F (1995) Selective lysis of autologous tumor cells by recurrent gamma delta tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes from renal carcinoma. J Immunol 154:3932–3940
Zhao X, Wei YQ, Kariya Y, Teshigawara K, Uchida A (1995) Accumulation of gamma/delta T cells in human dysgerminoma and seminoma: roles in autologous tumor killing and granuloma formation. Immunol Invest 24:607–618
Bagot M, Heslan M, Dubertret L, Roujeau JC, Tourine R, Levy JP (1985) Antigen-presenting properties of human epidermal cells compared with peripheral blood mononuclear cells. Br J Dermatol 113(suppl 28):55
Laad AD, Thomas ML, Fakih AR, Chiplunkar SV (1990) Human gamma delta T cells recognize heat shock protein-60 on oral tumor cells. Int J Cancer 80:709–714
Fisch P, Malkovsky M, Kovats S, Sturm E, Braakman E, Klein BS, Voss SD et al (1990) Recognition by human Vγ9/Vδ2 T cells of a GroEL homolog on Daudi Burkitt’s lymphoma cells. Science 250:1269–1273
Freedman MS, D’Souza S, Antel JP (1997) Gamma delta T-cell-human glial cell interactions In vitro induction of gamma-delta T-cell expansion by human glial cells. J Neuroimmunol 74:135–142
Suzuki Y, Fujimiya Y, Ohno T, Katakura R, Yoshimoto T (1999) Enhancing effect of tumor necrosis factor (TNF)-alpha, but not IFN-gamma, on the tumor-specific cytotoxicity of gammadelta T cells from glioblastoma patients. Cancer Lett 140:161–167
Schilbach KE, Geiselhart A, Wessels JT, Niethammer D, Handgretinger R (2000) Human gammadelta T lymphocytes exert natural and IL-2-induced cytotoxicity to neuroblastoma cells. J Immunother 23:536–548
Courvasier M, Moureau-Aubry A, Diez E, Bennouna J, Mosnier JF, Scotet E, Bonneville M et al (2005) Vγ9/Vδ2 T cell response to colon carcinoma cells. J Immunol 175(8):5481–5488
Ferrarini M, Ferrero E, Dagna L, Poggi A, Zocchi MR (2002) Human gammadelta T cells: a nonredundant system in the immune surveillance against cancer. Trends Immunol 23:14–18
Kunzmann V, Bauer E, Feurle J, Weissinger F, Tony HP, Wilhelm M (2000) Stimulation of γδ T cells by aminobisphosphonates and induction of antiplasmacell activity in multiple myeloma. Blood 96:384–392
Kunzmann V, Bauer E, Wilhelm M (1999) γδ T cell stimulation by pamidronate. N Engl J Med 340:737–738
Dieli F, Gebbia N, Poccia F, Caccamo N, Montesano C, Fulfaro F, Arcara C et al (2003) Induction of gammadelta T-lymphocyte effector functions by bisphosphonate zoledronic acid in cancer patients in vivo. Blood 102:2310–1
Ferlazzo V, Sferrazza C, Caccamo N, Di Fede G, Di Lorenzo G, D’Asaro M, Meraviglia S et al (2006) In vitro effects of aminobisphosphonates on Vgamma9Vdelta2 T cell activation and differentiation. Int J Immunopathol Pharmacol 19:309–317
Dieli F, Poccia F, Lipp M, Sireci G, Caccamo N, Di Sano C, Salerno A (2003) Differentiation of effector/Memory Vdelta2 T cells and migratory routes in lymph nodes or inflammatory sites. J Exp Med 198:391–397
Galluzzo S, Santini D, Vincenzi B, Caccamo N, Meraviglia F, Salerno A, Dieli F et al (2007) Immunomodulating role of bisphosphonates on human gamma delta T cells: an intriguing and promising aspect of their antitumour activity. Expert Opin Ther Targets 11(7):941–954
Gober HJ, Kistowska M, Angman L, Jeno P, Mori L, De Libero G (2003) Human T cell receptor gammadelta cells recognize endogenous mevalonate metabolites in tumor cells. J Exp Med 197:163–168
Watanabe N, Narita M, Yokoyama A, Sekiguchi A, Saito A, Tochiki N, Furukawa T et al (2006) Type I IFN-mediated enhancement of anti-leukemic cytotoxicity of gammadelta T cells expanded from peripheral blood cells by stimulation with zoledronate. Cytotherapy 8:118–129
Thompson K, Rogers MJ (2004) Statins prevent bisphosphonate-induced gamma, delta-T-cell proliferation and activation in vitro. J Bone Miner Res 19(2):278–288
Rogers MJ (2003) New insights into the molecular mechanisms of action of bisphosphonates. Curr Pharm Des 9(32):2643–2658
Acknowledgments
This work is in memory of Fabrizio Poccia. This work was supported by grants from MIUR (COFIN, 2005) and from “Giuliana Cardarelli Mazzi” cancer research foundation. Any financial/commercial conflicts have been disclosed.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no financial or commercial conflicts of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Santini, D., Martini, F., Fratto, M.E. et al. In vivo effects of zoledronic acid on peripheral γδ T lymphocytes in early breast cancer patients. Cancer Immunol Immunother 58, 31–38 (2009). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00262-008-0521-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00262-008-0521-6