Abstract
Background
Non-small cell lung carcinoma (NSCLC) patients have impaired cellular immune responses. It has been hypothesized that tumor cells expressing Fas Ligand (FasL) induce in T lymphocytes: (a) apoptosis (tumor counterattack) and (b) down-regulation of CD3ζ expression. However, the hypothesis of tumor counterattack is still controversial.
Methods
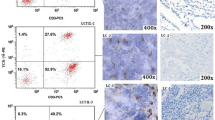
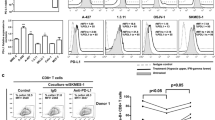
We analyzed FasL expression on NSCLC cell lines and on tumor cells from lung adenocarcinoma patients by flow cytometry and immunocytochemistry. FasL mRNA expression was detected in NSCLC cell lines using RT-PCR, and functional FasL was evaluated on Fas-expressing Jurkat T-cells by annexin-V-FITC staining and by SubG1 peak detection. Also, the proapoptotic effect of microvesicles released from NSCLC cell lines in Jurkat T-cells was studied. Alterations in the expression levels of CD3ζ, CD3ε, and CD28 [measured as mean fluorescence intensity (MFI)] were determined in Jurkat T-cells after co-culture with NSCLC cell lines or tumor-derived microvesicles. Furthermore, the expression levels of CD3ζ and CD3ε in CD4+T and CD8+T lymphocytes from lung adenocarcinoma patients was studied.
Results
Our results indicate that NSCLC cells neither FasL expressed nor induced apoptosis in Jurkat T-cells. Tumor-derived microvesicles did not induce apoptosis in Jurkat T-cells. In contrast, NSCLC cell lines down-regulated CD3ε but not CD3ζ chain expression in Jurkat T-cells; this effect was induced by soluble factors but not by microvesicles. In lung adenocarcinoma patients, significant decreases of MFI values for CD3ε, but not CD3ζ, were found in CD4+T and CD8+T cells from pleural effusion compared to peripheral blood and in peripheral blood of patients compared to healthy donors.
Conclusions
Our data do not support the tumor counterattack hypothesis for NSCLC. Nonetheless, down-regulation of CD3ε in T-cells induced by NSCLC cells might lead to T-cell dysfunction.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Andreola G, Rivoltini L, Castelli C, Huber V, Perego P, Deho P, Squarcina P, Accornero P, Lozupone F, Lugini L, Stringaro A, Molinari A, Arancia G, Gentile M, Parmiani G, Fais S (2002) Induction of lymphocyte apoptosis by tumor cell secretion of FasL-bearing microvesicles. J Exp Med 195:1303–1316
Baniyash M (2004) TCR zeta-chain downregulation: curtailing an excessive inflammatory immune response. Nat Rev Immunol 4:675–687
Broderick L, Brooks SP, Takita H, Baer AN, Bernstein JM, Bankert RB (2006) IL-12 reverses anergy to T cell receptor triggering in human lung tumor-associated memory T cells. Clin Immunol 118:159–169
Chappell DB, Zaks TZ, Rosenberg SA, Restifo NP (1999) Human melanoma cells do not express Fas (Apo-1/CD95) ligand. Cancer Res 59:59–62
Deakin AM, Singh K, Crowe JS, Ellis JH, Dalgleish A, Leicester RJ, Finlayson CJ, Miles WF, Life PF (1999) A lack of evidence for down-modulation of CD3 zeta expression in colorectal carcinoma and pregnancy using multiple detection methods. Clin Exp Immunol 118:197–204
Favre-Felix N, Fromentin A, Hammann A, Solary E, Martin F, Bonnotte B (2000) Cutting edge: the tumor counterattack hypothesis revisited: colon cancer cells do not induce T cell apoptosis via the Fas (CD95, APO-1) pathway. J Immunol 164:5023–5027
Fischer K, Mackensen A (2003) The flow cytometric PKH-26 assay for the determination of T-cell mediated cytotoxic activity. Methods 31:135–142
Gastman BR, Atarshi Y, Reichert TE, Saito T, Balkir L, Rabinowich H, Whiteside TL (1999) Fas ligand is expressed on human squamous cell carcinomas of the head and neck, and it promotes apoptosis of T lymphocytes. Cancer Res 59:5356–5364
Gastman BR, Johnson DE, Whiteside TL, Rabinowich H (1999) Caspase-mediated degradation of T-cell receptor zeta-chain. Cancer Res 59:1422–1427
Gastman BR, Johnson DE, Whiteside TL, Rabinowich H (2000) Tumor-induced apoptosis of T lymphocytes: elucidation of intracellular apoptotic events. Blood 95:2015–2023
Huber V, Fais S, Iero M, Lugini L, Canese P, Squarcina P, Zaccheddu A, Colone M, Arancia G, Gentile M, Seregni E, Valenti R, Ballabio G, Belli F, Leo E, Parmiani G, Rivoltini L (2005) Human colorectal cancer cells induce T-cell death through release of proapoptotic microvesicles: role in immune escape. Gastroenterology 128:1796–1804
Ibrahim R, Frederickson H, Parr A, Ward Y, Moncur J, Khleif SN (2006) Expression of FasL in squamous cell carcinomas of the cervix and cervical intraepithelial neoplasia and its role in tumor escape mechanism. Cancer 106:1065–1077
Kawasaki M, Kuwano K, Nakanishi Y, Hagimoto N, Takayama K, Pei XH, Maeyama T, Yoshimi M, Hara N (2000) Analysis of Fas and Fas ligand expression and function in lung cancer cell lines. Eur J Cancer 36:656–663
Kim JW, Wieckowski E, Taylor DD, Reichert TE, Watkins S, Whiteside TL (2005) Fas ligand-positive membranous vesicles isolated from sera of patients with oral cancer induce apoptosis of activated T lymphocytes. Clin Cancer Res 11:1010–1020
Kreyberg L, Liebow AA, Uehlinger EA (1981) Histological typing of lung tumours, 2nd edn. World Health Organization: International Histological Classification of Tumors, Geneva, pp 1–36
Lopez-Gonzalez JS, Aguilar-Cazares D, Prado-Garcia H, Nieto-Rodriguez A, Mandoki JJ, Avila-Moreno F, Rivera RM, Chavarria-Garces J (2002) Lack of correlation between growth inhibition by TGF-beta and the percentage of cells expressing type II TGF-beta receptor in human non-small cell lung carcinoma cell lines. Lung Cancer 38:149–158
Lopez-Gonzalez JS, Prado-Garcia H, Aguilar-Cazares D, Molina-Guarneros JA, Morales-Fuentes J, Mandoki JJ (2004) Apoptosis and cell cycle disturbances induced by coumarin and 7-hydroxycoumarin on human lung carcinoma cell lines. Lung Cancer 43:275–283
Ma S, Ochi H, Cui L, He W (2003) FasL-induced downregulation of CD28 expression on jurkat cells in vitro is associated with activation of caspases. Cell Biol Int 27:959–964
Maher S, Toomey D, Condron C, Bouchier-Hayes D (2002) Activation-induced cell death: the controversial role of Fas and Fas ligand in immune privilege and tumour counterattack. Immunol Cell Biol 80:131–137
Maki A, Matsuda M, Asakawa M, Kono H, Fujii H, Matsumoto Y (2004) Decreased expression of CD28 coincides with the down-modulation of CD3zeta and augmentation of caspase-3 activity in T cells from hepatocellular carcinoma-bearing patients and hepatitis C virus-infected patients. J Gastroenterol Hepatol 19:1348–1356
Martinez-Lorenzo MJ, Anel A, Gamen S, Monleon I, Lasierra P, Larrad L, Pineiro A, Alava MA, Naval J (1999) Activated human T cell release bioactive Fas ligand and APO2 ligand in microvesicles. J Immunol 163:1274–1281
Matsuda M, Petersson M, Lenkei R, Taupin JL, Magnusson I, Mellstedt H, Anderson P, Kiessling R (1995) Alterations in the signal-transducing molecules of T cells and NK cells in colorectal tumor-infiltrating, gut mucosal and peripheral lymphocytes: correlation with the stage of the disease. Int J Cancer 61:765–772
Meng Y, Kang S, Fishman DA (2005) Lysophosphatidic acid stimulates Fas ligand microvesicle release from ovarian cancer cells. Cancer Immunol Immunother 54:807–814
Niehans GA, Brunner T, Frizelle SP, Liston JC, Salerno CT, Knapp DJ, Green DR, Kratzke RA (1997) Human lung carcinomas express Fas ligand. Cancer Res 57:1007–1012
Onon TS, Kitchener HC, Duggan-Keen M, Stern PL (2003) No alteration in NK function or zeta chain expression in NK and T cells of cervical cancer patients. Gynecol Oncol 89:120–128
Prado-Garcia H, Aguilar-Cazares D, Flores-Vergara H, Mandoki JJ, Lopez-Gonzalez JS (2005) Effector, memory and naïve CD8+ T cells in peripheral blood and pleural effusion from lung adenocarcinoma patients. Lung Cancer 47:361–371
Radoja S, Saio M, Frey AB (2001) CD8+ tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes are primed for Fas-mediated activation-induced cell death but are not apoptotic in situ. J Immunol 166:6074–6083
Restifo NP (2000) Not so Fas: re-evaluating the mechanisms of immune privilege and tumor escape. Nat Med 6:493–495
Riccobon A, Gunelli R, Ridolfi R, De Paola F, Flamini E, Fiori M, Saltutti C, Petrini M, Fiammenghi L, Stefanelli M, Granato AM, Cuzzocrea DE, Amadori D (2007) Immunosuppression in renal cancer: differential expression of signal transduction molecules in tumor-infiltrating, near-tumor tissue, and peripheral blood lymphocytes. Cancer Invest 22:871–877
Schulze-Bergkamen H, Krammer PH (2004) Apoptosis in cancer—implications for therapy. Semin Oncol 31:90–119
Sikora J, Dworacki G, Giersz R, Zeromski J (2004) The role of monocytes/macrophages in TCR-zeta chain downregulation and apoptosis of T lymphocytes in malignant pleural effusions. J Biol Regul Homeost Agents 18:26–32
Sikora J, Dworacki G, Zeromski J (1998) Expression of Fas and Fas ligand and apoptosis in tumor-associated lymphocytes and in tumor cells from malignant pleural effusions. Nat Immun 16:244–255
Sikora J, Zeromski J (2002) Expression of TCR-zeta chain and apoptosis in subpopulations of tumor-associated lymphocytes (TALs) from malignant pleural effusions. Folia Histochem Cytobiol 40:347–351
Smith D, Sieg S, Kaplan D (1998) Technical note: aberrant detection of cell surface Fas ligand with anti-peptide antibodies. J Immunol 160:4159–4160
Sobin L, Witzens M (1997) UICC TNM classification of malignant tumors. Wiley-Liss, New York
Spiro SG, Silvestri GA (2005) One hundred years of lung cancer. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 172:523–529
Strater J, Walczak H, Hasel C, Melzner I, Leithauser F, Moller P (2001) CD95 ligand (CD95L) immunohistochemistry: a critical study on 12 antibodies. Cell Death Differ 8:273–278
Toomey D, Smyth G, Condron C, Kelly J, Byrne AM, Kay E, Conroy RM, Broe P, Bouchier-Hayes D (2003) Infiltrating immune cells, but not tumour cells, express FasL in non-small cell lung cancer: no association with prognosis identified in 3-year follow-up. Int J Cancer 103:408–412
Valenti R, Huber V, Iero M, Filipazzi P (2007) Tumor-released microvesicles as vehicles of immunosupression. Cancer Res 67:2912–2915
van de Corp, Falkenburg JH, Kester MG, Willemze R, Kluin-Nelemans JC (1999) Impaired expression of CD28 on T cells in hairy cell leukemia. Clin Immunol 93:256–262
Viard-Leveugle I, Veyrenc S, French LE, Brambilla C, Brambilla E (2003) Frequent loss of Fas expression and function in human lung tumours with overexpression of FasL in small cell lung carcinoma. J Pathol 201:268–277
Whiteside TL (1998) Immune cells in the tumor microenvironment. Mechanisms responsible for functional and signaling defects. Adv Exp Med Biol 451:167–171
Whiteside TL (2002) Tumor-induced death of immune cells: its mechanisms and consequences. Semin Cancer Biol 12:43–50
Woo EY, Chu CS, Goletz TJ, Schlienger K, Yeh H, Coukos G, Rubin SC, Kaiser LR, June CH (2001) Regulatory CD4(+)CD25(+) T cells in tumors from patients with early-stage non-small cell lung cancer and late-stage ovarian cancer. Cancer Res 61:4766–4772
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by CONACYT grants F643-M9406 and 46389-M.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Prado-Garcia, H., Aguilar-Cazares, D., Meneses-Flores, M. et al. Lung carcinomas do not induce T-cell apoptosis via the Fas/Fas ligand pathway but down-regulate CD3 epsilon expression. Cancer Immunol Immunother 57, 325–336 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00262-007-0372-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00262-007-0372-6