Abstract
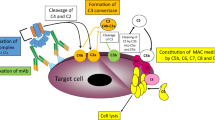
Complement-dependent cytotoxicity (CDC) is a key mechanism of Rituximab (RTX) action in killing non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma (NHL) cells both in vitro and probably in vivo. A DeImmunized, mouse/human chimeric monoclonal antibody (Mab), H17, specific for cell-associated complement C3 cleavage products, C3b and iC3b, was generated to enhance RTX-mediated killing of target cells by CDC. When NHL cell lines were treated with RTX and H17 in the presence of complement for 1 h, there was 40–70% more cell death than that observed with RTX alone. The enhancing effect of H17 was also seen over longer treatment periods. H17 was tested ex vivo against primary cells from NHL and chronic lymphocytic leukemia (CLL) patients. In RTX-resistant NHL samples, H17 enhanced RTX-mediated killing; in the remaining samples RTX + complement alone promoted more than 80% killing, and no significant enhancement was observed. The H17 antibody also increased RTX-mediated killing in four out of nine CLL samples. H17 may have therapeutic applications in NHL and CLL treatment as an adjunctive therapy to RTX. It might also enhance the activity of other therapeutic antibodies that work through CDC.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Boye J, Elter T, Engert A (2003) An overview of the current clinical use of the anti-CD20 monoclonal antibody rituximab. Ann Oncol 14:520
Cartron G, Dacheux L, Salles G, Solal-Celigny P, Bardos P, Colombat P, Watier H (2002) Therapeutic activity of humanized anti-CD20 monoclonal antibody and polymorphism in IgG Fc receptor FcgammaRIIIa gene. Blood 99:754
Clynes RA, Towers TL, Presta LG, Ravetch JV (2000) Inhibitory Fc receptors modulate in vivo cytoxicity against tumor targets. Nat Med 6:443
Cragg MS, Morgan SM, Chan HT, Morgan BP, Filatov AV, Johnson PW, French RR, Glennie MJ (2003) Complement-mediated lysis by anti-CD20 mAb correlates with segregation into lipid rafts. Blood 101:1045
Cragg MS, Glennie MJ (2004) Antibody specificity controls in vivo effector mechanisms of anti-CD20 reagents. Blood 103:2738
Di Gaetano N, Cittera E, Nota R, Vecchi A, Grieco V, Scanziani E, Botto M, Introna M, Golay J (2003) Complement activation determines the therapeutic activity of rituximab in vivo. J Immunol 171:1581
Fishelson Z, Donin N, Zell S, Schultz S, Kirschfink M (2003) Obstacles to cancer immunotherapy: expression of membrane complement regulatory proteins (mCRPs) in tumors. Mol Immunol 40:109
Frank M, Fries L (1989) Complement. In: Paul W (ed) Fundamental Immunology. 2nd edn, Raven Press, New York, p 679
Gelderman KA, Kuppen PJ, Bruin W, Fleuren GJ, Gorter A (2002) Enhancement of the complement activating capacity of 17–1A mAb to overcome the effect of membrane-bound complement regulatory proteins on colorectal carcinoma. Eur J Immunol 32:128
Gelderman KA, Tomlinson S, Ross GD, Gorter A (2004) Complement function in mAb-mediated cancer immunotherapy. Trends Immunol 25:158
Golay J, Zaffaroni L, Vaccari T, Lazzari M, Borleri GM, Bernasconi S, Tedesco F, Rambaldi A, Introna M (2000) Biologic response of B lymphoma cells to anti-CD20 monoclonal antibody rituximab in vitro: CD55 and CD59 regulate complement-mediated cell lysis. Blood 95:3900
Golay J, Lazzari M, Facchinetti V, Bernasconi S, Borleri G, Barbui T, Rambaldi A, Introna M (2001) CD20 levels determine the in vitro susceptibility to rituximab and complement of B-cell chronic lymphocytic leukemia: further regulation by CD55 and CD59. Blood 98:3383
Grossbard ML, Press OW, Appelbaum FR, Bernstein ID, Nadler LM (1992) Monoclonal antibody-based therapies of leukemia and lymphoma. Blood 80:863
Hainsworth JD, Litchy S, Burris HA III, Scullin DC Jr, Corso SW, Yardley DA, Morrissey L, Greco FA (2002) Rituximab as first-line and maintenance therapy for patients with indolent non-hodgkin’s lymphoma. J Clin Oncol 20:4261
Hainsworth JD, Litchy S, Barton JH, Houston GA, Hermann RC, Bradof JE, Greco FA (2003) Single-agent rituximab as first-line and maintenance treatment for patients with chronic lymphocytic leukemia or small lymphocytic lymphoma: a phase II trial of the Minnie Pearl Cancer Research Network. J Clin Oncol 21:1746
Harjunpaa A, Junnikkala S, Meri S (2000) Rituximab (anti-CD20) therapy of B-cell lymphomas: direct complement killing is superior to cellular effector mechanisms. Scand J Immunol 51:634
Hernandez-Ilizaliturri FJ, Jupudy V, Ostberg J, Oflazoglu E, Huberman A, Repasky E, Czuczman MS (2003) Neutrophils contribute to the biological antitumor activity of rituximab in a non-Hodgkin’s lymphoma severe combined immunodeficiency mouse model. Clin Cancer Res 9:5866
Huhn D, von Schilling C, Wilhelm M, Ho AD, Hallek M, Kuse R, Knauf W, Riedel U, Hinke A, Srock S, Serke S, Peschel C, Emmerich B (2001) Rituximab therapy of patients with B-cell chronic lymphocytic leukemia. Blood 98:1326
Juhl H, Helmig F, Baltzer K, Kalthoff H, Henne-Bruns D, Kremer B (1997) Frequent expression of complement resistance factors CD46, CD55, and CD59 on gastrointestinal cancer cells limits the therapeutic potential of monoclonal antibody 17–1A. J Surg Oncol 64:222
Jurianz K, Maslak S, Garcia-Schuler H, Fishelson Z, Kirschfink M (1999) Neutralization of complement regulatory proteins augments lysis of breast carcinoma cells targeted with rhumAb anti-HER2. Immunopharmacology 42:209
Jurianz K, Ziegler S, Garcia-Schuler H, Kraus S, Bohana-Kashtan O, Fishelson Z, Kirschfink M (1999) Complement resistance of tumor cells: basal and induced mechanisms. Mol Immunol 36:929
Kennedy AD, Solga MD, Schuman TA, Chi AW, Lindorfer MA, Sutherland WM, Foley PL, Taylor RP (2003) An anti-C3b(i) mAb enhances complement activation, C3b(i) deposition, and killing of CD20+ cells by rituximab. Blood 101:1071
Kennedy AD, Beum PV, Solga MD, DiLillo DJ, Lindorfer MA, Hess CE, Densmore JJ, Williams ME, Taylor RP (2004) Rituximab infusion promotes rapid complement depletion and acute CD20 loss in chronic lymphocytic leukemia. J Immunol 172:3280
Lindorfer MA, Jinivizian HB, Foley PL, Kennedy AD, Solga MD, Taylor RP (2003) B cell complement receptor 2 transfer reaction. J Immunol 170:3671
Manches O, Lui G, Chaperot L, Gressin R, Molens JP, Jacob MC, Sotto JJ, Leroux D, Bensa JC, Plumas J (2003) In vitro mechanisms of action of rituximab on primary non-Hodgkin lymphomas. Blood 101:949
McLaughlin P, Grillo-Lopez AJ, Link BK, Levy R, Czuczman MS, Williams ME, Heyman MR, Bence-Bruckler I, White CA, Cabanillas F, Jain V, Ho AD, Lister J, Wey K, Shen D, Dallaire BK (1998) Rituximab chimeric anti-CD20 monoclonal antibody therapy for relapsed indolent lymphoma: half of patients respond to a four-dose treatment program. J Clin Oncol 16:2825
Niehans GA, Cherwitz DL, Staley NA, Knapp DJ, Dalmasso AP (1996) Human carcinomas variably express the complement inhibitory proteins CD46 (membrane cofactor protein), CD55 (decay-accelerating factor), and CD59 (protectin). Am J Pathol 149:129
Nilsson B, Nilsson UR (1985) An assessment of the extent of antigenic analogy between physiologically bound C3 and C3 denatured by sodium dodecyl sulphate. Scand J Immunol 22:703
Nilsson B, Grossberger D, Nilsson Ekdahl K, Riegert P, Becherer DJ, Nilsson UR, Lambris JD (1992) Conformational differences between surface-bound and fluid-phase complement-component-C3 fragments. Epitope mapping by cDNA expression. Biochem J 282(Pt 3):715
Press OW, Leonard JP, Coiffier B, Levy R, Timmerman J (2001) Immunotherapy of Non-Hodgkin’s lymphomas. Hematology (Am Soc Hematol Educ Program) :221
Sokoloff MH, Nardin A, Solga MD, Lindorfer MA, Sutherland WM, Bankovich AJ, Zhau HE, Chung LW, Taylor RP (2000) Targeting of cancer cells with monoclonal antibodies specific for C3b(i). Cancer Immunol Immunother 49:551
Treon SP, Mitsiades C, Mitsiades N, Young G, Doss D, Schlossman R, Anderson KC (2001) Tumor Cell Expression of CD59 Is Associated With Resistance to CD20 Serotherapy in Patients With B-Cell Malignancies. J Immunother 24:263
von Mehren M, Adams GP, Weiner LM (2003) Monoclonal antibody therapy for cancer. Annu Rev Med 54:343
Weng WK, Levy R (2003) Two immunoglobulin G fragment C receptor polymorphisms independently predict response to rituximab in patients with follicular lymphoma. J Clin Oncol 21:3940
Acknowledgements
We are grateful to Juan Li for her help in developing the Alamar Blue assay. We thank Dr. Ronald P. Taylor for his comments on the manuscript and useful discussion. We also thank Dr. Steven Jones for his comments and help on the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Peng, W., Zhang, X., Mohamed, N. et al. A DeImmunized chimeric anti-C3b/iC3b monoclonal antibody enhances rituximab-mediated killing in NHL and CLL cells via complement activation. Cancer Immunol Immunother 54, 1172–1179 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00262-005-0686-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00262-005-0686-1