Abstract.
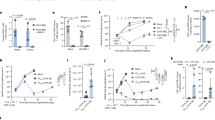
CD40–CD40 ligand (CD40L) interaction is an important costimulatory signal in the interaction between T cells and antigen-presenting cells (APC). In the present study, we determined whether the linkage of CD40L to the tumor-specific idiotype (Id) derived from a murine B-cell lymphoma, 38C13, could enhance its immunogenicity when presented by dendritic cells (DC). We showed that bone marrow-derived DC pulsed with Id-CD40L upregulated the expression of CD40, CD80, CD86, and major histocompatibility complex (MHC) class II molecules with the increased production of interleukin-12 (IL-12). Mice immunized with DC loaded with Id-CD40L showed high levels of anti-Id antibody response of both IgG2a and IgG1 isotypes. In addition, nylon wool-enriched T cells from these immunized mice showed a tumor-specific T-cell proliferative response upon stimulation with Id protein. Mice immunized with DC pulsed with Id alone failed to show any of these immune responses. Immunization with DC pulsed with Id-CD40L showed increased resistance to the challenge by 38C13 tumor, and tumor growth was significantly retarded. Together, these results show that linkage of CD40L to a self-tumor antigen enhances the anti-tumor immune response in DC-based treatment.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Electronic Publication
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chen, HW., Huang, HI., Lee, YP. et al. Linkage of CD40L to a self-tumor antigen enhances the antitumor immune responses of dendritic cell-based treatment. Cancer Immunol Immunother 51, 341–348 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00262-002-0283-5
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00262-002-0283-5