Abstract
Objective
Our study aimed to determine whether radiomics models based on contrast-enhanced computed tomography (CECT) have considerable ability to predict serosal involvement in gallbladder cancer (GBC) patients.
Materials and methods
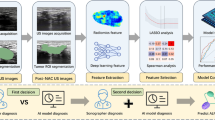
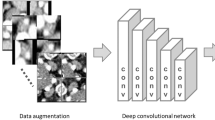
A total of 152 patients diagnosed with GBC were retrospectively enrolled and divided into the serosal involvement group and no serosal involvement group according to paraffin pathology results. The regions of interest (ROIs) in the lesion on all CT images were drawn by two radiologists using ITK-SNAP software (version 3.8.0). A total of 412 features were extracted from the CT images of each patient. The Mann‒Whitney U test was applied to identify features with significant differences between groups. Seven machine learning algorithms and a deep learning model based on fully connected neural networks (f-CNNs) were used for radiomics model construction. The prediction efficacy of the models was evaluated using receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve analysis.
Results
Through the Mann‒Whitney U test, 75 of the 412 features extracted from the CT images of patients were significantly different between groups (P < 0.05). Among all the algorithms, logistic regression achieved the highest performance with an area under the curve (AUC) of 0.944 (sensitivity 0.889, specificity 0.8); the f-CNN deep learning model had an AUC of 0.916, and the model showed high predictive power for serosal involvement, with a sensitivity of 0.733 and a specificity of 0.801.
Conclusion
Radiomics models based on features derived from CECT showed convincing performances in predicting serosal involvement in GBC.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Schmidt MA, Marcano-Bonilla L, Roberts LR. Gallbladder cancer: epidemiology and genetic risk associations. Chin Clin Oncol. 2019;8(4):31.
Jiang W, Zhao B, Li Y, Qi D, Wang D. Modification of the 8th American Joint Committee on Cancer staging system for gallbladder carcinoma to improve prognostic precision. BMC Cancer. 2020;20(1):1129.
Feo CF, Ginesu GC, Fancellu A, Perra T, Ninniri C, Deiana G, et al. Current management of incidental gallbladder cancer: A review. Int J Surg. 2022;98:106234.
Pilgrim CH, Groeschl RT, Turaga KK, Gamblin TC. Key factors influencing prognosis in relation to gallbladder cancer. Dig Dis Sci. 2013;58(9):2455-62.
Mahul B. Amin SBE, Frederick L. Greene, David R. Byrd, Robert K. Brookland, Mary Kay Washington, Jeffrey E. Gershenwald, Carolyn C. Compton, Kenneth R. Hess, Daniel C. AJCC Cancer Staging Manual. 8th ed. New York: Springer. 2017.
Cherkassky L, D'Angelica M. Gallbladder Cancer: Managing the Incidental Diagnosis. Surg Oncol Clin N Am. 2019;28(4):619-30.
Gupta P, Kumar M, Sharma V, Dutta U, Sandhu MS. Evaluation of gallbladder wall thickening: a multimodality imaging approach. Expert Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2020;14(6):463-73.
Sung YS, Park B, Park HJ, Lee SS. Radiomics and deep learning in liver diseases. J Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2021;36(3):561-8.
Bi WL, Hosny A, Schabath MB, Giger ML, Birkbak NJ, Mehrtash A, et al. Artificial intelligence in cancer imaging: Clinical challenges and applications. CA Cancer J Clin. 2019;69(2):127-57.
Mayerhoefer ME, Materka A, Langs G, Haggstrom I, Szczypinski P, Gibbs P, et al. Introduction to Radiomics. J Nucl Med. 2020;61(4):488-95.
Hatt M, Le Rest CC, Tixier F, Badic B, Schick U, Visvikis D. Radiomics: Data Are Also Images. J Nucl Med. 2019;60(Suppl 2):38S-44S.
Lambin P, Leijenaar RTH, Deist TM, Peerlings J, de Jong EEC, van Timmeren J, et al. Radiomics: the bridge between medical imaging and personalized medicine. Nat Rev Clin Oncol. 2017;14(12):749-62.
Binczyk F, Prazuch W, Bozek P, Polanska J. Radiomics and artificial intelligence in lung cancer screening. Transl Lung Cancer Res. 2021;10(2):1186-99.
Conti A, Duggento A, Indovina I, Guerrisi M, Toschi N. Radiomics in breast cancer classification and prediction. Semin Cancer Biol. 2021;72:238-50.
Ji GW, Zhang YD, Zhang H, Zhu FP, Wang K, Xia YX, et al. Biliary Tract Cancer at CT: A Radiomics-based Model to Predict Lymph Node Metastasis and Survival Outcomes. Radiology. 2019;290(1):90-8.
Tang Y, Yang CM, Su S, Wang WJ, Fan LP, Shu J. Machine learning-based Radiomics analysis for differentiation degree and lymphatic node metastasis of extrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma. BMC Cancer. 2021;21(1):1268.
Qin H, Hu X, Zhang J, Dai H, He Y, Zhao Z, et al. Machine-learning radiomics to predict early recurrence in perihilar cholangiocarcinoma after curative resection. Liver Int. 2021;41(4):837-50.
Xue B, Wu S, Zhang M, Hong J, Liu B, Xu N, et al. A radiomic-based model of different contrast-enhanced CT phase for differentiate intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma from inflammatory mass with hepatolithiasis. Abdom Radiol (NY). 2021;46(8):3835-44.
Hundal R, Shaffer EA. Gallbladder cancer: epidemiology and outcome. Clin Epidemiol. 2014;6:99-109.
Sadamoto Y, Kubo H, Harada N, Tanaka M, Eguchi T, Nawata H. Preoperative diagnosis and staging of gallbladder carcinoma by EUS. Gastrointest Endosc. 2003;58(4):536-41.
Sugimoto M, Irie H, Takasumi M, Hashimoto M, Oka Y, Takagi T, et al. A simple method for diagnosing gallbladder malignant tumors with subserosa invasion by endoscopic ultrasonography. BMC Cancer. 2021;21(1):288.
Hwang J, Kim YK, Choi D, Rhim H, Lee WJ, Hong SS, et al. Gadoxetic acid-enhanced MRI for T-staging of gallbladder carcinoma: emphasis on liver invasion. Br J Radiol. 2014;87(1033):20130608.
Kim SJ, Lee JM, Lee JY, Choi JY, Kim SH, Han JK, et al. Accuracy of preoperative T-staging of gallbladder carcinoma using MDCT. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2008;190(1):74-80.
Kwon YJ, Song KD, Ko SE, Hwang JA, Kim M. Diagnostic performance and inter-observer variability to differentiate between T1- and T2-stage gallbladder cancers using multi-detector row CT. Abdom Radiol (NY). 2022;47(4):1341-50.
Liu Z, Wang S, Dong D, Wei J, Fang C, Zhou X, et al. The Applications of Radiomics in Precision Diagnosis and Treatment of Oncology: Opportunities and Challenges. Theranostics. 2019;9(5):1303-22.
King MJ, Hectors S, Lee KM, Omidele O, Babb JS, Schwartz M, et al. Outcomes assessment in intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma using qualitative and quantitative imaging features. Cancer Imaging. 2020;20(1):43.
Yang C, Huang M, Li S, Chen J, Yang Y, Qin N, et al. Radiomics model of magnetic resonance imaging for predicting pathological grading and lymph node metastases of extrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma. Cancer Lett. 2020;470:1-7.
Park HJ, Park B, Park SY, Choi SH, Rhee H, Park JH, et al. Preoperative prediction of postsurgical outcomes in mass-forming intrahepatic cholangiocarcinoma based on clinical, radiologic, and radiomics features. Eur Radiol. 2021;31(11):8638-48.
Lewis S, Peti S, Hectors SJ, King M, Rosen A, Kamath A, et al. Volumetric quantitative histogram analysis using diffusion-weighted magnetic resonance imaging to differentiate HCC from other primary liver cancers. Abdom Radiol (NY). 2019;44(3):912-22.
Liu Z, Zhu G, Jiang X, Zhao Y, Zeng H, Jing J, et al. Survival Prediction in Gallbladder Cancer Using CT Based Machine Learning. Front Oncol. 2020;10:604288.
Choi TW, Kim JH, Park SJ, Ahn SJ, Joo I, Han JK. Risk stratification of gallbladder polyps larger than 10 mm using high-resolution ultrasonography and texture analysis. Eur Radiol. 2018;28(1):196-205.
Gupta P, Rana P, Ganeshan B, Kalage D, Irrinki S, Gupta V, et al. Computed tomography texture-based radiomics analysis in gallbladder cancer: initial experience. Clin Exp Hepatol. 2021;7(4):406-14.
Wang L, Zhang Y, Chen Y, Tan J, Wang L, Zhang J, et al. The Performance of a Dual-Energy CT Derived Radiomics Model in Differentiating Serosal Invasion for Advanced Gastric Cancer Patients After Neoadjuvant Chemotherapy: Iodine Map Combined With 120-kV Equivalent Mixed Images. Front Oncol. 2020;10:562945.
Ma W, Li W, Wang J, Wu R, Liu C, Feng F, et al. The Clinical Role of Preoperative Serum CA19-9 and Carcinoembryonic Antigen (CEA) Levels in Evaluating the Resectability of Advanced Gallbladder Cancer. Med Sci Monit. 2020;26:e925017.
Yamamoto Y, Sugiura T, Okamura Y, Ito T, Ashida R, Ohgi K, et al. Surgical Indication for Advanced Gallbladder Cancer Considering the Optimal Preoperative Carbohydrate Antigen 19-9 Cutoff Value. Dig Surg. 2020;37(5):390-400.
Chen Z, Liu Z, Zhang Y, Wang P, Gao H. Combination of CA19-9 and the Neutrophil-to-Lymphocyte Ratio for the Differential Diagnosis of Gallbladder Carcinoma. Cancer Manag Res. 2020;12:4475-82.
Funding
This study was funded by National High Level Hospital Clinical Research Funding (Grant No. 2022-PUMCH-B-003).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Zhou, S., Han, S., Chen, W. et al. Radiomics-based machine learning and deep learning to predict serosal involvement in gallbladder cancer. Abdom Radiol 49, 3–10 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00261-023-04029-2
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00261-023-04029-2