Abstract
Objective
The current study aimed to explore the feasibility of readout-segmented echo-planar imaging (RS-EPI) of the testis at 3.0 T, by comparing with single-shot echo-planar imaging (SS-EPI) in qualitative image quality and quantitative apparent diffusion coefficient (ADC) values.
Methods
66 patients undergoing scrotal MRI for various clinical indications were included retrospectively. RS-EPI image quality was rated from 1 (severe distortion or artifact, or nondiagnostic) to 4 (nearly no distortion or artifact, or outstanding). The comparative image quality (RS- vs. SS-EPI) was rated from − 2 (SS-EPI severe or greater conspicuity) to 2 (RS-EPI severe or greater conspicuity). The confidence interval of proportions (CIOP) of comparative image quality and Wilcoxon rank sum test were performed to assess the preferences between RS-EPI and SS-EPI. Paired samples t-test and Bland–Altman analysis were performed to compare the mean ADC values of RS-EPI and SS-EPI. The mean, maximum, and minimum ADC values measured by RS-EPI were compared in normal testicular parenchyma, benign and malignant intratesticular lesions.
Results
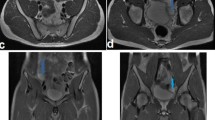
The evaluation of RS-EPI image quality showed RS-EPI with the characteristics of slight geometric distortion and susceptibility artifact, and good lesion conspicuity. The assessment of comparative image quality showed SS-EPI with obvious geometric distortion and susceptibility artifact, and RS-EPI preferred in lesion conspicuity. The CIOP ranged from 97 to 100% among three readers, with preferring to RS-EPI improving image quality (P < 0.001). There was a strong correlation and good agreement between mean ADC values measured by RS-EPI and SS-EPI. The mean, maximum and minimum ADC values by RS-EPI were significantly different in normal testicular parenchyma, benign and malignant intratesticular lesions.
Conclusion
RS-EPI DWI of the testis improved image quality in geometric distortion, susceptibility artifacts, and lesion conspicuity, and provided highly correlated and consistent mean ADC values when compared to SS-EPI DWI, indicating the feasibility of RS-EPI DWI of testes.
Graphical abstract




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Maki D, Watanabe Y, Nagayama M, Ishimori T, Okumura A, Amoh Y, Nakashita S, Terai A, Dodo Y. Diffusion-weighted magnetic resonance imaging in the detection of testicular torsion: feasibility study. J Magn Reson Imaging. 2011; 34 (5): 1137-1142.
Ufuk F, Herek D, Herek Ö, Akbulut M. Diffusion-weighted imaging and color doppler ultrasound in evaluation of partial testicular torsion in rat model. Pol J Radiol. 2017; 82: 542-546.
Tsili AC, Sylakos A, Ntorkou A, Stavrou S, Astrakas LG, Sofikitis N, Argyropoulou MI. Apparent diffusion coefficient values and dynamic contrast enhancement patterns in differentiating seminomas from nonseminomatous testicular neoplasms. Eur J Radiol. 2015; 84(7): 1219-1226.
Wang H, Guan J, Lin J, Zhang Z, Li S, Guo Y, Cai H. Diffusion-weighted and magnetization transfer imaging in testicular spermatogenic function evaluation: preliminary results. J Magn Reson Imaging. 2018; 47(1): 186-190.
Han BH, Park SB, Seo JT, Chun YK. Usefulness of testicular volume, apparent diffusion coefficient, and normalized apparent diffusion coefficient in the MRI evaluation of infertile men with azoospermia. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2018; 210(3): 543-548.
Porter DA, Heidemann RM. High resolution diffusion-weighted imaging using readout-segmented echo-planar imaging, parallel imaging and a two-dimensional navigator-based reacquisition. Magn Reson Med. 2009; 62(2): 468-475.
Bogner W, Pinker-Domenig K, Bickel H, Chmelik M, Weber M, Helbich TH, Trattnig S, Gruber S. Readout-segmented echo-planar imaging improves the diagnostic performance of diffusion-weighted MR breast examinations at 3.0 T. Radiology. 2012; 263(1): 64-76.
Friedli I, Crowe LA, Viallon M, Porter DA, Martin PY, de Seigneux S, Vallée JP. Improvement of renal diffusion-weighted magnetic resonance imaging with readout-segmented echo-planar imaging at 3T. Magn Reson Imaging. 2015; 33(6): 701-708.
Friedli I, Crowe LA, de Perrot T, Berchtold L, Martin PY, de Seigneux S, Vallée JP. Comparison of readout-segmented and conventional single-shot for echo-planar diffusion-weighted imaging in the assessment of kidney interstitial fibrosis. J Magn Reson Imaging. 2017; 46(6): 1631-1640.
Kim TH, Baek MY, Park JE, Ryu YJ, Cheon JE, Kim IO, Choi YH. Comparison of DWI methods in the pediatric brain: PROPELLER turbo spin-echo imaging versus readout-segmented echo-planar imaging versus single-shot echo-planar imaging. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2018; 210(6): 1352-1358.
Koyasu S, Iima M, Umeoka S, Morisawa N, Porter DA, Ito J, Le Bihan D, Togashi K. The clinical utility of reduced-distortion readout-segmented echo-planar imaging in the head and neck region: initial experience. Eur Radiol. 2014; 24(12): 3088-3096
Song C, Cheng P, Cheng J, Zhang Y, Sun M, Xie S, Zhang X. Differential diagnosis of nasopharyngeal carcinoma and nasopharyngeal lymphoma based on DCE-MRI and RESOLVE-DWI. Eur Radiol. 2020; 30(1): 110-118.
Min X, Feng Z, Wang L, Cai J, Yan X, Li B, Ke Z, Zhang P, You H. Characterization of testicular germ cell tumors: Whole-lesion histogram analysis of the apparent diffusion coefficient at 3T. Eur J Radiol. 2018; 98: 25-31.
Liebig PA, Heidemann RM, Hensel B, Porter DA. A new approach to accelerate readout segmented EPI with compressed sensing. Magn Reson Med. 2020; 84(1): 321-326.
Li Q, Jiang T, Wang T, Huang Y, Hu X, Zhang L, Liu W, Fu C, Gu Y. Improved readout-segmented echo-planner diffusion-weighted magnetic resonance imaging of nasopharyngeal carcinoma using simultaneous multislice acquisitions at 3 T. J Comput Assist Tomogr. 2022; 46(5): 815-822.
Jiang L, Zhang J, Chen J, Li Q, Liu W, Wu J, Liu D, Zhang J. rFOV-DWI and SMS-RESLOVE-DWI in patients with thyroid nodules: Comparison of image quality and apparent diffusion coefficient measurements. Magn Reson Imaging. 2022; 91: 62-68.
Ciritsis A, Rossi C, Marcon M, Van VDP, Boss A. Accelerated diffusion-weighted imaging for lymph node assessment in the pelvis applying simultaneous multislice acquisition: A healthy volunteer study. Medicine (Baltimore). 2018; 97(32): e11745.
Tsili AC, Argyropoulou MI, Giannakis D, Tsampalas S, Sofikitis N, Tsampoulas K. Diffusion-weighted MR imaging of normal and abnormal scrotum: preliminary results. Asian J Androl. 2012; 14(4): 649-654.
Tsili AC, Giannakis D, Sylakos A, Ntorkou A, Astrakas LG, Sofikitis N, Argyropoulou MI. Apparent diffusion coefficient values of normal testis and variations with age. Asian J Androl. 2014; 16(3): 493-497.
Nissan N, Anaby D, Tavor I, Kleinbaum Y, Dotan Z, Konen E, Portnoy O. The diffusion tensor imaging properties of the normal testicles at 3 Tesla magnetic resonance imaging. Acad Radiol. 2019; 26(8): 1010-1016.
Tsili AC, Ntorkou A, Astrakas L, Boukali E, Giannakis D, Maliakas V, Sofikitis N, Argyropoulou MI. Magnetic resonance diffusion tensor imaging of the testis: Preliminary observations. Eur J Radiol. 2017; 95: 265-270.
Min X, Feng Z, Wang L, Cai J, Li B, Ke Z, Zhang P, You H, Yan X. Multi-model analysis of diffusion-weighted imaging of normal testes at 3.0 T: preliminary findings. Acad Radiol. 2018; 25(4): 445-452.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
No conflict of interest exits in the submission of this manuscript, and manuscript is approved by all authors for publication.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Yao, F., Huang, M., Li, J. et al. Readout-segmented diffusion weighted imaging of the testis at 3.0 T: comparison with single-shot echo-planar imaging. Abdom Radiol 48, 2131–2138 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00261-023-03899-w
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00261-023-03899-w