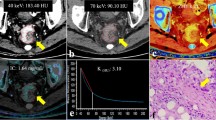
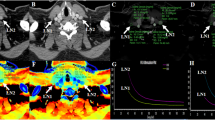
Abstract
Purpose
To investigate the added value of spectral parameters derived from dual-layer spectral detector CT (SDCT) in diagnosing metastatic lymph nodes (LNs) of pT1-2 (stage 1–2 determined by pathology) rectal cancer.
Methods
A total of 80 LNs (57 non-metastatic LNs and 23 metastatic LNs) from 42 patients with pT1-T2 rectal cancer were retrospectively analyzed. The short-axis diameter of LNs was measured, then its border and enhancement homogeneity were evaluated. All spectral parameters, including iodine concentration (IC), effective atomic number (Zeff), normalized IC (nIC), normalized Zeff (nZeff), and slope of the attenuation curve (λ), were measured or calculated. The chi-square test, Fisher’s exact test, independent-samples t-test, or Mann–Whitney U test was used to compare the differences of each parameter between the non-metastatic group and the metastatic group. Multivariable logistic regression analyses were used to determine the independent factors for predicting LN metastasis. Diagnostic performances were assessed by ROC curve analysis and compared with the DeLong test.
Results
The short-axis diameter, border, enhancement homogeneity, and each spectral parameter of LNs showed significant differences between the two groups (P < 0.05). The nZeff and short-axis diameter were independent predictors of metastatic LNs (P < 0.05), with areas under the curve (AUC) of 0.870 and 0.772, sensitivity of 82.5% and 73.9%, and specificity of 82.6% and 78.9%. After combining nZeff and the short-axis diameter, the AUC (0.966) was the highest with sensitivity of 100% and specificity of 87.7%.
Conclusion
The spectral parameters derived from SDCT might help us to improve the diagnostic accuracy of metastatic LNs in patients with pT1-2 rectal cancer, the highest diagnostic performance can be achieved after combining nZeff with the short-axis diameter of LNs.
Graphical abstract



Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- LNM:
-
Lymph node metastasis
- LNs:
-
Lymph nodes
- MRF:
-
Mesorectal fascia
- NCCN:
-
National comprehensive cancer network
- TME:
-
Total mesorectal excision
- DECT:
-
Dual-energy CT
- SDCT:
-
Spectral detector CT
- LNs:
-
Lymph nodes
- ROI:
-
Region of interest
- SBI:
-
Spectral base image
- IC:
-
Iodine concentration
- Zeff :
-
Effective atomic number
- nIC:
-
Normalized iodine concentration
- nZeff :
-
Normalized effective atomic number
- λ:
-
Slope of the attenuation curve
- ROC:
-
Receiver operating characteristic
- AUC:
-
Area under the curve
References
Sung H, Ferlay J, Siegel RL, Laversanne M, Soerjomataram I, Jemal A, Bray F. Global Cancer Statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN Estimates of Incidence and Mortality Worldwide for 36 Cancers in 185 Countries. CA Cancer J Clin 2021;71(3):209-49. https://doi:https://doi.org/10.3322/caac.21660.
Tang Y, Rao S, Yang C, Hu Y, Sheng R, Zeng M. Value of MRI morphologic features with pT1-2 rectal cancer in determining lymph node metastasis. J Surg Oncol 2018;118(3):544-50. https://doi:https://doi.org/10.1002/jso.25173.
Li H, Chen GW, Liu YS, Pu H, Yin LL, Hou NY, Chen XL. Assessment of histologic prognostic factors of resectable rectal cancer: comparison of diagnostic performance using various apparent diffusion coefficient parameters. Sci Rep 2020;10(1):11554. https://doi:https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-020-68328-0.
Benson AB, Venook AP, Al-Hawary MM, Azad N, Chen YJ, Ciombor KK, Cohen S, Cooper HS, Deming D, Garrido-Laguna I, Grem JL, Gunn A, Hecht JR, Hoffe S, Hubbard J, Hunt S, Jeck W, Johung KL, Kirilcuk N, Krishnamurthi S, Maratt JK, Messersmith WA, Meyerhardt J, Miller ED, Mulcahy MF, Nurkin S, Overman MJ, Parikh A, Patel H, Pedersen K, Saltz L, Schneider C, Shibata D, Skibber JM, Sofocleous CT, Stotsky-Himelfarb E, Tavakkoli A, Willett CG, Gregory K, Gurski L. Rectal Cancer, Version 2.2022, NCCN Clinical Practice Guidelines in Oncology. J Natl Compr Canc Netw 2022;20(10):1139-1167. https://doi:https://doi.org/10.6004/jnccn.2022.0051.
Yang Z, Zhang X, Fang M, Li G, Duan X, Mao J, Shen J. Preoperative Diagnosis of Regional Lymph Node Metastasis of Colorectal Cancer With Quantitative Parameters From Dual-Energy CT. AJR Am J Roentgenol 2019;213(1):W17-25. https://doi:https://doi.org/10.2214/AJR.18.20843.
Liu H, Yan F, Pan Z, Lin X, Luo X, Shi C, Chen X, Wang B, Zhang H. Evaluation of dual energy spectral CT in differentiating metastatic from non-metastatic lymph nodes in rectal cancer: Initial experience. Eur J Radiol 2015;84(2):228-34. https://doi:https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejrad.2014.11.016.
Drljevic-Nielsen A, Mains JR, Thorup K, Andersen MB, Rasmussen F, Donskov F. Early reduction in spectral dual-layer detector CT parameters as favorable imaging biomarkers in patients with metastatic renal cell carcinoma. Eur Radiol 2022. https://doi:https://doi.org/10.1007/s00330-022-08793-5. [Epub ahead of print]
Gao L, Lu X, Wen Q, Hou Y. Added value of spectral parameters for the assessment of lymph node metastasis of lung cancer with dual-layer spectral detector computed tomography. Quant Imaging Med Surg 2021;11(6):2622-33. https://doi:https://doi.org/10.21037/qims-20-1045.
Hu X, Gu Q, Zhang K, Deng D, Li L, Li P, Shen H. Dual-Energy Computed Tomography for the Diagnosis of Mediastinal Lymph Node Metastasis in Lung Cancer Patients: A Preliminary Study. J Comput Assist Tomogr 2021;45(3):490-4. https://doi:https://doi.org/10.1097/RCT.0000000000001157.
Nagano H, Takumi K, Nakajo M, Fukukura Y, Kumagae Y, Jinguji M, Tani A, Yoshiura T. Dual-Energy CT-Derived Electron Density for Diagnosing Metastatic Mediastinal Lymph Nodes in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer: Comparison With Conventional CT and FDG PET/CT Findings. AJR Am J Roentgenol 2022;218(1):66-74. https://doi:https://doi.org/10.2214/AJR.21.26208.
Wang X, Zhao X, Luo M, Yang Z, Liu Y. Dual-layer detector spectral CT imaging technology in differential diagnosis of the matastatic and non-matastatic lymph nodes in patients with colorectal cancer. Radiol Practice 2021;36(12):1543-7. https://doi:https://doi.org/10.13609/j.cnki.1000-0313.2021.12.016. [Article in Chinese]
Wang Y, Wen Z, Ma Y, Liu Y, Que Y, Yu S. Value of dual-layer spectral detector CT in diagnosing regional lymph node metastasis of colorectal cancer. Chin J Radiol 2021;55(12):1253-8. https://doi:https://doi.org/10.3760/cma.j.cn112149-20201202-01271. [Article in Chinese]
Jin D, Ni X, Zhang X, Yin H, Zhang H, Xu L, Wang R, Fan G. Multiphase Dual-Energy Spectral CT-Based Deep Learning Method for the Noninvasive Prediction of Head and Neck Lymph Nodes Metastasis in Patients With Papillary Thyroid Cancer. Front Oncol 2022;12:869895. https://doi:https://doi.org/10.3389/fonc.2022.869895.
Yoon J, Choi Y, Jang J, Shin NY, Ahn KJ, Kim BS. Preoperative assessment of cervical lymph node metastases in patients with papillary thyroid carcinoma: Incremental diagnostic value of dual-energy CT combined with ultrasound. Plos One 2021;16(12):e261233. https://doi:https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0261233.
An C, Li D, Li S, Li W, Tong T, Liu L, Jiang D, Jiang L, Ruan G, Hai N, Fu Y, Wang K, Zhuo S, Tian J. Deep learning radiomics of dual-energy computed tomography for predicting lymph node metastases of pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. Eur J Nucl Med Mol Imaging 2022;49(4):1187-99. https://doi:https://doi.org/10.1007/s00259-021-05573-z.
Brown G, Richards CJ, Bourne MW, Newcombe RG, Radcliffe AG, Dallimore NS, Williams GT. Morphologic predictors of lymph node status in rectal cancer with use of high-spatial-resolution MR imaging with histopathologic comparison. Radiology 2003;227(2):371-7. https://doi:https://doi.org/10.1148/radiol.2272011747.
Gröne J, Loch FN, Taupitz M, Schmidt C, Kreis ME. Accuracy of Various Lymph Node Staging Criteria in Rectal Cancer with Magnetic Resonance Imaging. J Gastrointest Surg 2018;22(1):146-53. https://doi:https://doi.org/10.1007/s11605-017-3568-x.
Rollvén E, Abraham-Nordling M, Holm T, Blomqvist L. Assessment and diagnostic accuracy of lymph node status to predict stage III colon cancer using computed tomography. Cancer Imaging 2017;17(1):3. https://doi:https://doi.org/10.1186/s40644-016-0104-2.
Patino M, Prochowski A, Agrawal MD, Simeone FJ, Gupta R, Hahn PF, Sahani DV. Material Separation Using Dual-Energy CT: Current and Emerging Applications. Radiographics 2016;36(4):1087-105. https://doi:https://doi.org/10.1148/rg.2016150220.
Rizzo S, Radice D, Femia M, De Marco P, Origgi D, Preda L, Barberis M, Vigorito R, Mauri G, Mauro A, Bellomi M. Metastatic and non-metastatic lymph nodes: quantification and different distribution of iodine uptake assessed by dual-energy CT. Eur Radiol 2018;28(2):760-9. https://doi:https://doi.org/10.1007/s00330-017-5015-5.
Fan S, Li X, Zheng L, Hu D, Ren X, Ye Z. Correlations between the iodine concentrations from dual energy computed tomography and molecular markers Ki-67 and HIF-1α in rectal cancer: A preliminary study. Eur J Radiol 2017;96:109-14. https://doi:https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejrad.2017.08.026.
Jeong HS, Jones D, Liao S, Wattson DA, Cui CH, Duda DG, Willett CG, Jain RK, Padera TP. Investigation of the Lack of Angiogenesis in the Formation of Lymph Node Metastases. J Natl Cancer Inst 2015;107(9). https://doi:https://doi.org/10.1093/jnci/djv155.
Al-Najami I, Lahaye MJ, Beets-Tan RGH, Baatrup G. Dual-energy CT can detect malignant lymph nodes in rectal cancer. Eur J Radiol 2017;90:81-8. https://doi:https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejrad.2017.02.005.
Beets-Tan RGH, Lambregts DMJ, Maas M, Bipat S, Barbaro B, Curvo-Semedo L, Fenlon HM, Gollub MJ, Gourtsoyianni S, Halligan S, Hoeffel C, Kim SH, Laghi A, Maier A, Rafaelsen SR, Stoker J, Taylor SA, Torkzad MR, Blomqvist L. Magnetic resonance imaging for clinical management of rectal cancer: Updated recommendations from the 2016 European Society of Gastrointestinal and Abdominal Radiology (ESGAR) consensus meeting. Eur Radiol 2018;28(4):1465-75. https://doi:https://doi.org/10.1007/s00330-017-5026-2.
Funding
This work was supported by the Startup Fund for scientific research, Fujian Medical University (Grant number: 2020QH1333).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The author declares that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Liu, J., Pan, H., Lin, Q. et al. Added value of spectral parameters in diagnosing metastatic lymph nodes of pT1-2 rectal cancer. Abdom Radiol 48, 1260–1267 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00261-023-03854-9
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00261-023-03854-9