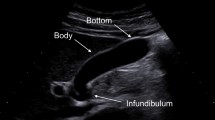
Abstract
The rising incidence combined with pregnancy-related physiological changes make gallbladder and biliary pathology high on the differential for pregnant patients presenting with right upper abdominal pain. Imaging plays a crucial role in determining surgical versus non-surgical management in pregnant patients with biliary or gallbladder pathology. Ultrasound (first-line) and magnetic resonance with magnetic resonance cholangiopancreatography (second-line) are the imaging techniques of choice in pregnant patients with suspected biliary pathology due to their lack of ionizing radiation. MRI/MRCP offers an excellent non-invasive imaging option, providing detailed anatomical detail without known harmful fetal side effects. This article reviews physiological changes in pregnancy that lead to gallstone and biliary pathology, key imaging findings on US and MRI/MRCP, and management pathways.
Graphical abstract








Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
Not applicable.
Code availability
Not applicable.
Abbreviations
- CBD:
-
Common bile duct
- ERCP:
-
Endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography
- GBCA:
-
Gadolinium-based contrast agents
- ICP:
-
Intrahepatic cholestasis of pregnancy
- MRCP:
-
Magnetic resonance cholangiopancreatography
- MRI:
-
Magnetic resonance imaging
- PTBD:
-
Percutaneous transhepatic biliary drainage
- RUQ:
-
Right upper quadrant
- SAR:
-
Specific absorption rate
- US:
-
Ultrasound
References
Dietrich CS, Hill CC, Hueman M (2008) Surgical Diseases Presenting in Pregnancy. Surgical Clinics of North America 88:403–419. https://doi.org/https://doi.org/10.1016/j.suc.2007.12.003
Ellington SR, Flowers L, Legardy-Williams JK, et al (2015) Recent trends in hepatic diseases during pregnancy in the United States, 2002–2010. Am J Obstet Gynecol 212:524.e1-524.e7. https://doi.org/https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ajog.2014.10.1093
Schwulst SJ, Son M (2020) Management of Gallstone Disease During Pregnancy. JAMA Surg 155:1162–1163. https://doi.org/https://doi.org/10.1001/jamasurg.2020.3683
Rana P, Gupta P, Chaluvashetty SB, et al (2020) Interventional radiological management of hepatobiliary disorders in pregnancy. Clin Exp Hepatol 6:176–184. https://doi.org/https://doi.org/10.5114/ceh.2020.99508
Date RS, Kaushal M, Ramesh A (2008) A review of the management of gallstone disease and its complications in pregnancy. The American Journal of Surgery 196:599–608. https://doi.org/https://doi.org/10.1016/j.amjsurg.2008.01.015
Cheng V, Matsushima K, Sandhu K, et al (2021) Surgical trends in the management of acute cholecystitis during pregnancy. Surg Endosc 35:5752–5759. https://doi.org/https://doi.org/10.1007/s00464-020-08054-w
Kuy S, Roman SA, Desai R, Sosa JA (2009) Outcomes following cholecystectomy in pregnant and nonpregnant women. Surgery 146:358–366. https://doi.org/https://doi.org/10.1016/j.surg.2009.03.033
Lydon-Rochelle M, Holt VL, Martin DP, Easterling TR (2000) Association between method of delivery and maternal rehospitalization. JAMA 283:2411–6. https://doi.org/https://doi.org/10.1001/jama.283.18.2411
Boyer JL (2013) Bile formation and secretion. Compr Physiol 3:1035–78. https://doi.org/https://doi.org/10.1002/cphy.c120027
Portincasa P, van Erpecum KJ, Vanberge-Henegouwen GP (1997) Cholesterol crystallisation in bile. Gut 41:138–41. https://doi.org/https://doi.org/10.1136/gut.41.2.138
Ko CW, Beresford SAA, Schulte SJ, et al (2005) Incidence, natural history, and risk factors for biliary sludge and stones during pregnancy. Hepatology 41:359–65. https://doi.org/https://doi.org/10.1002/hep.20534
Kern F, Everson GT, DeMark B, et al (1981) Biliary lipids, bile acids, and gallbladder function in the human female. Effects of pregnancy and the ovulatory cycle. J Clin Invest 68:1229–42. https://doi.org/https://doi.org/10.1172/JCI110369
Cirillo DJ, Wallace RB, Rodabough RJ, et al (2005) Effect of estrogen therapy on gallbladder disease. JAMA 293:330–9. https://doi.org/https://doi.org/10.1001/jama.293.3.330
Bolukbas FF, Bolukbas C, Horoz M, et al (2006) Risk factors associated with gallstone and biliary sludge formation during pregnancy. J Gastroenterol Hepatol 21:1150–3. https://doi.org/https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1440-1746.2006.04444.x
Maringhini A, Ciambra M, Baccelliere P, et al (1993) Biliary sludge and gallstones in pregnancy: incidence, risk factors, and natural history. Ann Intern Med 119:116–20. https://doi.org/https://doi.org/10.7326/0003-4819-119-2-199307150-00004
Eloranta ML, Häkli T, Hiltunen M, et al (2003) Association of single nucleotide polymorphisms of the bile salt export pump gene with intrahepatic cholestasis of pregnancy. Scand J Gastroenterol 38:648–52. https://doi.org/https://doi.org/10.1080/00365520310000807
Dixon PH, van Mil SWC, Chambers J, et al (2009) Contribution of variant alleles of ABCB11 to susceptibility to intrahepatic cholestasis of pregnancy. Gut 58:537–44. https://doi.org/https://doi.org/10.1136/gut.2008.159541
Pataia V, Dixon PH, Williamson C (2017) Pregnancy and bile acid disorders. Am J Physiol Gastrointest Liver Physiol 313:G1–G6. https://doi.org/https://doi.org/10.1152/ajpgi.00028.2017
Glantz A, Marschall H-U, Mattsson L-A (2004) Intrahepatic cholestasis of pregnancy: Relationships between bile acid levels and fetal complication rates. Hepatology 40:467–74. https://doi.org/https://doi.org/10.1002/hep.20336
Sarker M, Zamudio AR, DeBolt C, Ferrara L (2022) Beyond stillbirth: association of intrahepatic cholestasis of pregnancy severity and adverse outcomes. Am J Obstet Gynecol 227:517.e1-517.e7. https://doi.org/https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ajog.2022.06.013
Schwarze V, Froelich MF, Marschner C, et al (2021) Safe and pivotal approaches using contrast-enhanced ultrasound for the diagnostic workup of non-obstetric conditions during pregnancy, a single-center experience. Arch Gynecol Obstet 303:103–112. https://doi.org/https://doi.org/10.1007/s00404-020-05735-8
(2017) Committee Opinion No. 723: Guidelines for Diagnostic Imaging During Pregnancy and Lactation. Obstetrics and gynecology 130:e210–e216. https://doi.org/10.1097/AOG.0000000000002355
Saltybaeva N, Platon A, Poletti P-A, et al (2020) Radiation Dose to the Fetus From Computed Tomography of Pregnant Patients—Development and Validation of a Web-Based Tool. Invest Radiol 55:762–768. https://doi.org/https://doi.org/10.1097/RLI.0000000000000701
Wrazidlo R, Walder L, Estler A, et al (2022) Radiation Dose Reduction in Contrast-Enhanced Abdominal CT: Comparison of Photon-Counting Detector CT with 2nd Generation Dual-Source Dual-Energy CT in an oncologic cohort. Acad Radiol. https://doi.org/https://doi.org/10.1016/j.acra.2022.05.021
Mervak BM, Altun E, McGinty KA, et al (2019) MRI in pregnancy: Indications and practical considerations. Journal of Magnetic Resonance Imaging 49:621–631. https://doi.org/https://doi.org/10.1002/jmri.26317
Tso DK, Almeida RR, Prabhakar AM, et al (2019) Accuracy and timeliness of an abbreviated emergency department MRCP protocol for choledocholithiasis. Emerg Radiol 26:427–432. https://doi.org/https://doi.org/10.1007/s10140-019-01689-w
Chartier AL, Bouvier MJ, McPherson DR, et al (2019) The Safety of Maternal and Fetal MRI at 3 T. American Journal of Roentgenology 213:1170–1173. https://doi.org/https://doi.org/10.2214/AJR.19.21400
Strizek B, Jani JC, Mucyo E, et al (2015) Safety of MR Imaging at 1.5 T in Fetuses: A Retrospective Case-Control Study of Birth Weights and the Effects of Acoustic Noise. Radiology 275:530–7. https://doi.org/https://doi.org/10.1148/radiol.14141382
Greenberg TD, Hoff MN, Gilk TB, et al (2020) ACR guidance document on MR safe practices: Updates and critical information 2019. Journal of Magnetic Resonance Imaging 51:331–338. https://doi.org/https://doi.org/10.1002/jmri.26880
Jabehdar Maralani P, Kapadia A, Liu G, et al (2022) Canadian Association of Radiologists Recommendations for the Safe Use of MRI During Pregnancy. Canadian Association of Radiologists Journal 73:56–67. https://doi.org/https://doi.org/10.1177/08465371211015657
Prayer D, Malinger G, Brugger PC, et al (2017) ISUOG Practice Guidelines: performance of fetal magnetic resonance imaging. Ultrasound in Obstetrics & Gynecology 49:671–680. https://doi.org/https://doi.org/10.1002/uog.17412
Mühler MR, Clément O, Salomon LJ, et al (2011) Maternofetal Pharmacokinetics of a Gadolinium Chelate Contrast Agent in Mice. Radiology 258:455–460. https://doi.org/https://doi.org/10.1148/radiol.10100652
Kanal E, Barkovich AJ, Bell C, et al (2013) ACR guidance document on MR safe practices: 2013. Journal of Magnetic Resonance Imaging 37:501–530. https://doi.org/https://doi.org/10.1002/jmri.24011
Ray JG, Vermeulen MJ, Bharatha A, et al (2016) Association Between MRI Exposure During Pregnancy and Fetal and Childhood Outcomes. JAMA 316:952–61. https://doi.org/https://doi.org/10.1001/jama.2016.12126
Winterstein AG, Thai TN, Nduaguba S, et al (2022) Risk of fetal or neonatal death or neonatal intensive care unit admission associated with gadolinium magnetic resonance imaging exposure during pregnancy. Am J Obstet Gynecol. https://doi.org/https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ajog.2022.10.005
Tran TT, Ahn J, Reau NS (2016) ACG Clinical Guideline: Liver Disease and Pregnancy. Am J Gastroenterol 111:176–196. https://doi.org/https://doi.org/10.1038/ajg.2015.430
Tang S-J, Mayo MJ, Rodriguez-Frias E, et al (2009) Safety and utility of ERCP during pregnancy. Gastrointest Endosc 69:453–61. https://doi.org/https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gie.2008.05.024
Cappell MS (2003) The fetal safety and clinical efficacy of gastrointestinal endoscopy during pregnancy. Gastroenterol Clin North Am 32:123–79. https://doi.org/https://doi.org/10.1016/s0889-8553(02)00137-1
Laudanno O, Garrido J, Ahumarán G, et al (2020) Long-term follow-up after fetal radiation exposure during endoscopic retrograde cholangiopancreatography. Endosc Int Open 8:E1909–E1914. https://doi.org/https://doi.org/10.1055/a-1293-7783
Meves V, Pohl J (2014) Trans-Abdominal Ultrasound Guided ERC in a Pregnant Woman With Bile Duct Stones. Video Journal and Encyclopedia of GI Endoscopy 2:9–11. https://doi.org/https://doi.org/10.1016/j.vjgien.2014.02.001
Shelton J, Linder JD, Rivera-Alsina ME, Tarnasky PR (2008) Commitment, confirmation, and clearance: new techniques for nonradiation ERCP during pregnancy (with videos). Gastrointest Endosc 67:364–8. https://doi.org/https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gie.2007.09.036
Adelstein SJ (1999) Administered radionuclides in pregnancy. Teratology 59:236–239. https://doi.org/https://doi.org/10.1002/(SICI)1096-9926(199904)59:4<236::AID-TERA9>3.0.CO;2-6
Mintz M, Grumbach K, Arger P, Coleman B (1985) Sonographic evaluation of bile duct size during pregnancy. American Journal of Roentgenology 145:575–578. https://doi.org/https://doi.org/10.2214/ajr.145.3.575
Lanzafame RJ (1995) Laparoscopic cholecystectomy during pregnancy. Surgery 118:627–31; discussion 631-3. https://doi.org/https://doi.org/10.1016/s0039-6060(05)80028-5
Nasioudis D, Tsilimigras D, Economopoulos KP (2016) Laparoscopic cholecystectomy during pregnancy: A systematic review of 590 patients. Int J Surg 27:165–175. https://doi.org/https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijsu.2016.01.070
Lammert F, Gurusamy K, Ko CW, et al (2016) Gallstones. Nat Rev Dis Primers 2:16024. https://doi.org/https://doi.org/10.1038/nrdp.2016.24
Rybicki FJ (2000) The WES Sign. Radiology 214:881–882. https://doi.org/https://doi.org/10.1148/radiology.214.3.r00mr38881
Håkansson K, Leander P, Ekberg O, Håkansson HO (2000) MR imaging in clinically suspected acute cholecystitis. A comparison with ultrasonography. Acta Radiol 41:322–8. https://doi.org/https://doi.org/10.1080/028418500127345587
Watanabe Y, Nagayama M, Okumura A, et al (2007) MR imaging of acute biliary disorders. Radiographics 27:477–95. https://doi.org/https://doi.org/10.1148/rg.272055148
Heller MT, Tublin ME, Hosseinzadeh K, Fargiano A (2011) Imaging of Hepatobiliary Disorders Complicating Pregnancy. American Journal of Roentgenology 197:W528–W536. https://doi.org/https://doi.org/10.2214/AJR.10.5128
Cauldwell M, Mackie FL, Steer PJ, et al (2020) Pregnancy outcomes in women with primary biliary cholangitis and primary sclerosing cholangitis: a retrospective cohort study. BJOG 127:876–884. https://doi.org/https://doi.org/10.1111/1471-0528.16119
Ajne G (2020) Chronic cholestatic liver disease and pregnancy — not to be confused with intrahepatic cholestasis of pregnancy. BJOG 127:885–885. https://doi.org/https://doi.org/10.1111/1471-0528.16178
Mali P (2016) Pancreatitis in pregnancy: etiology, diagnosis, treatment, and outcomes. Hepatobiliary & Pancreatic Diseases International 15:434–438. https://doi.org/https://doi.org/10.1016/S1499-3872(16)60075-9
al Samaraee A, Bhattacharya V (2019) Challenges encountered in the management of gall stones induced pancreatitis in pregnancy. International Journal of Surgery 71:72–78. https://doi.org/https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijsu.2019.09.016
Inamdar S, Berzin TM, Sejpal D v, et al (2016) Pregnancy is a Risk Factor for Pancreatitis After Endoscopic Retrograde Cholangiopancreatography in a National Cohort Study. Clinical gastroenterology and hepatology 14:107–14. https://doi.org/https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cgh.2015.04.175
Spalluto LB, Woodfield CA, DeBenedectis CM, Lazarus E (2012) MR Imaging Evaluation of Abdominal Pain during Pregnancy: Appendicitis and Other Nonobstetric Causes. RadioGraphics 32:317–334. https://doi.org/https://doi.org/10.1148/rg.322115057
Craig WD, Wagner BJ, Travis MD (2008) Pyelonephritis: Radiologic-Pathologic Review. RadioGraphics 28:255–276. https://doi.org/https://doi.org/10.1148/rg.281075171
Pedrosa I, Levine D, Eyvazzadeh AD, et al (2006) MR Imaging Evaluation of Acute Appendicitis in Pregnancy. Radiology 238:891–899. https://doi.org/https://doi.org/10.1148/radiol.2383050146
Nunes JO, Turner MA, Fulcher AS (2005) Abdominal Imaging Features of HELLP Syndrome: A 10-Year Retrospective Review. American Journal of Roentgenology 185:1205–1210. https://doi.org/https://doi.org/10.2214/AJR.04.0817
Hepburn IS, Schade RR (2008) Pregnancy-Associated Liver Disorders. Dig Dis Sci 53:2334–2358. https://doi.org/https://doi.org/10.1007/s10620-007-0167-9
Jorge AM, Keswani RN, Veerappan A, et al (2015) Non-operative Management of Symptomatic Cholelithiasis in Pregnancy is Associated with Frequent Hospitalizations. Journal of Gastrointestinal Surgery 19:598–603. https://doi.org/https://doi.org/10.1007/s11605-015-2757-8
Pearl JP, Price RR, Tonkin AE, et al (2017) SAGES guidelines for the use of laparoscopy during pregnancy. Surg Endosc 31:3767–3782. https://doi.org/https://doi.org/10.1007/s00464-017-5637-3
Rios-Diaz AJ, Oliver EA, Bevilacqua LA, et al (2020) Is It Safe to Manage Acute Cholecystitis Nonoperatively During Pregnancy? Ann Surg 272:449–456. https://doi.org/https://doi.org/10.1097/SLA.0000000000004210
Shergill AK, Ben-Menachem T, Chandrasekhara V, et al (2012) Guidelines for endoscopy in pregnant and lactating women. Gastrointest Endosc 76:18–24. https://doi.org/https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gie.2012.02.029
Sharma BC, Agarwal DK, Baijal SS, et al (1998) Effect of endoscopic sphincterotomy on gall bladder bile lithogenicity and motility. Gut 42:288–292. https://doi.org/https://doi.org/10.1136/gut.42.2.288
Little MW, Briggs JH, Tapping CR, et al (2013) Percutaneous cholecystostomy: the radiologist’s role in treating acute cholecystitis. Clin Radiol 68:654–60. https://doi.org/https://doi.org/10.1016/j.crad.2013.01.017
Allmendinger N, Hallisey MJ, Ohki SK, Straub JJ (1995) Percutaneous cholecystostomy treatment of acute cholecystitis in pregnancy. Obstetrics and gynecology 86:653–4. https://doi.org/https://doi.org/10.1016/0029-7844(95)00087-8
Nennstiel S, Treiber M, Faber A, et al (2019) Comparison of Ultrasound and Fluoroscopically Guided Percutaneous Transhepatic Biliary Drainage. Dig Dis 37:77–86. https://doi.org/https://doi.org/10.1159/000493120
Miyazaki M, Shibuya K, Tokue H, Tsushima Y (2013) Percutaneous transhepatic biliary drainage assisted by real-time virtual sonography: a retrospective study. BMC Gastroenterol 13:127. https://doi.org/https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-230X-13-127
McCollough CH, Schueler BA, Atwell TD, et al (2007) Radiation Exposure and Pregnancy: When Should We Be Concerned? RadioGraphics 27:909–917. https://doi.org/https://doi.org/10.1148/rg.274065149
Funding
No funding or research support for this article.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors made substantial contributions to the conception or design of the work; drafted the work or revised it critically for important intellectual content; approved the version to be published; and agreed to be accountable for all aspects of the work in ensuring that questions related to the accuracy or integrity of any part of the work are appropriately investigated and resolved.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflicts of interest
No conflict of interest or competing interests.
Ethical approval
Not applicable.
Consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Sundaram, K.M., Morgan, M.A., Depetris, J. et al. Imaging of benign gallbladder and biliary pathologies in pregnancy. Abdom Radiol 48, 1921–1932 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00261-023-03832-1
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00261-023-03832-1