Abstract
Purpose
This retrospective study aimed to evaluate the clinical safety and efficacy of super-selective transcatheter vesical arterial chemoembolization with epirubicin-loaded CalliSpheres® beads (DEB-TACE) for treating muscle-invasive bladder cancer with hematuria.
Methods
We reviewed the retrospective records of 20 muscle-invasive bladder cancer patients with hematuria who were treated with super-selective transcatheter vesical arterial by oxaliplatin and 100–300-μm CalliSpheres loaded with epirubicin. The primary outcomes were the technical and clinical success rates. The secondary outcomes were complications, treatment responses, quality of life (QOL), median overall survival, and 1- and 2-year survival rates. QOL was routinely assessed by nurses at admission and during telephone follow-up 4 weeks after discharge.
Results
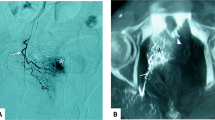
The technical success rate was 80.0% (16/20). Bleeding was controlled after the first embolization in 18/20 patients and after re-embolization within 7 days of the first embolization in the remaining two patients. The clinical success rate was 90% (18/20). After 4 weeks of follow-up, the mean hematocrit and hemoglobin levels improved significantly (P < 0.05). Four patients (20.0%) showed hematuria recurrence during a 4–8-month follow-up period. There were no severe complications, such as necrosis of the bladder, genitals, perineal skin, or procedure-related deaths. The complete response, partial response, stable disease, and progressive disease frequencies were 5.0%, 55.0%, 25.0%, and 15.0%, respectively, resulting in an objective response rate of 60.0% and a disease control rate of 85.0% after 1 month. 4 weeks after embolization, QOL was significantly higher than that pre-operation, except for social/family status (P < 0.05). The median overall survival was 18.5 months, and the 1- and 2-year survival rates were 75.0% and 46.7%, respectively.
Conclusion
DEB-TACE is safe and effective for treating muscle-invasive bladder cancer with hematuria, preserving bladder function and improving the QOL.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
General Office of the National Health. Guidelines for Diagnosis and treatment of Bladder Cancer 2022 (2022) Commission. http://www.nhc.gov.cn/yzygj/s7659/202204/a0e67177df1f439898683e1333957c74/files/7224e506d4a24b90a9df0424888ba38a.pdf Accessed 11 April 2022
Abt D, Bywater M, Engeler DS, Schmid HP (2013) Therapeutic options for intractable hematuria in advanced bladder cancer. Int J Urol 20 (7):651-660. https://doi.org/10.1111/iju.12113
Ghahestani SM, Shakhssalim N (2009) Palliative treatment of intractable hematuria in context of advanced bladder cancer: a systematic review. Urol J 6 (3):149-156
Hald T, Mygind T (1974) Control of life-threatening vesical hemorrhage by unilateral hypogastric artery muscle embolization. J Urol 112 (1):60-63. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0022-5347(17)59642-1
Loffroy R, Pottecher P, Cherblanc V, Favelier S, Estivalet L, Koutlidis N, Moulin M, Cercueil JP, Cormier L, Krausé D (2014) Current role of transcatheter arterial embolization for bladder and prostate hemorrhage. Diagn Interv Imaging 95 (11):1027-1034. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.diii.2014.03.008
Tsitskari M, Spiliopoulos S, Konstantos C, Palialexis K, Reppas L, Brountzos E (2020) Long-term results of super-selective trans-catheter embolization of the vesical arteries for the treatment of intractable bladder haematuria. CVIR Endovasc 3 (1):97. https://doi.org/10.1186/s42155-020-00188-1
Chen C, Kim PH, Shin JH, Yoon KW, Chung MS, Li HL, Hong B (2021) Transcatheter arterial embolization for intractable, nontraumatic bladder hemorrhage in cancer patients: a single-center experience and systematic review. Jpn J Radiol 39 (3):273-282. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11604-020-01051-y
Korkmaz M, Şanal B, Aras B, Bozkaya H, Çınar C, Güneyli S, Gök M, Adam G, Düzgün F, Oran I (2016) The short- and long-term effectiveness of transcatheter arterial embolization in patients with intractable hematuria. Diagn Interv Imaging 97 (2):197-201. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.diii.2015.06.020
Nabi G, Sheikh N, Greene D, Marsh R (2003) Therapeutic transcatheter arterial embolization in the management of intractable haemorrhage from pelvic urological malignancies: preliminary experience and long-term follow-up. BJU Int 92 (3):245-247. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1464-410x.2003.04328.x
Huang B, Huang G, Li W, Chen L, Mao X, Chen J (2021) Intra-arterial chemotherapy combined with intravesical chemotherapy compared with intravesical BCG immunotherapy retrospectively in high-risk non-muscle-invasive bladder cancer after transurethral resection of the bladder tumor. J Cancer Res Clin Oncol 147 (6):1781-1788. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00432-020-03453-x
Liang S, Zou Q, Han B, Jing Y, Cui D, An X, Gao Y, Hu J, Xia S (2015) Intra-arterial chemotherapy for muscle-invasive bladder cancer following transurethral resection. Urol Int 94 (4):406-411. https://doi.org/10.1159/000369301
Wentland AL, Desser TS, Troxell ML, Kamaya A (2019) Bladder cancer and its mimics: a sonographic pictorial review with CT/MR and histologic correlation. Abdom Radiol (NY) 44 (12):3827-3842. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00261-019-02276-w
Gao WJ, Liu YY, Yuan CR (2012) International evaluation system for adverse events of chemotherapeutic drugs in cancer treatment: CTCAE v4.0. Tumor 32 (02):142–144. https://doi.org/10.3781/j.issn.1000-7431.2012.02.013
Cella DF, Tulsky DS, Gray G, Sarafian B, Linn E, Bonomi A, Silberman M, Yellen SB, Winicour P, Brannon J, Eckberg K, Lloyd S, Purl S, Blendowski C, Goodman M, Barnicle M, Stewart I, McHale M, Bonomi P, Kaplan E, Taylor S, Thomas C, Harris J (1993) The Functional Assessment of Cancer Therapy scale: development and validation of the general measure. J Clin Oncol 11 (3):570-579. https://doi.org/10.1200/JCO.1993.11.3.570
Bilhim T, Casal D, Furtado A, Pais D, O'Neill JE, Pisco JM (2011) Branching patterns of the male internal iliac artery: imaging findings. Surg Radiol Anat 33 (2):151-159. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00276-010-0716-3
Delgal A, Cercueil JP, Koutlidis N, Michel F, Kermarrec I, Mourey E, Cormier L, Krausé D, Loffroy R (2010) Outcome of transcatheter arterial embolization for bladder and prostate hemorrhage. J Urol 183 (5):1947-1953. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.juro.2010.01.003
Kim MS, Hong HP, Kang KA, Lee YR, Joo KJ, Cho YS, Lee YG (2021) Superselective vesical artery embolization for intractable bladder hemorrhage related to pelvic malignancy. Acta Radiol 62 (9):1229-1237. https://doi.org/10.1177/0284185120952781
Mohan S, Kumar S, Dubey D, Phadke RV, Baijal SS, Kathuria M (2019) Superselective vesical artery embolization in the management of intractable hematuria secondary to hemorrhagic cystitis. World J Urol 37 (10):2175-2182. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00345-018-2604-0
Melchiorre F, Patella F, Pescatori L, Pesapane F, Fumarola E, Biondetti P, Brambillasca P, Monaco C, Ierardi AM, Franceschelli G, Carrafiello G (2018) DEB-TACE: a standard review. Future Oncol 14 (28):2969-2984. https://doi.org/10.2217/fon-2018-0136
Rossi SM, Murray T, McDonough L, Kelly H (2021) Loco-regional drug delivery in oncology: current clinical applications and future translational opportunities. Expert Opin Drug Deliv 18 (5):607-623. https://doi.org/10.1080/17425247.2021.1856074
Liguori G, Amodeo A, Mucelli FP, Patel H, Marco D, Belgrano E, Trombetta C (2010) Intractable haematuria: long-term results after selective embolization of the internal iliac arteries. BJU Int 106 (4):500-503. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1464-410X.2009.09192.x
Pisco JM, Martins JM, Correia MG (1989) Internal iliac artery: embolization to control hemorrhage from pelvic neoplasms. Radiology 172 (2):337-339. https://doi.org/10.1148/radiology.172.2.2748811
Washington S, Osterberg EC, Elliott SP, Hittelman AB, Breyer BN (2016) Acute bladder necrosis after pelvic arterial embolization for pelvic trauma: lessons learned from two cases of immediate postembolization bladder necrosis. Case Rep Urol 2016:7594192. https://doi.org/10.1155/2016/7594192
Tarkhanov A, Bartal G, Druzhin S, Shakhbazyan R, Grebenev E, Kartashov M (2018) Bladder wall and surrounding tissue necrosis following bilateral superselective embolization of internal iliac artery branches due to uncontrollable haematuria related to bladder tumor: case report. CVIR Endovasc 1 (1):34. https://doi.org/10.1186/s42155-018-0043-z
You JX, Wang JB, Zhao Q, Zheng LZ, Fan XD, Su LX, Wen MZ, Yang XT (2019) Efficacy of superselective bladder arterial chemoembolization for the treatment of advanced bladder cancer with bleeding. J Intervent Radiol 28 (07):647-651. 10.3969/ j.issn.1008-794X.2019.07.008
Botteman MF, Pashos CL, Hauser RS, Laskin BL, Redaelli A (2003) Quality of life aspects of bladder cancer: a review of the literature. Qual Life Res 12 (6):675-688. https://doi.org/10.1023/a:1025144617752
Mohamed NE, Gilbert F, Lee CT, Sfakianos J, Knauer C, Mehrazin R, Badr H, Wittmann D, Downs T, Berry D, Given B, Wiklund P, Steineck G (2016) Pursuing quality in the application of bladder cancer quality of life research. Bladder Cancer 2 (2):139-149. https://doi.org/10.3233/BLC-160051
Guo XY, Zhang WH, Li BG, Li F, Xing WG, Yu HP, Si TG, Guo Z (2015) Clinical significance of embolization on quality of life of elderly patients with bladder hemorrhage. Cancer Res Prev Treat 42 (04):378-381. https://doi.org/10.3971/j.issn.1000-8578.2015.04.013
Funding
This study was supported by the Launch Fund of Fujian Medical University (Grant No.: 2019QH1164) and General project of Fujian Natural Science Foundation (Grant No.: 2020J011096).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors contributed to the study’s conception and design. YZ and JC performed material preparation, data collection, data analysis, and drafting the article. YZ and JC have contributed equally to this work. Pingzhou Chen performed management of the patients and data collection. YT, SW, and SC provided critical revision of the manuscript. ZF performed project administration and supervision. YZ and JC wrote the first draft of the manuscript, and all authors commented on previous versions of the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
This study was conducted in accordance with the provisions of the Declaration of Helsinki and was approved by the institutional review board of Fujian Provincial Hospital, Fuzhou, China. The requirement for written informed consent was waived owing to the study’s retrospective nature.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Zhou, Y., Chen, J., Chen, P. et al. Super-selective transcatheter vesical arterial chemoembolization with drug-loaded beads for muscle-invasive bladder cancer with hematuria. Abdom Radiol 48, 780–786 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00261-022-03748-2
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00261-022-03748-2