Abstract
Purpose
To determine if pancreas radiomics-based AI model can detect the CT imaging signature of type 2 diabetes (T2D).
Methods
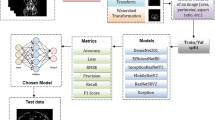
Total 107 radiomic features were extracted from volumetrically segmented normal pancreas in 422 T2D patients and 456 age-matched controls. Dataset was randomly split into training (300 T2D, 300 control CTs) and test subsets (122 T2D, 156 control CTs). An XGBoost model trained on 10 features selected through top-K-based selection method and optimized through threefold cross-validation on training subset was evaluated on test subset.
Results
Model correctly classified 73 (60%) T2D patients and 96 (62%) controls yielding F1-score, sensitivity, specificity, precision, and AUC of 0.57, 0.62, 0.61, 0.55, and 0.65, respectively. Model’s performance was equivalent across gender, CT slice thicknesses, and CT vendors (p values > 0.05). There was no difference between correctly classified versus misclassified patients in the mean (range) T2D duration [4.5 (0–15.4) versus 4.8 (0–15.7) years, p = 0.8], antidiabetic treatment [insulin (22% versus 18%), oral antidiabetics (10% versus 18%), both (41% versus 39%) (p > 0.05)], and treatment duration [5.4 (0–15) versus 5 (0–13) years, p = 0.4].
Conclusion
Pancreas radiomics-based AI model can detect the imaging signature of T2D. Further refinement and validation are needed to evaluate its potential for opportunistic T2D detection on millions of CTs that are performed annually.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
American Diabetes Association. https://www.diabetes.org/risk-test. Accessed June 8, 2022.
Bantie GM, Wondaye AA, Arike EB, Melaku MT, Ejigu ST, Lule A, et al. (2019) Prevalence of undiagnosed diabetes mellitus and associated factors among adult residents of Bahir Dar city, northwest Ethiopia: a community-based cross-sectional study. BMJ Open 9(10):e030158. https://doi.org/10.1136/bmjopen-2019-030158.
Cowie CC (2019) Diabetes Diagnosis and Control: Missed Opportunities to Improve Health : The 2018 Kelly West Award Lecture. Diabetes Care 42(6):994-1004. https://doi.org/10.2337/dci18-0047.
Hsueh L, Wu W, Hirsh AT, de Groot M, Mather KJ, Stewart JC (2020) Undiagnosed diabetes among immigrant and racial/ethnic minority adults in the United States: National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey 2011-2018. Ann Epidemiol 51:14-9. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.annepidem.2020.07.009.
Kopitar L, Kocbek P, Cilar L, Sheikh A, Stiglic G (2020) Early detection of type 2 diabetes mellitus using machine learning-based prediction models. Sci Rep 10(1):11981. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-020-68771-z.
Association AD (2020) 2. Classification and Diagnosis of Diabetes: Standards of Medical Care in Diabetes—2021. Diabetes Care 44(Supplement_1):S15-S33 https://doi.org/10.2337/dc21-S002.
Macauley M, Percival K, Thelwall PE, Hollingsworth KG, Taylor R (2015) Altered volume, morphology and composition of the pancreas in type 2 diabetes. PLoS One 10(5):e0126825. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0126825.
Saisho Y (2015) beta-cell dysfunction: Its critical role in prevention and management of type 2 diabetes. World J Diabetes 6(1):109-24. https://doi.org/10.4239/wjd.v6.i1.109.
Zeng N, Wang Y, Cheng Y, Huang Z, Song B (2022) Imaging evaluation of the pancreas in diabetic patients. Abdominal Radiology 47(2):715-26. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00261-021-03340-0.
Smith-Bindman R, Kwan ML, Marlow EC, Theis MK, Bolch W, Cheng SY, et al. (2019) Trends in Use of Medical Imaging in US Health Care Systems and in Ontario, Canada, 2000-2016. JAMA 322(9):843-56. https://doi.org/10.1001/jama.2019.11456.
Chu LC, Park S, Kawamoto S, Fouladi DF, Shayesteh S, Zinreich ES, et al. (2019) Utility of CT Radiomics Features in Differentiation of Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma From Normal Pancreatic Tissue. AJR Am J Roentgenol 213(2):349-57. https://doi.org/10.2214/AJR.18.20901.
Hanania AN, Bantis LE, Feng Z, Wang H, Tamm EP, Katz MH, et al. (2016) Quantitative imaging to evaluate malignant potential of IPMNs. Oncotarget 7(52):85776–84 https://doi.org/10.18632/oncotarget.11769.
Mashayekhi R, Parekh VS, Faghih M, Singh VK, Jacobs MA, Zaheer A (2020) Radiomic features of the pancreas on CT imaging accurately differentiate functional abdominal pain, recurrent acute pancreatitis, and chronic pancreatitis. Eur J Radiol 123:108778. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejrad.2019.108778.
Overbeek KA, Goggins MG, Dbouk M, Levink IJM, Koopmann BDM, Chuidian M, et al. (2022) Timeline of Development of Pancreatic Cancer and Implications for Successful Early Detection in High-Risk Individuals. Gastroenterology 162(3):772–85 e4 https://doi.org/10.1053/j.gastro.2021.10.014.
Qureshi TA, Gaddam S, Wachsman AM, Wang L, Azab L, Asadpour V, et al. (2022) Predicting pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma using artificial intelligence analysis of pre-diagnostic computed tomography images. Cancer Biomark 33(2):211-7. https://doi.org/10.3233/CBM-210273.
Mukherjee S, Patra A, Khasawneh H, Korfiatis P, Rajamohan N, Suman G, et al. (2022) Radiomics-Based Machine-Learning Models Can Detect Pancreatic Cancer on Prediagnostic CTs at a Substantial Lead Time Prior to Clinical Diagnosis. Gastroenterology. https://doi.org/10.1053/j.gastro.2022.06.066.
Burns JE, Yao J, Chalhoub D, Chen JJ, Summers RM (2020) A Machine Learning Algorithm to Estimate Sarcopenia on Abdominal CT. Acad Radiol 27(3):311-20. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.acra.2019.03.011.
Graffy PM, Liu J, O'Connor S, Summers RM, Pickhardt PJ (2019) Automated segmentation and quantification of aortic calcification at abdominal CT: application of a deep learning-based algorithm to a longitudinal screening cohort. Abdom Radiol (NY) 44(8):2921-8. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00261-019-02014-2.
Graffy PM, Liu J, Pickhardt PJ, Burns JE, Yao J, Summers RM (2019) Deep learning-based muscle segmentation and quantification at abdominal CT: application to a longitudinal adult screening cohort for sarcopenia assessment. Br J Radiol 92(1100):20190327. https://doi.org/10.1259/bjr.20190327.
Pickhardt PJ, Graffy PM, Zea R, Lee SJ, Liu J, Sandfort V, et al. (2020) Automated CT biomarkers for opportunistic prediction of future cardiovascular events and mortality in an asymptomatic screening population: a retrospective cohort study. Lancet Digit Health 2(4):e192-e200. https://doi.org/10.1016/S2589-7500(20)30025-X.
Pickhardt PJ, Graffy PM, Zea R, Lee SJ, Liu J, Sandfort V, et al. (2020) Automated Abdominal CT Imaging Biomarkers for Opportunistic Prediction of Future Major Osteoporotic Fractures in Asymptomatic Adults. Radiology 297(1):64-72. https://doi.org/10.1148/radiol.2020200466.
Pickhardt PJ, Graffy PM, Zea R, Lee SJ, Liu J, Sandfort V, et al. (2021) Utilizing Fully Automated Abdominal CT-Based Biomarkers for Opportunistic Screening for Metabolic Syndrome in Adults Without Symptoms. AJR Am J Roentgenol 216(1):85-92. https://doi.org/10.2214/AJR.20.23049.
BLINDED. https://doi.org/10.2214/AJR.20.24567.
MIRC CTP [Available from: http://mircwiki.rsna.org/index.php?title=CTP-The_RSNA_Clinical_Trial_Processor. Accessed June 8, 2022.
Fedorov A, Beichel R, Kalpathy-Cramer J, Finet J, Fillion-Robin JC, Pujol S, et al. (2012) 3D Slicer as an image computing platform for the Quantitative Imaging Network. Magn Reson Imaging 30(9):1323-41. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mri.2012.05.001.
van Griethuysen JJM, Fedorov A, Parmar C, Hosny A, Aucoin N, Narayan V, et al. (2017) Computational Radiomics System to Decode the Radiographic Phenotype. Cancer Res 77(21):e104-e7. https://doi.org/10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-17-0339.
scikit-learn:f_classif. https://scikit-learn.org/stable/modules/generated/sklearn.feature_selection.f_classif.html. Accessed June 8, 2022.
XGBoost https://xgboost.readthedocs.io/en/stable/)]. https://xgboost.readthedocs.io/en/stable/. Accessed June 8, 2022.
Kim SY, Kim H, Cho JY, Lim S, Cha K, Lee KH, et al. (2014) Quantitative assessment of pancreatic fat by using unenhanced CT: pathologic correlation and clinical implications. Radiology 271(1):104-12. https://doi.org/10.1148/radiol.13122883.
Lim S, Bae JH, Chun EJ, Kim H, Kim SY, Kim KM, et al. (2014) Differences in pancreatic volume, fat content, and fat density measured by multidetector-row computed tomography according to the duration of diabetes. Acta Diabetol 51(5):739-48. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00592-014-0581-3.
Jang S, Kim JH, Choi SY, Park SJ, Han JK (2020) Application of computerized 3D-CT texture analysis of pancreas for the assessment of patients with diabetes. PLoS One 15(1):e0227492. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0227492.
Lu C-Q, Wang Y-C, Meng X-P, Zhao H-T, Zeng C-H, Xu W, et al. (2019) Diabetes risk assessment with imaging: a radiomics study of abdominal CT. European Radiology 29(5):2233-42. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00330-018-5865-5.
Suman G, Panda A, Korfiatis P, Edwards ME, Garg S, Blezek DJ, et al. (2020) Development of a volumetric pancreas segmentation CT dataset for AI applications through trained technologists: a study during the COVID 19 containment phase. Abdominal Radiology 45(12):4302-10. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00261-020-02741-x.
Zhao B (2021) Understanding Sources of Variation to Improve the Reproducibility of Radiomics. Front Oncol 11:633176. https://doi.org/10.3389/fonc.2021.633176.
Tallam H, Elton DC, Lee S, Wakim P, Pickhardt PJ, Summers RM (2022) Fully Automated Abdominal CT Biomarkers for Type 2 Diabetes Using Deep Learning. Radiology: 211914 https://doi.org/10.1148/radiol.211914.
Chen T, Guestrin C. XGBoost: A Scalable Tree Boosting System. Proceedings of the 22nd ACM SIGKDD International Conference on Knowledge Discovery and Data Mining; San Francisco, California, USA: Association for Computing Machinery; 2016. p. 785–94.
Gilbeau JP, Poncelet V, Libon E, Derue G, Heller FR (1992) The density, contour, and thickness of the pancreas in diabetics: CT findings in 57 patients. AJR Am J Roentgenol 159(3):527-31. https://doi.org/10.2214/ajr.159.3.1503017.
Lu J, Guo M, Wang H, Pan H, Wang L, Yu X, et al. (2019) Association between Pancreatic Atrophy and Loss of Insulin Secretory Capacity in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus. J Diabetes Res 2019:6371231. https://doi.org/10.1155/2019/6371231.
Panda A, Korfiatis P, Suman G, Garg SK, Polley EC, Singh DP, et al. (2021) Two-stage deep learning model for fully automated pancreas segmentation on computed tomography: Comparison with intra-reader and inter-reader reliability at full and reduced radiation dose on an external dataset. Med Phys 48(5):2468-81. https://doi.org/10.1002/mp.14782.
Funding
None related to this work. Unrelated to this work (Dr. Goenka): Research grant from the Centene Charitable Foundation; Champions for Hope Pancreatic Cancer Research Program of the Funk-Zitiello Foundation; Advance the Practice Award from the Department of Radiology, Mayo Clinic, Rochester, Minnesota; CA190188, Department of Defense (DoD), Office of the Congressionally Directed Medical Research Programs (CDMRP); R01CA256969, National Cancer Institute (NCI) of the National Institutes of Health (NIH); R01CA272628-01, National Cancer Institute (NCI) of the National Institutes of Health (NIH); Institutional research grant from Sofie Biosciences; Advisory Board (ad hoc), BlueStar Genomics.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
Authors have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Wright, D.E., Mukherjee, S., Patra, A. et al. Radiomics-based machine learning (ML) classifier for detection of type 2 diabetes on standard-of-care abdomen CTs: a proof-of-concept study. Abdom Radiol 47, 3806–3816 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00261-022-03668-1
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00261-022-03668-1