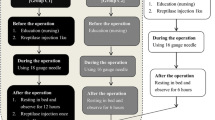
Abstract
Purpose
To assess the impact of elevated blood pressure on the rate of major hemorrhagic complication after renal transplant biopsy.
Methods
Pre-procedural systolic (SBP), diastolic (SBP), and mean arterial (MAP) blood pressure for consecutive patients undergoing US-guided renal transplant biopsies from 08/01/2015 to 7/31/2017 were retrospectively recorded. Patients who had a major bleeding complication were identified. The risk of complication as a function of SBP, DBP, and MAP was statistically analyzed, with significance set at p < 0.05.
Results
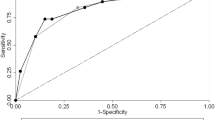
Of 1689 biopsies, there were 10 bleeding complications (10/1689, 0.59%). There was no statistically significant difference between biopsies with complication compared to those without complication based on SBP (p = 0.351), DBP (p = 0.088), or MAP (p = 0.132). Using risk dichotomization criteria, the odds ratio for hemorrhagic complication when the patient had SBP ≥ 180 mmHg and DBP ≥ 95 mmHg was 75.63 (95% CI 6.87–516.8, p = 0.002).
Conclusion
The rate of hemorrhagic complication from renal transplant biopsy is low, and there is no statistically significant threshold for increased biopsy risk based on SBP, DBP, or MAP alone. The risk of complication was significantly higher only when both the SBP is ≥ 180 mmHg and DBP is ≥ 95 mmHg.
Graphic abstract

Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The data that support the findings of this study are available from the corresponding author upon reasonable request.
Abbreviations
- SBP:
-
Systolic blood pressure
- DBP:
-
Diastolic blood pressure
- MAP:
-
Mean arterial pressure
- US:
-
Ultrasound
- EMR:
-
Electronic medical record
References
Patel MD, Young SW, Scott Kriegshauser J, Dahiya N. Ultrasound-guided renal transplant biopsy: practical and pragmatic considerations. Abdominal radiology (New York) 2018;43(10):2597-2603. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00261-018-1484-5
Patel AG, Kriegshauser JS, Young SW, Dahiya N, Patel MD. Detection of Bleeding Complications After Renal Transplant Biopsy. AJR Am J Roentgenol 2021;216(2):428-435. https://doi.org/10.2214/AJR.20.22990
Baffour FI, Hickson LJ, Stegall MD, Dean PG, Gunderson TM, Atwell TD, Kurup AN, Schmitz JJ, Park WD, Schmit GD. Effects of Aspirin Therapy on Ultrasound-Guided Renal Allograft Biopsy Bleeding Complications. Journal of vascular and interventional radiology: JVIR 2017;28(2):188-194. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jvir.2016.10.021
Redfield RR, McCune KR, Rao A, Sadowski E, Hanson M, Kolterman AJ, Robbins J, Guite K, Mohamed M, Parajuli S, Mandelbrot DA, Astor BC, Djamali A. Nature, timing, and severity of complications from ultrasound-guided percutaneous renal transplant biopsy. Transplant international: official journal of the European Society for Organ Transplantation 2016;29(2):167-172. https://doi.org/10.1111/tri.12660
Morgan TA, Chandran S, Burger IM, Zhang CA, Goldstein RB. Complications of Ultrasound-Guided Renal Transplant Biopsies. American journal of transplantation: official journal of the American Society of Transplantation and the American Society of Transplant Surgeons 2016;16(4):1298-1305. https://doi.org/10.1111/ajt.13622
Kriegshauser JS, Patel MD, Young SW, Chen F, Eversman WG, Chang YH. Risk of bleeding after native renal biopsy as a function of preprocedural systolic and diastolic blood pressure. Journal of vascular and interventional radiology: JVIR 2015;26(2):206-212. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jvir.2014.10.020
Potretzke TA, Gunderson TM, Aamodt D, Weisbrod AJ, Hesley GK, Welch TJ, Atwell TD. Incidence of bleeding complications after percutaneous core needle biopsy in hypertensive patients and comparison to normotensive patients. Abdominal radiology (New York) 2016;41(4):637-642. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00261-016-0653-7
Peters B, Andersson Y, Stegmayr B, Mölne J, Jensen G, Dahlberg P, Holm-Gunnarsson I, Ekberg J, Bjurström K, Haux SB, Hadimeri H. A study of clinical complications and risk factors in 1,001 native and transplant kidney biopsies in Sweden. Acta radiologica (Stockholm, Sweden: 1987) 2014;55(7):890–896. https://doi.org/10.1177/0284185113506190
Corapi KM, Chen JL, Balk EM, Gordon CE. Bleeding complications of native kidney biopsy: a systematic review and meta-analysis. American journal of kidney diseases: the official journal of the National Kidney Foundation 2012;60(1):62-73. https://doi.org/10.1053/j.ajkd.2012.02.330
Korbet SM, Volpini KC, Whittier WL. Percutaneous renal biopsy of native kidneys: a single-center experience of 1,055 biopsies. Am J Nephrol 2014;39(2):153-162. https://doi.org/10.1159/000358334
Shidham GB, Siddiqi N, Beres JA, Logan B, Nagaraja HN, Shidham SG, Piering WF. Clinical risk factors associated with bleeding after native kidney biopsy. Nephrology (Carlton) 2005;10(3):305-310. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1440-1797.2005.00394.x
Stratta P, Canavese C, Marengo M, Mesiano P, Besso L, Quaglia M, Bergamo D, Monga G, Mazzucco G, Ciccone G. Risk management of renal biopsy: 1387 cases over 30 years in a single centre. Eur J Clin Invest 2007;37(12):954-963. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2362.2007.01885.x
Luciano RL, Moeckel GW. Update on the Native Kidney Biopsy: Core Curriculum 2019. American journal of kidney diseases: the official journal of the National Kidney Foundation 2019;73(3):404-415. https://doi.org/10.1053/j.ajkd.2018.10.011
Whittier WL, Korbet SM. The Kidney Biopsy. In: Lam AO, ed. UpToDate2020.
Ponticelli C, Cucchiari D, Graziani G. Hypertension in kidney transplant recipients. Transplant international: official journal of the European Society for Organ Transplantation 2011;24(6):523-533. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1432-2277.2011.01242.x
Peters B, Nasic S, Jensen G, Stegmayr B. Renal transplant biopsy complications: assessment of risk factors and potential of desmopressin to decrease risk of hemorrhage. Acta radiologica (Stockholm, Sweden: 1987) 2020;61(12):1717–1723. https://doi.org/10.1177/0284185120910590
Kriegshauser JS, Osborn HH, Naidu SG, Huettl EA, Patel MD. Developing Interventional Radiology Anticoagulation Guidelines: Process and Benefits (dagger). Journal of clinical medicine 2018;7(4). https://doi.org/10.3390/jcm7040085
Patel MD, Phillips CJ, Young SW, Kriegshauser JS, Chen F, Eversman WG, Silva AC, Lorans R. US-guided renal transplant biopsy: efficacy of a cortical tangential approach. Radiology 2010;256(1):290-296.
Patel MD, Miranda R, Phillips CJ, Young SW, Liu PT, Roberts CC, Johnson CD. Impact of a quality assessment program on radiologist performance in ultrasound-guided renal transplant biopsy. Journal of the American College of Radiology: JACR 2011;8(5):355-359. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jacr.2010.08.014
U.S. Department of Health and Human Services, Common Terminology Criteria for Adverse Events (CTCAE) version 5.0. https://ctep.cancer.gov/protocolDevelopment/electronic_applications/ctc.htm#ctc_50. Published 2017. Updated November 27, 2017. Accessed 2020 February 17, 2020.
Funding
No funding was received for conducting this study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
All authors contributed to the study conception and design. Material preparation, data collection and analysis were performed by MDP, WTW, AGP, and NZ. The first draft of the manuscript was written by MDP; all authors commented on previous versions of the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors have no relevant financial or non-financial interests to disclose.
Ethical approval
This retrospective chart review study involving human participants was in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and national research committee and with the 1964 Helsinki Declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards. The Human Investigation Committee (IRB) of Mayo Clinic approved this study.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Wang, W.T., Patel, A.G., Zhang, N. et al. The impact of blood pressure on the risk of major bleeding complication after renal transplant biopsy. Abdom Radiol 47, 409–415 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00261-021-03282-7
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00261-021-03282-7