Abstract
Purpose
Percutaneous radiofrequency ablation (RFA) and microwave ablation (MWA) are well-validated interventions for hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC). The purpose of this study was to compare their safety and efficacy through a meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials (RCT).
Methods
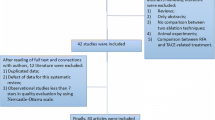
MEDLINE, Pubmed, and the Cochrane Library were queried up to September 2020 using the terms “microwave”, “radiofrequency”, “hepatocellular”, and “randomized”. Only RCTs investigating MWA versus RFA for HCC were included. Baseline study characteristics, complete ablation rate, ablation time, overall survival, local recurrence, and complication rates were investigated.
Results
Among the five original studies included, a total of 413 and 431 patients were treated with RFA and MWA, respectively. All studies focused on very early and early-stage HCC only (Barcelona Clinic Liver Cancer Stage 0 and A). No statistical significance was observed in terms of complete ablation rate (96.7 vs 96.9%, p = 0.882), overall survival (6 month: 95.7 vs 100%, p = 0.492; 1 year: 91.9 vs 94.1%, p = 0.264; 3 year: 77.5 vs 78.4%, p = 0.905), recurrence-free survival (6 month: 99.1 vs 99.7%, p = 0.717; 1 year: 94.6 vs 93.9%, p = 0.675; 3 year: 76.8 vs 77.1%, p = 0.935), and complication rates (p > 0.05 in all types). The mean ablation time of MWA was significantly shorter than RFA (26.9 vs 14.1 min, p < 0.001).
Conclusion
For very early and early-stage HCC, RFA and MWA are equally safe and effective, though the former is associated with a longer ablation time.





Similar content being viewed by others
Availability of data and material
The present study is a meta-analysis of publish articles.
Abbreviations
- CA:
-
Complete ablation rate
- HCC:
-
Hepatocellular carcinoma
- MWA:
-
Microwave ablation
- OS:
-
Overall survival
- RCT:
-
Randomized controlled trial
- RFA:
-
Radiofrequency ablation
- RFS:
-
Recurrence-free survival
References
J.D. Yang, L.R. Roberts, Epidemiology and management of hepatocellular carcinoma, Infectious Disease Clinics, 24 (2010) 899-919.
S. Shiina, Image-guided percutaneous ablation therapies for hepatocellular carcinoma, Journal of gastroenterology, 44 (2009) 122-131.
V. Patel, C.A. Ritchie, C. Padula, J.M. McKinney, Radiofrequency Ablation, Where It Stands in Interventional Radiology Today, Seminars in Interventional Radiology, Thieme Medical Publishers, 2019, pp. 398-404.
L.S. Poulou, E. Botsa, I. Thanou, P.D. Ziakas, L. Thanos, Percutaneous microwave ablation vs radiofrequency ablation in the treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma, World journal of hepatology, 7 (2015) 1054.
M.B. Glassberg, S. Ghosh, J.W. Clymer, R.A. Qadeer, N.C. Ferko, B. Sadeghirad, G.W. Wright, J.F. Amaral, Microwave ablation compared with radiofrequency ablation for treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma and liver metastases: a systematic review and meta-analysis, OncoTargets and therapy, 12 (2019) 6407.
A.A. van Tilborg, H.J. Scheffer, M.C. de Jong, L.G. Vroomen, K. Nielsen, C. van Kuijk, P.M. van den Tol, M.R. Meijerink, MWA versus RFA for perivascular and peribiliary CRLM: a retrospective patient-and lesion-based analysis of two historical cohorts, Cardiovascular and interventional radiology, 39 (2016) 1438-1446.
W. Shady, E.N. Petre, K.G. Do, M. Gonen, H. Yarmohammadi, K.T. Brown, N.E. Kemeny, M. D’Angelica, P.T. Kingham, S.B. Solomon, Percutaneous microwave versus radiofrequency ablation of colorectal liver metastases: ablation with clear margins (A0) provides the best local tumor control, Journal of Vascular and Interventional Radiology, 29 (2018) 268-275. e261.
R. Vasnani, M. Ginsburg, O. Ahmed, T. Doshi, J. Hart, H. Te, T.G. Van Ha, Radiofrequency and microwave ablation in combination with transarterial chemoembolization induce equivalent histopathologic coagulation necrosis in hepatocellular carcinoma patients bridged to liver transplantation, Hepatobiliary surgery and nutrition, 5 (2016) 225.
M. Ginsburg, S.P. Zivin, K. Wroblewski, T. Doshi, R.J. Vasnani, T.G. Van Ha, Comparison of combination therapies in the management of hepatocellular carcinoma: transarterial chemoembolization with radiofrequency ablation versus microwave ablation, Journal of vascular and interventional radiology, 26 (2015) 330-341.
K. Ohmoto, N. Yoshioka, Y. Tomiyama, N. Shibata, T. Kawase, K. Yoshida, M. Kuboki, S. Yamamoto, Comparison of therapeutic effects between radiofrequency ablation and percutaneous microwave coagulation therapy for small hepatocellular carcinomas, Journal of gastroenterology and hepatology, 24 (2009) 223-227.
Y.R. Huo, G.D. Eslick, Microwave ablation compared to radiofrequency ablation for hepatic lesions: a meta-analysis, Journal of Vascular and Interventional Radiology, 26 (2015) 1139-1146. e1132.
W. Tan, Q. Deng, S. Lin, Y. Wang, G. Xu, Comparison of microwave ablation and radiofrequency ablation for hepatocellular carcinoma: a systematic review and meta-analysis, International Journal of Hyperthermia, 36 (2019) 264-272.
A. Kamal, A.A.A. Elmoety, Y.A.M. Rostom, M.S. Shater, S.A. Lashen, Percutaneous radiofrequency versus microwave ablation for management of hepatocellular carcinoma: a randomized controlled trial, Journal of gastrointestinal oncology, 10 (2019) 562-571.
N. Vietti Violi, R. Duran, B. Guiu, J.P. Cercueil, C. Aube, A. Digklia, I. Pache, P. Deltenre, J.F. Knebel, A. Denys, Efficacy of microwave ablation versus radiofrequency ablation for the treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma in patients with chronic liver disease: a randomised controlled phase 2 trial, The lancet. Gastroenterology & hepatology, 3 (2018) 317-325.
T. Shibata, Y. Iimuro, Y. Yamamoto, Y. Maetani, F. Ametani, K. Itoh, J. Konishi, Small hepatocellular carcinoma: Comparison of radio-frequency ablation and percutaneous microwave coagulation therapy, Radiology, 223 (2002) 331-337.
E. Sheta, F. El-Kalla, M. El-Gharib, A. Kobtan, M. Elhendawy, S. Abd-Elsalam, L. Mansour, I. Amer, Comparison of single-session transarterial chemoembolization combined with microwave ablation or radiofrequency ablation in the treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma: a randomized-controlled study, European journal of gastroenterology & hepatology, 28 (2016) 1198-1203.
A. Abdelaziz, T. Elbaz, H.I. Shousha, S. Mahmoud, M. Ibrahim, A. Abdelmaksoud, M. Nabeel, Efficacy and survival analysis of percutaneous radiofrequency versus microwave ablation for hepatocellular carcinoma: an Egyptian multidisciplinary clinic experience, Surgical endoscopy, 28 (2014) 3429-3434.
J. Yu, X.L. Yu, Z.Y. Han, Z.G. Cheng, F.Y. Liu, H.Y. Zhai, M.J. Mu, Y.M. Liu, P. Liang, Percutaneous cooled-probe microwave versus radiofrequency ablation in early-stage hepatocellular carcinoma: a phase III randomised controlled trial, Gut, 66 (2017) 1172-1173.
F. Izzo, V. Granata, R. Grassi, R. Fusco, R. Palaia, P. Delrio, G. Carrafiello, D. Azoulay, A. Petrillo, S.A. Curley, Radiofrequency Ablation and Microwave Ablation in Liver Tumors: An Update, Oncologist, 24 (2019).
A. Facciorusso, G. Serviddio, N. Muscatiello, Local ablative treatments for hepatocellular carcinoma: an updated review, World journal of gastrointestinal pharmacology and therapeutics, 7 (2016) 477.
F. Primavesi, S. Swierczynski, E. Klieser, T. Kiesslich, T. Jäger, R. Urbas, J. Hutter, D. Neureiter, D. Öfner, S. Stättner, Thermographic real-time-monitoring of surgical radiofrequency and microwave ablation in a perfused porcine liver model, Oncology letters, 15 (2018) 2913-2920.
G.-J. Qian, N. Wang, Q. Shen, Y.H. Sheng, J.-Q. Zhao, M. Kuang, G.-J. Liu, M.-C. Wu, Efficacy of microwave versus radiofrequency ablation for treatment of small hepatocellular carcinoma: experimental and clinical studies, European radiology, 22 (2012) 1983-1990.
T.A. Potretzke, T.J. Ziemlewicz, J.L. Hinshaw, M.G. Lubner, S.A. Wells, C.L. Brace, P. Agarwal, F.T. Lee Jr, Microwave versus radiofrequency ablation treatment for hepatocellular carcinoma: a comparison of efficacy at a single center, Journal of Vascular and Interventional Radiology, 27 (2016) 631-638.
W. Liu, Y. Zheng, W. He, R. Zou, J. Qiu, J. Shen, Z. Yang, Y. Zhang, C. Wang, Y. Wang, Microwave vs radiofrequency ablation for hepatocellular carcinoma within the Milan criteria: a propensity score analysis, Alimentary pharmacology & therapeutics, 48 (2018) 671-681.
D.M. Lloyd, K.N. Lau, F. Welsh, K.-F. Lee, D.J. Sherlock, M.A. Choti, J.B. Martinie, D.A. Iannitti, International multicentre prospective study on microwave ablation of liver tumours: preliminary results, HPB, 13 (2011) 579-585.
J.K. Heimbach, L.M. Kulik, R.S. Finn, C.B. Sirlin, M.M. Abecassis, L.R. Roberts, A.X. Zhu, M.H. Murad, J.A. Marrero, AASLD guidelines for the treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma, Hepatology (Baltimore, Md.), 67 (2018) 358-380.
E.A.F.T.S.O.T. Liver, EASL clinical practice guidelines: management of hepatocellular carcinoma, Journal of hepatology, 69 (2018) 182-236.
S. Young, J. Golzarain, Locoregional Therapies in the Treatment of 3-to 5-cm Hepatocellular Carcinoma: Critical Review of the Literature, American Journal of Roentgenology, (2020) 1-12.
D. Haemmerich, D.J. Schutt, Sequential activation of multiple grounding pads reduces skin heating during radiofrequency tumor ablation, International Journal of Hyperthermia, 23 (2007) 555-566.
S. Clasen, H. Rempp, R. Hoffmann, H. Graf, P.L. Pereira, C.D. Claussen, Image-guided radiofrequency ablation of hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC): is MR guidance more effective than CT guidance?, European Journal of Radiology, 83 (2014) 111-116.
Y. Minami, N. Nishida, M. Kudo, Therapeutic response assessment of RFA for HCC: contrast-enhanced US, CT and MRI, World Journal of Gastroenterology: WJG, 20 (2014) 4160.
A. Kambadakone, V. Baliyan, H. Kordbacheh, R.N. Uppot, A. Thabet, D.A. Gervais, R.S. Arellano, Imaging guided percutaneous interventions in hepatic dome lesions: Tips and tricks, World journal of hepatology, 9 (2017) 840.
Funding
None.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
All authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yu, Q., Liu, C., Navuluri, R. et al. Percutaneous microwave ablation versus radiofrequency ablation of hepatocellular carcinoma: a meta-analysis of randomized controlled trials. Abdom Radiol 46, 4467–4475 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00261-021-03080-1
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00261-021-03080-1