Abstract
Purpose
To compare automated versus standard of care manual processing of 2D gradient recalled echo (GRE) liver MR Elastography (MRE) in children and young adults.
Materials and methods
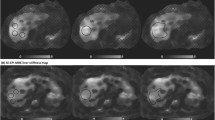
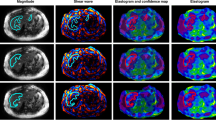
2D GRE liver MRE data from research liver MRI examinations performed as part of an autoimmune liver disease registry between March 2017 and March 2020 were analyzed retrospectively. All liver MRE data were acquired at 1.5 T with 60 Hz mechanical vibration frequency. For manual processing, two independent readers (R1, R2) traced regions of interest on scanner generated shear stiffness maps. Automated processing was performed using MREplus+ (Resoundant Inc.) using 90% (A90) and 95% (A95) confidence masks. Agreement was evaluated using intra-class correlation coefficients (ICC) and Bland–Altman analyses. Classification performance was evaluated using receiver operating characteristic curve (ROC) analyses.
Results
In 65 patients with mean age of 15.5 ± 3.8 years (range 8–23 years; 35 males) median liver shear stiffness was 2.99 kPa (mean 3.55 ± 1.69 kPa). Inter-reader agreement for manual processing was very strong (ICC = 0.99, mean bias = 0.01 kPa [95% limits of agreement (LoA): − 0.41 to 0.44 kPa]). Correlation between manual and A95 automated processing was very strong (R1: ICC = 0.988, mean bias = 0.13 kPa [95% LoA: − 0.40 to 0.68 kPa]; R2: ICC = 0.987, mean bias = 0.13 kPa [95% LoA: − 0.44 to 0.69 kPa]). Automated measurements were perfectly replicable (ICC = 1.0; mean bias = 0 kPa).
Conclusion
Liver shear stiffness values obtained using automated processing showed excellent agreement with manual processing. Automated processing of liver MRE was perfectly replicable.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Yin M, Talwalkar JA, Glaser KJ, Manduca A, Grimm RC, Rossman PJ, Fidler JL, Ehman RL. Assessment of hepatic fibrosis with magnetic resonance elastography. Clinical gastroenterology and hepatology : the official clinical practice journal of the American Gastroenterological Association 2007;5(10):1207-1213.e1202. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cgh.2007.06.012
Huwart L, Sempoux C, Vicaut E, Salameh N, Annet L, Danse E, Peeters F, ter Beek LC, Rahier J, Sinkus R, Horsmans Y, Van Beers BE. Magnetic resonance elastography for the noninvasive staging of liver fibrosis. Gastroenterology 2008;135(1):32-40. https://doi.org/10.1053/j.gastro.2008.03.076
Venkatesh SK, Yin M, Ehman RL. Magnetic resonance elastography of liver: technique, analysis, and clinical applications. Journal of magnetic resonance imaging : JMRI 2013;37(3):544-555. https://doi.org/10.1002/jmri.23731
Xanthakos SA, Podberesky DJ, Serai SD, Miles L, King EC, Balistreri WF, Kohli R. Use of magnetic resonance elastography to assess hepatic fibrosis in children with chronic liver disease. J Pediatr 2014;164(1):186-188. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpeds.2013.07.050
Singh S, Venkatesh SK, Wang Z, Miller FH, Motosugi U, Low RN, Hassanein T, Asbach P, Godfrey EM, Yin M, Chen J, Keaveny AP, Bridges M, Bohte A, Murad MH, Lomas DJ, Talwalkar JA, Ehman RL. Diagnostic performance of magnetic resonance elastography in staging liver fibrosis: a systematic review and meta-analysis of individual participant data. Clinical gastroenterology and hepatology : the official clinical practice journal of the American Gastroenterological Association 2015;13(3):440-451.e446. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cgh.2014.09.046
Trout AT, Anupindi SA, Gee MS, Khanna G, Xanthakos SA, Serai SD, Baikpour M, Calle-Toro JS, Ozturk A, Zhang B, Dillman JR. Normal Liver Stiffness Measured with MR Elastography in Children. Radiology 2020:201513. https://doi.org/10.1148/radiol.2020201513
Sawh MC, Newton KP, Goyal NP, Angeles JE, Harlow K, Bross C, Schlein AN, Hooker JC, Sy EZ, Glaser KJ, Yin M, Ehman RL, Sirlin CB, Schwimmer JB. Normal range for MR elastography measured liver stiffness in children without liver diseas. Journal of Magnetic Resonance Imaging 2020;51(3):919-927. https://doi.org/10.1002/JMRI.26905
Venkatesh SK, Ehman RL. Magnetic resonance elastography of abdomen. Abdom Imaging 2015;40(4):745-759. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00261-014-0315-6
Dzyubak B, Glaser K, Yin M, Talwalkar J, Chen J, Manduca A, Ehman RL. Automated liver stiffness measurements with magnetic resonance elastography. Journal of Magnetic Resonance Imaging 2013;38(2):371-379. https://doi.org/10.1002/jmri.23980
Hoodeshenas S, Welle CL, Navin PJ, Dzyubak B, Eaton JE, Ehman RL, Venkatesh SK. Magnetic Resonance Elastography in Primary Sclerosing Cholangitis: Interobserver Agreement for Liver Stiffness Measurement with Manual and Automated Methods. Academic Radiology 2019;26(12):1625-1632. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.acra.2019.02.004
Joshi M, Dillman J, Towbin A, Serai S, Trout A. MR elastography: high rate of technical success in pediatric and young adult patients. Pediatric Radiology 2017;47:838-343. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00247-017-3831-z
Dzyubak B, Venkatesh SK, Manduca A, Glaser KJ, Ehman RL. Automated liver elasticity calculation for MR elastography. Journal of Magnetic Resonance Imaging 2016;43(5):1055-1063. https://doi.org/10.1002/jmri.25072
Trout AT, Sheridan RM, Serai SD, Xanthakos SA, Su W, Zhang B, Wallihan DB. Diagnostic Performance of MR Elastography for Liver Fibrosis in Children and Young Adults with a Spectrum of Liver Diseases. Radiology 2018;287(3):824-832. https://doi.org/10.1148/radiol.2018172099
Wuensch K, Evans J. Straightforward Statistics for the Behavioral Sciences. . Journal of the American Statistical Association 1996;91(436). https://doi.org/10.2307/2291607
Schwimmer JB, Behling C, Angeles JE, Paiz M, Durelle J, Africa J, Newton KP, Brunt EM, Lavine JE, Abrams SH, Masand P, Krishnamurthy R, Wong K, Ehman RL, Yin M, Glaser KJ, Dzyubak B, Wolfson T, Gamst AC, Hooker J, Haufe W, Schlein A, Hamilton G, Middleton MS, Sirlin CB. Magnetic resonance elastography measured shear stiffness as a biomarker of fibrosis in pediatric nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Hepatology (Baltimore, Md) 2017;66(5):1474-1485. https://doi.org/10.1002/hep.29241
Funding
This work was not funded by a grant or any other source of external funding.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gandhi, D.B., Pednekar, A., Braimah, A.B. et al. Assessment of agreement between manual and automated processing of liver MR elastography for shear stiffness estimation in children and young adults with autoimmune liver disease. Abdom Radiol 46, 3927–3934 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00261-021-03073-0
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00261-021-03073-0