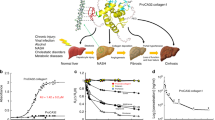
Abstract
Liver fibrosis is a common pathway shared by all progressive chronic liver diseases (CLD) regardless of the underlying etiologies. With liver biopsy being the gold standard in assessing fibrosis degree, there is a large unmet clinical need to develop non-invasive imaging tools that can directly and repeatedly quantify fibrosis throughout the liver for a more accurate assessment of disease burden, progression, and treatment response. Type I collagen is a particularly attractive target for molecular imaging as its excessive deposition is specific to fibrosis, and it is present in concentrations suitable for many imaging modalities. Novel molecular MRI contrast agents designed to bind with collagen provide direct quantification of collagen deposition, which have been validated across animal species and liver injury models. Collagen-targeted molecular imaging probes hold great promise not only as a tool for initial staging and surveillance of fibrosis progression, but also as a marker of fibrosis regression in drug trials.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Friedman SL (2008) Mechanisms of hepatic fibrogenesis. Gastroenterology 134 (6):1655–1669. https://doi.org/10.1053/j.gastro.2008.03.003
Vernon G, Baranova A, Younossi ZM (2011) Systematic review: the epidemiology and natural history of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease and non-alcoholic steatohepatitis in adults. Aliment Pharmacol Ther 34 (3):274–285. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2036.2011.04724.x
Estes C, Anstee QM, Arias-Loste MT, Bantel H, Bellentani S, Caballeria J, Colombo M, Craxi A, Crespo J, Day CP, Eguchi Y, Geier A, Kondili LA, Kroy DC, Lazarus JV, Loomba R, Manns MP, Marchesini G, Nakajima A, Negro F, Petta S, Ratziu V, Romero-Gomez M, Sanyal A, Schattenberg JM, Tacke F, Tanaka J, Trautwein C, Wei L, Zeuzem S, Razavi H (2018) Modeling NAFLD disease burden in China, France, Germany, Italy, Japan, Spain, United Kingdom, and United States for the period 2016–2030. J Hepatol 69 (4):896–904. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhep.2018.05.036
Bruix J, Sherman M, Practice Guidelines Committee AAftSoLD (2005) Management of hepatocellular carcinoma. Hepatology 42 (5):1208–1236. https://doi.org/10.1002/hep.20933
Friedman SL (2003) Liver fibrosis -- from bench to bedside. J Hepatol 38 Suppl 1:S38–53. https://doi.org/10.1016/s0168-8278(02)00429-4
Puoti C, Guarisco R, Bellis L, Spilabotti L (2009) Diagnosis, management, and treatment of hepatitis C. Hepatology 50 (1):322; author reply 324–325. https://doi.org/10.1002/hep.23015
Sumida Y, Nakajima A, Itoh Y (2014) Limitations of liver biopsy and non-invasive diagnostic tests for the diagnosis of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease/nonalcoholic steatohepatitis. World journal of gastroenterology 20 (2):475–485. https://doi.org/10.3748/wjg.v20.i2.475
Bravo AA, Sheth SG, Chopra S (2001) Liver biopsy. N Engl J Med 344 (7):495–500. https://doi.org/10.1056/NEJM200102153440706
Rosenberg WM, Voelker M, Thiel R, Becka M, Burt A, Schuppan D, Hubscher S, Roskams T, Pinzani M, Arthur MJ, European Liver Fibrosis G (2004) Serum markers detect the presence of liver fibrosis: a cohort study. Gastroenterology 127 (6):1704–1713. https://doi.org/10.1053/j.gastro.2004.08.052
Parkes J, Guha IN, Roderick P, Rosenberg W (2006) Performance of serum marker panels for liver fibrosis in chronic hepatitis C. J Hepatol 44 (3):462–474. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhep.2005.10.019
Chen J, Talwalkar JA, Yin M, Glaser KJ, Sanderson SO, Ehman RL (2011) Early detection of nonalcoholic steatohepatitis in patients with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease by using MR elastography. Radiology 259 (3):749–756. https://doi.org/10.1148/radiol.11101942
Salameh N, Larrat B, Abarca-Quinones J, Pallu S, Dorvillius M, Leclercq I, Fink M, Sinkus R, Van Beers BE (2009) Early detection of steatohepatitis in fatty rat liver by using MR elastography. Radiology 253 (1):90–97. https://doi.org/10.1148/radiol.2523081817
Nobili V, Vizzutti F, Arena U, Abraldes JG, Marra F, Pietrobattista A, Fruhwirth R, Marcellini M, Pinzani M (2008) Accuracy and reproducibility of transient elastography for the diagnosis of fibrosis in pediatric nonalcoholic steatohepatitis. Hepatology 48 (2):442–448. https://doi.org/10.1002/hep.22376
Yin M, Glaser KJ, Talwalkar JA, Chen J, Manduca A, Ehman RL (2016) Hepatic MR Elastography: Clinical Performance in a Series of 1377 Consecutive Examinations. Radiology 278 (1):114–124. https://doi.org/10.1148/radiol.2015142141
Hagan M, Asrani SK, Talwalkar J (2015) Non-invasive assessment of liver fibrosis and prognosis. Expert Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol 9 (10):1251–1260. https://doi.org/10.1586/17474124.2015.1075391
Sandrin L, Fourquet B, Hasquenoph JM, Yon S, Fournier C, Mal F, Christidis C, Ziol M, Poulet B, Kazemi F, Beaugrand M, Palau R (2003) Transient elastography: a new noninvasive method for assessment of hepatic fibrosis. Ultrasound in medicine & biology 29 (12):1705–1713
Ziol M, Handra-Luca A, Kettaneh A, Christidis C, Mal F, Kazemi F, de Ledinghen V, Marcellin P, Dhumeaux D, Trinchet JC, Beaugrand M (2005) Noninvasive assessment of liver fibrosis by measurement of stiffness in patients with chronic hepatitis C. Hepatology 41 (1):48–54. https://doi.org/10.1002/hep.20506
Cohen EB, Afdhal NH (2010) Ultrasound-based hepatic elastography: origins, limitations, and applications. J Clin Gastroenterol 44 (9):637–645. https://doi.org/10.1097/MCG.0b013e3181e12c39
Singh S, Venkatesh SK, Wang Z, Miller FH, Motosugi U, Low RN, Hassanein T, Asbach P, Godfrey EM, Yin M, Chen J, Keaveny AP, Bridges M, Bohte A, Murad MH, Lomas DJ, Talwalkar JA, Ehman RL (2015) Diagnostic performance of magnetic resonance elastography in staging liver fibrosis: a systematic review and meta-analysis of individual participant data. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol 13 (3):440–451 e446. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cgh.2014.09.046
Huwart L, Sempoux C, Vicaut E, Salameh N, Annet L, Danse E, Peeters F, ter Beek LC, Rahier J, Sinkus R, Horsmans Y, Van Beers BE (2008) Magnetic resonance elastography for the noninvasive staging of liver fibrosis. Gastroenterology 135 (1):32–40. https://doi.org/10.1053/j.gastro.2008.03.076
Horowitz JM, Venkatesh SK, Ehman RL, Jhaveri K, Kamath P, Ohliger MA, Samir AE, Silva AC, Taouli B, Torbenson MS, Wells ML, Yeh B, Miller FH (2017) Evaluation of hepatic fibrosis: a review from the society of abdominal radiology disease focus panel. Abdom Radiol (NY) 42 (8):2037–2053. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00261-017-1211-7
Hernandez-Gea V, Friedman SL (2011) Pathogenesis of liver fibrosis. Annu Rev Pathol 6:425–456. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev-pathol-011110-130246
Exposito JY, Valcourt U, Cluzel C, Lethias C (2010) The fibrillar collagen family. Int J Mol Sci 11 (2):407–426. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms11020407
Rojkind M, Giambrone MA, Biempica L (1979) Collagen types in normal and cirrhotic liver. Gastroenterology 76 (4):710–719
Helm PA, Caravan P, French BA, Jacques V, Shen L, Xu Y, Beyers RJ, Roy RJ, Kramer CM, Epstein FH (2008) Postinfarction myocardial scarring in mice: molecular MR imaging with use of a collagen-targeting contrast agent. Radiology 247 (3):788–796. https://doi.org/10.1148/radiol.2473070975
Caravan P, Das B, Dumas S, Epstein FH, Helm PA, Jacques V, Koerner S, Kolodziej A, Shen L, Sun WC, Zhang Z (2007) Collagen-targeted MRI contrast agent for molecular imaging of fibrosis. Angew Chem Int Ed Engl 46 (43):8171–8173. https://doi.org/10.1002/anie.200700700
Polasek M, Fuchs BC, Uppal R, Schuhle DT, Alford JK, Loving GS, Yamada S, Wei L, Lauwers GY, Guimaraes AR, Tanabe KK, Caravan P (2012) Molecular MR imaging of liver fibrosis: a feasibility study using rat and mouse models. J Hepatol 57 (3):549–555. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhep.2012.04.035
Fuchs BC, Wang H, Yang Y, Wei L, Polasek M, Schuhle DT, Lauwers GY, Parkar A, Sinskey AJ, Tanabe KK, Caravan P (2013) Molecular MRI of collagen to diagnose and stage liver fibrosis. J Hepatol 59 (5):992–998. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhep.2013.06.026
Farrar CT, DePeralta DK, Day H, Rietz TA, Wei L, Lauwers GY, Keil B, Subramaniam A, Sinskey AJ, Tanabe KK, Fuchs BC, Caravan P (2015) 3D molecular MR imaging of liver fibrosis and response to rapamycin therapy in a bile duct ligation rat model. J Hepatol 63 (3):689–696. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhep.2015.04.029
Inagaki Y, Higashiyama R, Higashi K (2012) Novel anti-fibrotic modalities for liver fibrosis: molecular targeting and regenerative medicine in fibrosis therapy. J Gastroenterol Hepatol 27 Suppl 2:85–88. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1440-1746.2011.07006.x
Kisseleva T, Brenner DA (2011) Anti-fibrogenic strategies and the regression of fibrosis. Best Pract Res Clin Gastroenterol 25 (2):305–317. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bpg.2011.02.011
Friedman SL, Sheppard D, Duffield JS, Violette S (2013) Therapy for fibrotic diseases: nearing the starting line. Sci Transl Med 5 (167):167sr161. https://doi.org/10.1126/scitranslmed.3004700
Popov Y, Schuppan D (2009) Targeting liver fibrosis: strategies for development and validation of antifibrotic therapies. Hepatology 50 (4):1294–1306. https://doi.org/10.1002/hep.23123
Neuschwander-Tetri BA, Loomba R, Sanyal AJ, Lavine JE, Van Natta ML, Abdelmalek MF, Chalasani N, Dasarathy S, Diehl AM, Hameed B, Kowdley KV, McCullough A, Terrault N, Clark JM, Tonascia J, Brunt EM, Kleiner DE, Doo E, Network NCR (2015) Farnesoid X nuclear receptor ligand obeticholic acid for non-cirrhotic, non-alcoholic steatohepatitis (FLINT): a multicentre, randomised, placebo-controlled trial. Lancet 385 (9972):956–965. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(14)61933-4
Sanyal AJ, Brunt EM, Kleiner DE, Kowdley KV, Chalasani N, Lavine JE, Ratziu V, McCullough A (2011) Endpoints and clinical trial design for nonalcoholic steatohepatitis. Hepatology 54 (1):344–353. https://doi.org/10.1002/hep.24376
Vergniol J, Foucher J, Terrebonne E, Bernard PH, le Bail B, Merrouche W, Couzigou P, de Ledinghen V (2011) Noninvasive tests for fibrosis and liver stiffness predict 5-year outcomes of patients with chronic hepatitis C. Gastroenterology 140 (7):1970–1979, 1979 e1971–1973. https://doi.org/10.1053/j.gastro.2011.02.058
Kim JH, Kim MN, Han KH, Kim SU (2015) Clinical application of transient elastography in patients with chronic viral hepatitis receiving antiviral treatment. Liver international : official journal of the International Association for the Study of the Liver 35 (4):1103–1115. https://doi.org/10.1111/liv.12628
Suda T, Okawa O, Masaoka R, Gyotoku Y, Tokutomi N, Katayama Y, Tamano M (2017) Shear wave elastography in hepatitis C patients before and after antiviral therapy. World J Hepatol 9 (1):64–68. https://doi.org/10.4254/wjh.v9.i1.64
Bachofner JA, Valli PV, Kroger A, Bergamin I, Kunzler P, Baserga A, Braun D, Seifert B, Moncsek A, Fehr J, Semela D, Magenta L, Mullhaupt B, Terziroli Beretta-Piccoli B, Mertens JC (2017) Direct antiviral agent treatment of chronic hepatitis C results in rapid regression of transient elastography and fibrosis markers fibrosis-4 score and aspartate aminotransferase-platelet ratio index. Liver international : official journal of the International Association for the Study of the Liver 37 (3):369–376. https://doi.org/10.1111/liv.13256
Laharie D, Seneschal J, Schaeverbeke T, Doutre MS, Longy-Boursier M, Pellegrin JL, Chabrun E, Villars S, Zerbib F, de Ledinghen V (2010) Assessment of liver fibrosis with transient elastography and FibroTest in patients treated with methotrexate for chronic inflammatory diseases: a case-control study. J Hepatol 53 (6):1035–1040. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhep.2010.04.043
Hoodeshenas S, Yin M, Venkatesh SK (2018) Magnetic Resonance Elastography of Liver: Current Update. Top Magn Reson Imaging 27 (5):319–333. https://doi.org/10.1097/RMR.0000000000000177
Mathew RP, Venkatesh SK (2018) Imaging of Hepatic Fibrosis. Curr Gastroenterol Rep 20 (10):45. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11894-018-0652-7
Popov Y, Sverdlov DY, Sharma AK, Bhaskar KR, Li S, Freitag TL, Lee J, Dieterich W, Melino G, Schuppan D (2011) Tissue transglutaminase does not affect fibrotic matrix stability or regression of liver fibrosis in mice. Gastroenterology 140 (5):1642–1652. https://doi.org/10.1053/j.gastro.2011.01.040
Neef M, Ledermann M, Saegesser H, Schneider V, Reichen J (2006) Low-dose oral rapamycin treatment reduces fibrogenesis, improves liver function, and prolongs survival in rats with established liver cirrhosis. J Hepatol 45 (6):786–796. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhep.2006.07.030
Erstad DJ, Farrar CT, Ghoshal S, Masia R, Ferreira DS, Chen YI, Choi JK, Wei L, Waghorn PA, Rotile NJ, Tu C, Graham-O'Regan KA, Sojoodi M, Li S, Li Y, Wang G, Corey KE, Or YS, Jiang L, Tanabe KK, Caravan P, Fuchs BC (2018) Molecular magnetic resonance imaging accurately measures the antifibrotic effect of EDP-305, a novel farnesoid X receptor agonist. Hepatol Commun 2 (7):821–835. https://doi.org/10.1002/hep4.1193
Levine D, McDonald RJ, Kressel HY (2018) Gadolinium Retention After Contrast-Enhanced MRI. JAMA 320 (18):1853–1854. https://doi.org/10.1001/jama.2018.13362
Le Fur M, Caravan P (2019) The biological fate of gadolinium-based MRI contrast agents: a call to action for bioinorganic chemists. Metallomics 11 (2):240–254. https://doi.org/10.1039/c8mt00302e
Farrar CT, Gale EM, Kennan R, Ramsay I, Masia R, Arora G, Looby K, Wei L, Kalpathy-Cramer J, Bunzel MM, Zhang C, Zhu Y, Akiyama TE, Klimas M, Pinto S, Diyabalanage H, Tanabe KK, Humblet V, Fuchs BC, Caravan P (2018) CM-101: Type I Collagen-targeted MR Imaging Probe for Detection of Liver Fibrosis. Radiology 287 (2):581–589. https://doi.org/10.1148/radiol.2017170595
Salarian M, Turaga RC, Xue S, Nezafati M, Hekmatyar K, Qiao J, Zhang Y, Tan S, Ibhagui OY, Hai Y, Li J, Mukkavilli R, Sharma M, Mittal P, Min X, Keilholz S, Yu L, Qin G, Farris AB, Liu ZR, Yang JJ (2019) Early detection and staging of chronic liver diseases with a protein MRI contrast agent. Nat Commun 10 (1):4777. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41467-019-11984-2
Waghorn PA, Jones CM, Rotile NJ, Koerner SK, Ferreira DS, Chen HH, Probst CK, Tager AM, Caravan P (2017) Molecular Magnetic Resonance Imaging of Lung Fibrogenesis with an Oxyamine-Based Probe. Angew Chem Int Ed Engl 56 (33):9825–9828. https://doi.org/10.1002/anie.201704773
Akam EA, Abston E, Rotile NJ, Slattery HR, Zhou IY, Lanuti M, Caravan P (2020) Improving the reactivity of hydrazine-bearing MRI probes for in vivo imaging of lung fibrogenesis. Chemical Science 11 (1):224–231. https://doi.org/10.1039/C9SC04821A
Chen HH, Waghorn PA, Wei L, Tapias LF, Schu Hle DT, Rotile NJ, Jones CM, Looby RJ, Zhao G, Elliott JM, Probst CK, Mino-Kenudson M, Lauwers GY, Tager AM, Tanabe KK, Lanuti M, Fuchs BC, Caravan P (2017) Molecular imaging of oxidized collagen quantifies pulmonary and hepatic fibrogenesis. JCI Insight 2 (11). https://doi.org/10.1172/jci.insight.91506
Zhu B, Wei L, Rotile N, Day H, Rietz T, Farrar CT, Lauwers GY, Tanabe KK, Rosen B, Fuchs BC, Caravan P (2017) Combined magnetic resonance elastography and collagen molecular magnetic resonance imaging accurately stage liver fibrosis in a rat model. Hepatology 65 (3):1015–1025. https://doi.org/10.1002/hep.28930
Atanasova I, Sojoodi M, Leitao HS, Shuvaev S, Geraldes C, Masia R, Guimaraes AS, Tanabe KK, Fuchs BC, Caravan P (2020) Molecular Magnetic Resonance Imaging of Fibrin Deposition in the Liver as an Indicator of Tissue Injury and Inflammation. Invest Radiol 59 (4):209–216. https://doi.org/10.1097/RLI.0000000000000631
Scotton CJ, Krupiczojc MA, Konigshoff M, Mercer PF, Lee YC, Kaminski N, Morser J, Post JM, Maher TM, Nicholson AG, Moffatt JD, Laurent GJ, Derian CK, Eickelberg O, Chambers RC (2009) Increased local expression of coagulation factor X contributes to the fibrotic response in human and murine lung injury. J Clin Invest 119 (9):2550–2563. https://doi.org/10.1172/JCI33288
Shea BS, Probst CK, Brazee PL, Rotile NJ, Blasi F, Weinreb PH, Black KE, Sosnovik DE, Van Cott EM, Violette SM, Caravan P, Tager AM (2017) Uncoupling of the profibrotic and hemostatic effects of thrombin in lung fibrosis. JCI Insight 2 (9). https://doi.org/10.1172/jci.insight.86608
Uppal R, Medarova Z, Farrar CT, Dai G, Moore A, Caravan P (2012) Molecular imaging of fibrin in a breast cancer xenograft mouse model. Invest Radiol 47 (10):553–558. https://doi.org/10.1097/RLI.0b013e31825dddfb
Zhou IY, Jordan VC, Rotile N, Akam EA, Krishnan S, Arora G, Krishnan H, Slattery HR, Warner N, Mercaldo N, Farrar CT, Wellen J, Martinez R, Schlerman F, Tanabe KK, Fuchs BC, Caravan P (2020) Advanced MRI of liver fibrosis and treatment response in a rat model of nonalcoholic steatohepatitis. Radiology 296 (1):67–75. https://doi.org/10.1148/radiol.2020192118
Arena U, Vizzutti F, Corti G, Ambu S, Stasi C, Bresci S, Moscarella S, Boddi V, Petrarca A, Laffi G, Marra F, Pinzani M (2008) Acute viral hepatitis increases liver stiffness values measured by transient elastography. Hepatology 47 (2):380–384. https://doi.org/10.1002/hep.22007
Petta S, Maida M, Macaluso FS, Di Marco V, Camma C, Cabibi D, Craxi A (2015) The severity of steatosis influences liver stiffness measurement in patients with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Hepatology 62 (4):1101–1110. https://doi.org/10.1002/hep.27844
Eddowes PJ, McDonald N, Davies N, Semple SIK, Kendall TJ, Hodson J, Newsome PN, Flintham RB, Wesolowski R, Blake L, Duarte RV, Kelly CJ, Herlihy AH, Kelly MD, Olliff SP, Hubscher SG, Fallowfield JA, Hirschfield GM (2018) Utility and cost evaluation of multiparametric magnetic resonance imaging for the assessment of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease. Alimentary pharmacology & therapeutics 47 (5):631–644. https://doi.org/10.1111/apt.14469
Pavlides M, Banerjee R, Tunnicliffe EM, Kelly C, Collier J, Wang LM, Fleming KA, Cobbold JF, Robson MD, Neubauer S, Barnes E (2017) Multiparametric magnetic resonance imaging for the assessment of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease severity. Liver international : official journal of the International Association for the Study of the Liver 37 (7):1065–1073. https://doi.org/10.1111/liv.13284
Spuentrup E, Ruhl KM, Botnar RM, Wiethoff AJ, Buhl A, Jacques V, Greenfield MT, Krombach GA, Gunther RW, Vangel MG, Caravan P (2009) Molecular magnetic resonance imaging of myocardial perfusion with EP-3600, a collagen-specific contrast agent: initial feasibility study in a swine model. Circulation 119 (13):1768–1775. https://doi.org/10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.108.826388
Caravan P, Yang Y, Zachariah R, Schmitt A, Mino-Kenudson M, Chen HH, Sosnovik DE, Dai G, Fuchs BC, Lanuti M (2013) Molecular magnetic resonance imaging of pulmonary fibrosis in mice. Am J Respir Cell Mol Biol 49 (6):1120–1126. https://doi.org/10.1165/rcmb.2013-0039OC
Polasek M, Yang Y, Schuhle DT, Yaseen MA, Kim YR, Sung YS, Guimaraes AR, Caravan P (2017) Molecular MR imaging of fibrosis in a mouse model of pancreatic cancer. Sci Rep 7 (1):8114. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-017-08838-6
Murphy AP, Greally E, O'Hogain D, Blamire A, Caravan P, Straub V (2019) Noninvasive quantification of fibrosis in skeletal and cardiac muscle in mdx mice using EP3533 enhanced magnetic resonance imaging. Magn Reson Med 81 (4):2728–2735. https://doi.org/10.1002/mrm.27578
Desogere P, Tapias LF, Rietz TA, Rotile N, Blasi F, Day H, Elliott J, Fuchs BC, Lanuti M, Caravan P (2017) Optimization of a Collagen-Targeted PET Probe for Molecular Imaging of Pulmonary Fibrosis. J Nucl Med 58 (12):1991–1996. https://doi.org/10.2967/jnumed.117.193532
Desogere P, Tapias LF, Hariri LP, Rotile NJ, Rietz TA, Probst CK, Blasi F, Day H, Mino-Kenudson M, Weinreb P, Violette SM, Fuchs BC, Tager AM, Lanuti M, Caravan P (2017) Type I collagen-targeted PET probe for pulmonary fibrosis detection and staging in preclinical models. Sci Transl Med 9 (384). https://doi.org/10.1126/scitranslmed.aaf4696
Wahsner J, Desogere P, Abston E, Graham-O'Regan KA, Wang J, Rotile NJ, Schirmer MD, Santos Ferreira DD, Sui J, Fuchs BC, Lanuti M, Caravan P (2019) (68)Ga-NODAGA-Indole: An Allysine-Reactive Positron Emission Tomography Probe for Molecular Imaging of Pulmonary Fibrogenesis. J Am Chem Soc 141 (14):5593–5596. https://doi.org/10.1021/jacs.8b12342
Montesi SB, Izquierdo-Garcia D, Desogere P, Abston E, Liang LL, Digumarthy S, Seethamraju R, Lanuti M, Caravan P, Catana C (2019) Type I Collagen-targeted Positron Emission Tomography Imaging in Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis: First-in-Human Studies. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 200 (2):258–261. https://doi.org/10.1164/rccm.201903-0503LE
Funding
We acknowledge support from the National Institute of Diabetes and Digestive and Kidney Diseases with Grants DK104956, DK104302, DK121789.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
P.C. has equity in and is a consultant to Collagen Medical LLC which owns the patent rights to EP-3533 and CM-101, has equity in Reveal Pharmaceuticals Inc, and has research support from Pliant Therapeutics, Celgene, and Indalo Therapeutics. B.C.F. is an employee of Ferring Pharmaceuticals.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhou, I.Y., Tanabe, K.K., Fuchs, B.C. et al. Collagen-targeted molecular imaging in diffuse liver diseases. Abdom Radiol 45, 3545–3556 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00261-020-02677-2
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00261-020-02677-2