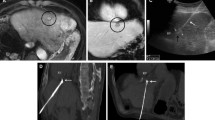
Abstract
Objective
To report the technique of hydrodissection of the sub-diaphragmatic bare area of the liver, in order to protect the diaphragm/heart during percutaneous thermal ablation (PTA) of sub-cardiac hepatic tumours.
Materials and methods
Between January 2016 and December 2018, five patients (four female, one male; mean age 56.2 years) with five sub-cardiac liver tumours (two hepatocellular carcinoma, three metastases; mean size 39 mm) abutting the bare area (segments II/IVA) with expected ablation zones ≤ 5 mm from the myocardium were treated with PTA and adjunctive hydrodissection. Time to perform hydrodissection, distance between superior hepatic and diaphragmatic/pericardial surfaces before and after hydrodissection, ablation efficacy, complications, and local tumour progression (LTP) at last imaging follow-up were recorded.
Results
Technical feasibility was 100%, with mean hydrodissection-volume of 126 ml (range 80–200 ml) and median hydrodissection-time of 9 min (range 8–45 min). Liver-diaphragmatic and liver-pericardial distance increased, respectively, from 2.4 mm (range 0–8 mm) to 10.8 mm (range 6–19 mm) and from 4 mm (range 1–10 mm) to 12.6 mm (range 8–20 mm) post-hydrodissection. All procedures were performed at full-power with complete tumour ablation and without complications (including peri-procedural haemodynamic/electrocardiographic disturbances, pericardial effusion and diaphragmatic hernia) or evidence of LTP at mean 12.2-month (range 1–26 month) follow-up.
Conclusion
Hydrodissection of the sub-diaphragmatic bare area of the liver is technically feasible and may potentially optimize safety PTA of sub-cardiac hepatic tumours.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Garnon J, Cazzato RL, Caudrelier J, Nouri-Neuville M, Rao P, Boatta E, Ramamurthy N, Koch G, Gangi A. Adjunctive thermoprotection during percutaneous thermal ablation procedures: review of current techniques. Cardiovasc Intervent Radiol. 2019;42(3):344–357. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00270-018-2089-7
Rhim H, Lim HK. Radiofrequency ablation for hepatocellular carcinoma abutting the diaphragm: the value of artificial ascites. Abdom Imaging. 2009 May-Jun;34(3):371–80. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00261-008-9408-4.
Bhagavatula SK, Chick JF, Chauhan NR, Shyn PB. Artificial ascites and pneumoperitoneum to facilitate thermal ablation of liver tumors: a pictorial essay. Abdom Radiol (NY). 2017 Feb;42(2):620–630. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00261-016-0910-9.
Kim S, Kim TU, Lee JW, Lee TH, Lee SH, Jeon TY, Kim KH. The perihepatic space: comprehensive anatomy and CT features of pathologic conditions. Radiographics.2007 Jan-Feb;27(1):129–43.
Coffin A, Boulay-Coletta I, Sebbag-Sfez D, Zins M. Radioanatomy of the retroperitoneal space. Diagn Interv Imaging. 2015 Feb;96(2):171–86. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.diii.2014.06.015.
Carberry GA, Smolock AR, Cristescu M, Wells SA, Ziemlewicz TJ, Lubner MG,Hinshaw JL, Brace CL, Lee FT Jr. Safety and Efficacy of Percutaneous Microwave Hepatic Ablation Near the Heart. J Vasc Interv Radiol. 2017 Apr;28(4):490–497. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jvir.2016.12.1216.
Schullian P, Putzer D, Laimer G, Levy E, Bale R. Feasibility, safety, and long-term efficacy of stereotactic radiofrequency ablation for tumors adjacent to the diaphragm in the hepatic dome: a case-control study. Eur Radiol. 2019 Sep 5. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00330-019-06399-y.
Smolock AR, Lubner MG, Ziemlewicz TJ, Hinshaw JL, Kitchin DR, Brace CL, Lee FT Jr. Microwave ablation of hepatic tumors abutting the diaphragm is safe and effective. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2015 Jan;204(1):197–203. https://doi.org/10.2214/ajr.14.12879.
Kang TW, Rhim H, Kim EY, et al. Percutaneous radiofrequency ablation for the hepatocellular carcinoma abutting the diaphragm: assessment of safety and therapeutic efficacy. Korean J Radiol. 2009;10(1):34–42. https://doi.org/10.3348/kjr.2009.10.1.34
Kwan J, Appuhamy C, Lim GHT, Huang IKH, Quek L, Pua U. Safety and Efficacy of Percutaneous Thermal Ablation of Juxta-Cardiac Hepatic Tumours. Cardiovasc Intervent Radiol. 2018 Jun;41(6):920–927. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00270-018-1938-8. Epub 2018 Mar 26.
Kwon JH, Won JY, Han K, Han S, Kim D, Kim H, Kim GM, Kim MD, Lee DY. Safety and Efficacy of Percutaneous Cryoablation for Small Hepatocellular Carcinomas Adjacent to the Heart. J Vasc Interv Radiol. 2019 Aug;30(8):1223–1228. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jvir.2018.12.030. Epub 2019 Apr 5.
Cha DI, Kang TW, Song KD, Lee MW, Rhim H, Lim HK, Sinn DH, Kim K. Radiofrequency ablation for subcardiac hepatocellular carcinoma: therapeutic outcomes and risk factors for technical failure. Eur Radiol. 2019 May;29(5):2706–2715. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00330-018-5868-2. Epub 2018 Nov 30.
Saito T, Chiba T, Ogasawara S, et al. Fatal Diaphragmatic Hernia following Radiofrequency Ablation for Hepatocellular Carcinoma: A Case Report and Literature Review. Case Rep Oncol. 2015;8(2):238–245. Published 2015 May 28. https://doi.org/10.1159/000431310
Silverman ER, Lai YH, Osborn IP, Yudkowitz FS. Percutaneous radiofrequency ablation of hepatocellular lesions in segment II of the liver: a risk factor for cardiac tamponade. J Clin Anesth. 2013 Nov;25(7):587–90. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclinane.2013.04.014.
Chung MW, Ha SY, Choi JH, Park HJ, Myung DS, Cho SB, Lee WS, Kim JW, Oh HH, Joo YE. Cardiac tamponade after radiofrequency ablation for hepatocellular carcinoma: Case report and literature review. Medicine (Baltimore). 2018 Dec;97(49):e13532. https://doi.org/10.1097/md.0000000000013532.
Patel IJ, Davidson JC. Standards of Practice Committee, with Cardiovascular and Interventional Radiological Society of Europe (CIRSE) Endorsement. Consensus guidelines for periprocedural management of coagulation status and hemostasis risk in percutaneous image-guided interventions. J Vasc Interv Radiol. 2012; 23(6):727–36
Campbell C, Lubner MG, Hinshaw JL, Muñoz del Rio A, Brace CL. Contrast media-doped hydrodissection during thermal ablation: optimizing contrast media concentration for improved visibility on CT images. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2012 Sep;199(3):677–82.
Sato R, Aramaki T, Yoza K, Iwai K, Moriguchi M, Asakura K, Endo M, Ito T. “Direct MPR”: A Useful Tool for Oblique CT Fluoroscopy-Assisted Puncture. Cardiovasc Intervent Radiol. 2017 Aug;40(8):1261–1266. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00270-017-1642-0.
Garnon J, Koch G, Caudrelier J, Ramamurthy N, Auloge P, Cazzato RL, Gangi A. Hydrodissection of the Gallbladder Bed: A Technique for Ablations Located Close to the Gallbladder. Cardiovasc Intervent Radiol. 2019 Jul;42(7):1029–1035. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00270-019-02218-5.
Garnon J, Koch G, Caudrelier J, Boatta E, Rao P, Nouri-Neuville M, Ramamurthy N, Cazzato RL, Gangi A. Hydrodissection of the Retrohepatic Space: A Technique to Physically Separate a Liver Tumour from the Inferior Vena Cava and the Ostia of the Hepatic Veins. Cardiovasc Intervent Radiol. 2019 Jan;42(1):137–144. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00270-018-2105-y.
Brennan DD, Ganguli S, Brecher CW, Goldberg SN. Thinking outside the abdominal box: safe use of the epipericardial fat pad window for percutaneous radiofrequency ablation of hepatic dome tumors. J Vasc Interv Radiol. 2008 Jan;19(1):133–6. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jvir.2007.08.023.
Qi H, Zhang H, Wan C, Xie L, Song Z, Fan W. CT-guided microwave ablation through the lungs for treating liver tumors near the diaphragm. Oncotarget. 2017;8(45):79270–79278. Published 2017 Apr 26. https://doi.org/10.18632/oncotarget.17422
Raman SS, Aziz D, Chang X, Sayre J, Lassman C, Lu D. Minimizing diaphragmatic injury during radiofrequency ablation: efficacy of intraabdominal carbon dioxide insufflation. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2004;183:197–200.
Knuttinen MG, Van Ha TG, Reilly C, Montag A, Straus C. Unintended thermal injuries from radiofrequency ablation: organ protection with an angioplasty balloon catheter in an animal model. J Clin Imaging Sci. 2014;4:1. Published 2014 Jan 30. https://doi.org/10.4103/2156-7514.126018
Lyu T, Wang X, Su Z, et al. Irreversible electroporation in primary and metastatic hepatic malignancies: A review. Medicine (Baltimore). 2017;96(17):e6386. https://doi.org/10.1097/md.0000000000006386
Abe T, Amano H, Takechi H, Fujikuni N, Sasada T, Yoshida M, Yamaki M, Nakahara M, Noriyuki T. Late-onset diaphragmatic hernia after percutaneous radiofrequency ablation of hepatocellular carcinoma: a case study. Surg Case Rep. 2016 Dec;2(1):25. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40792-016-0148-3.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Garnon, J., Cazzato, R.L., Auloge, P. et al. Adjunctive hydrodissection of the bare area of liver during percutaneous thermal ablation of sub-cardiac hepatic tumours. Abdom Radiol 45, 3352–3360 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00261-020-02463-0
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00261-020-02463-0