Abstract
Purpose
To predict the histologic grade of small clear cell renal cell carcinomas (ccRCCs) using texture analysis and machine learning algorithms.
Methods
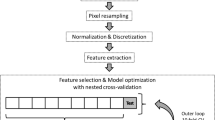
Fifty-two noncontrast (NC), 26 corticomedullary (CM) phase, and 35 nephrographic (NG) phase CTs of small (< 4 cm) surgically resected ccRCCs were retrospectively identified. Surgical pathology classified the tumors as low- or high-Fuhrman histologic grade. The axial image with the largest cross-sectional tumor area was exported and segmented. Six histogram and 31 texture (gray-level co-occurrences (GLC) and gray-level run-lengths (GLRL)) features were calculated for each tumor in each phase. T testing compared feature values in low- and high-grade ccRCCs, with a (Benjamini–Hochberg) false discovery rate of 10%. Area under the receiver operating curve (AUC) was calculated for each feature to assess prediction of low- and high-grade ccRCCs in each phase. Histogram, texture, and combined histogram and texture data sets were used to train and test four algorithms (k-nearest neighbor (KNN), support vector machine (SVM), random forests, and decision tree) with tenfold cross-validation; AUCs were calculated for each algorithm in each phase to assess prediction of low- and high-grade ccRCCs.
Results
Zero, 23, and 0 features in the NC, CM, and NG phases had statistically significant differences between low and high-grade ccRCCs. CM histogram skewness and GLRL short run emphasis had the highest AUCs (0.82) in predicting histologic grade. All four algorithms had the highest AUCs (0.97) predicting histologic grade using CM histogram features. The algorithms’ AUCs decreased using histogram or texture features from NC or NG phases.
Conclusion
The histologic grade of small ccRCCs can be accurately predicted with machine learning algorithms using CM histogram features, which outperform NC and NG phase image data.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Jayson M, Sanders H. Increased incidence of serendipitously discovered renal cell carcinoma. Urology 1998; 51: 203-205
Cooperberg MR, Mallin K, Ritchey J, Villalta JD, Carroll PR, Kane CJ. Decreasing size at diagnosis of stage 1 renal cell carcinoma: analysis from the National Cancer Data Base, 1993 to 2004. Journal of Urology 2008; 179: 2131-2135
Nguyen MM, Gill IS, Ellison LM. The evolving presentation of renal carcinoma in the United States: trends from the Surveillance, Epidemiology, and End Results program.. Journal of Urology 2006; 176: 2397-2400
Hollingsworth JM, Miller DC, Daignault S, Hollenbeck BK. Rising incidence of small renal masses: a need to reassess treatment effect.. Journal of the National Cancer Institute 2006; 98: 1331-1334
Campbell S, Uzzo RG, Allaf ME, Bass EB, Cadeddu JA, Chang A, Clark PE, Davis BJ, Derweesh IH, Giambarresi L, Gervais DA, Hu SL, Lane BR, Leibovich BC, Pierorazio PM. Renal Mass and Localized Renal Cancer: AUA Guideline. Journal of Urology 2017; 198: 520-529
Ficarra V, Righetti R, Martignoni G, D’Amico A, Pilloni S, Rubilotta E, Malossini G, Mobilio G. Prognostic value of renal cell carcinoma nuclear grading: multivariate analysis of 333 cases.. Urologia internationalis 2001; 67: 130-134
Gumundsson E, Hellborg H, Lundstam S, Erikson S, Ljungberg B, Swedish Kidney Cancer Quality Register Group. Metastatic potential in renal cell carcinomas <=7 cm: Swedish Kidney Cancer Quality Register data. European urology 2011; 60: 975-982
Fuhrman SA, Lasky LC, Limas C. Prognostic significance of morphologic parameters in renal cell carcinoma.. American Journal of Surgical Pathology 1982; 6: 655-663
Zisman A, Pantuck AJ, Dorey F, Said JW, Shvarts O, Quintana D, Gitlitz BJ, deKernion JB, Figlin RA, Belldegrun AS. Improved prognostication of renal cell carcinoma using an integrated staging system.. Journal of Clinical Oncology 2001; 19: 1649-1657
Rioux-Leclercq N, Karakiewicz PI, Trinh Q, Ficarra V, Cindolo L, de la Taille A, Tostain J, Zigeuner R, Mejean A, Patard J. Prognostic ability of simplified nuclear grading of renal cell carcinoma.. Cancer 2007; 109: 868-874
Sun M, Lughezzani G, Jeldres C, Isbarn H, Shariat SF, Arjane P, Widmer H, Pharand D, Latour M, Perrotte P, Patard J, Karakiewicz PI. A proposal for reclassification of the Fuhrman grading system in patients with clear cell renal cell carcinoma.. European urology 2009; 56: 775-781
Becker A, Hickmann D, Hansen J, Meyer C, Rink M, Schmid M, Eichelberg C, Strini K, Chromecki T, Jesche J, Regier M, Randazzo M, Tilki D, Ahyai S, Dahlem R, Fisch M, Zigeuner R, Chun FKH. Critical analysis of a simplified Fuhrman grading scheme for prediction of cancer specific mortality in patients with clear cell renal cell carcinoma–Impact on prognosis. European Journal of Surgical Oncology 2016; 42: 419-425
Ball MW, Bezerra SM, Gorin MA, Cowan M, Pavlovich CP, Pierorazio PM, Netto GJ, Allaf ME. Grade heterogeneity in small renal masses: potential implications for renal mass biopsy. Journal of Urology 2015; 193: 36-40
Patel HD, Johnson MH, Pierorazio PM, Sozio SM, Sharma R, Iyoha E, Bass EB, Allaf ME. Diagnostic Accuracy and Risks of Biopsy in the Diagnosis of a Renal Mass Suspicious for Localized Renal Cell Carcinoma: Systematic Review of the Literature. [Review]. Journal of Urology 2016; 195: 1340-134
Blumenfeld AJ, Guru K, Fuchs GJ, Kim HL. Percutaneous biopsy of renal cell carcinoma underestimates nuclear grade. Urology 2010; 76: 610-613
Lubner MG, Smith AD, Sandrasegaran K, Sahani DV, Pickhardt PJ. CT Texture Analysis: Definitions, Applications, Biologic Correlates, and Challenges. Radiographics 2017; 37: 1483-1503
Erickson BJ, Korfiatis P, Akkus Z, Kline TL. Machine Learning for Medical Imaging. Radiographics 2017; 37: 505-515
Chartrand G, Cheng PM, Vorontsov E, Drozdzal M, Turcotte S, Pal CJ, Kadoury S, Tang A. Deep Learning: A Primer for Radiologists. Radiographics 2017; 37: 2113-2131
Cruz JA, Wishart DS. Applications of machine learning in cancer prediction and prognosis. Cancer Informatics [Electronic Resource] 2007; 2: 59-77
Lubner MG, Stabo N, Abel EJ, Del Rio AM, Pickhardt PJ. CT Textural Analysis of Large Primary Renal Cell Carcinomas: Pretreatment Tumor Heterogeneity Correlates With Histologic Findings and Clinical Outcomes. AJR.American Journal of Roentgenology 2016; 207: 96-105
Shu J, Tang Y, Cui J, Yang R, Meng X, Cai Z, Zhang J, Xu W, Wen D, Yin H. Clear cell renal cell carcinoma: CT-based radiomics features for the prediction of Fuhrman grade. European Journal of Radiology 2018; 109: 8-12
Ding J, Xing Z, Jiang Z, Chen J, Pan L, Qiu J, Xing W. CT-based radiomic model predicts high grade of clear cell renal cell carcinoma. European Journal of Radiology 2018; 103: 51-56
Chen C, Kang Q, Xu B, Guo H, Wei Q, Wang T, Ye H, Wu X. Differentiation of low- and high-grade clear cell renal cell carcinoma: Tumor size versus CT perfusion parameters. Clinical imaging 2017; 46: 14-19
Ishigami K, Leite LV, Pakalniskis MG, Lee DK, Holanda DG, Kuehn DM. Tumor grade of clear cell renal cell carcinoma assessed by contrast-enhanced computed tomography. Springerplus 2014; 3: 694
Wei X. Gray Level Run Length Matrix Toolbox, Version 1.0.0.0. https://www.mathworks.com/matlabcentral/fileexchange/17482-gray-level-run-length-matrix-toolbox. Accessed 1 September 2017.
Supervised learning algorithms; scikit-learn 0.21.2. https://scikit-learn.org/stable/supervised_learning.html#supervised-learning. Accessed 15 Mar 2019
Albiges L, Salem M, Rini B, Escudier B. Vascular endothelial growth factor-targeted therapies in advanced renal cell carcinoma. Hematology - Oncology Clinics of North America 2011; 25: 813-833
Li L, Kaelin WGJ. New insights into the biology of renal cell carcinoma. Hematology - Oncology Clinics of North America 2011; 25: 667-686
Schieda N, Thornhill RE, Al-Subhi M, McInnes MDF, Shabana WM, van der Pol CB, Flood TA. Diagnosis of Sarcomatoid Renal Cell Carcinoma With CT: Evaluation by Qualitative Imaging Features and Texture Analysis. AJR.American Journal of Roentgenology 2015; 204: 1013-1023
Choi SY, Sung DJ, Yang KS, Kim KA, Yeom SK, Sim KC, Han NY, Park BJ, Kim MJ, Cho SB, Lee JH. Small (< 4 cm) clear cell renal cell carcinoma: correlation between CT findings and histologic grade. Abdominal Radiology 2016; 41: 1160-1169
Kierans AS, Rusinek H, Lee A, Shaikh MB, Triolo M, Huang WC, Chandarana H. Textural differences in apparent diffusion coefficient between low- and high-stage clear cell renal cell carcinoma. AJR.American Journal of Roentgenology 2014; 203: W637-44
Halverson SJ, Kunju LP, Bhalla R, Gadzinski AJ, Alderman M, Miller DC, Montgomery JS, Weizer AZ, Wu A, Hafez KS, Wolf JSJ. Accuracy of determining small renal mass management with risk stratified biopsies: confirmation by final pathology. Journal of Urology 2013; 189: 441-446
Kim SH, Kim CS, Kim MJ, Cho JY, Cho SH. Differentiation of Clear Cell Renal Cell Carcinoma From Other Subtypes and Fat-Poor Angiomyolipoma by Use of Quantitative Enhancement Measurement During Three-Phase MDCT. AJR.American Journal of Roentgenology 2016; 206: W21-8
Lee-Felker SA, Felker ER, Tan N, Margolis DJA, Young JR, Sayre J, Raman SS. Qualitative and quantitative MDCT features for differentiating clear cell renal cell carcinoma from other solid renal cortical masses. AJR.American Journal of Roentgenology 2014; 203: W516-24
Kay FU, Canvasser NE, Xi Y, Pinho DF, Costa DN, Diaz de Leon A, Khatri G, Leyendecker JR, Yokoo T, Lay AH, Kavoussi N, Koseoglu E, Cadeddu JA, Pedrosa I. Diagnostic Performance and Interreader Agreement of a Standardized MR Imaging Approach in the Prediction of Small Renal Mass Histology. Radiology 2018; 287: 543-553
Canvasser NE, Kay FU, Xi Y, Pinho DF, Costa D, de Leon AD, Khatri G, Leyendecker JR, Yokoo T, Lay A, Kavoussi N, Koseoglu E, Cadeddu JA, Pedrosa I. Diagnostic Accuracy of Multiparametric Magnetic Resonance Imaging to Identify Clear Cell Renal Cell Carcinoma in cT1a Renal Masses. Journal of Urology 2017; 198: 780-786
Raman SP, Chen Y, Schroeder JL, Huang P, Fishman EK. CT texture analysis of renal masses: pilot study using random forest classification for prediction of pathology. Academic Radiology 2014; 21: 1587-1596
Lubner MG, Stabo N, Lubner SJ, del Rio AM, Song C, Halberg RB, Pickhardt PJ. CT textural analysis of hepatic metastatic colorectal cancer: pre-treatment tumor heterogeneity correlates with pathology and clinical outcomes. Abdominal Imaging 2015; 40: 2331-2337
D’Onofrio M, Ciaravino V, Cardobi N, De Robertis R, Cingarlini S, Landoni L, Capelli P, Bassi C, Scarpa A. CT Enhancement and 3D Texture Analysis of Pancreatic Neuroendocrine Neoplasms. Scientific Reports 2019; 9: 2176
Ng F, Kozarski R, Ganeshan B, Goh V. Assessment of tumor heterogeneity by CT texture analysis: can the largest cross-sectional area be used as an alternative to whole tumor analysis?. European Journal of Radiology 2013; 82: 342-348
Shen C, Liu Z, Guan M, Song J, Lian Y, Wang S, Tang Z, Dong D, Kong L, Wang M, Shi D, Tian J. 2D and 3D CT Radiomics Features Prognostic Performance Comparison in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer. Translational Oncology 2017; 10: 886-894
Miles KA, Ganeshan B, Griffiths MR, Young RCD, Chatwin CR. Colorectal cancer: texture analysis of portal phase hepatic CT images as a potential marker of survival. Radiology 2009; 250: 444-452
Buch K, Li B, Qureshi MM, Kuno H, Anderson SW, Sakai O. Quantitative Assessment of Variation in CT Parameters on Texture Features: Pilot Study Using a Nonanatomic Phantom. Ajnr: American Journal of Neuroradiology 2017; 38: 981-985
He L, Huang Y, Ma Z, Liang C, Liang C, Liu Z. Effects of contrast-enhancement, reconstruction slice thickness and convolution kernel on the diagnostic performance of radiomics signature in solitary pulmonary nodule. Scientific Reports 2016; 6: 34921
Delahunt B, Cheville JC, Martignoni G, Humphrey PA, Magi-Galluzzi C, McKenney J, Egevad L, Algaba F, Moch H, Grignon DJ, Montironi R, Srigley JR, Members of the ISUP Renal Tumor Panel. The International Society of Urological Pathology (ISUP) grading system for renal cell carcinoma and other prognostic parameters. American Journal of Surgical Pathology 2013; 37: 1490-1504
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
All authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
IRB statement
This is an IRB-approved HIPAA-compliant study.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Haji-Momenian, S., Lin, Z., Patel, B. et al. Texture analysis and machine learning algorithms accurately predict histologic grade in small (< 4 cm) clear cell renal cell carcinomas: a pilot study. Abdom Radiol 45, 789–798 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00261-019-02336-1
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00261-019-02336-1