Abstract
Purpose
To evaluate the impact of complex-averaging on image quality (IQ) and diagnostic accuracy of acquired and calculated high b value (aHBV, cHBV) images in diffusion-weighted prostate MRI.
Materials and methods
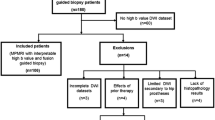
This retrospective study included 84 patients who underwent multiparametric prostate MRI at 3 Tesla without endorectal coil. DWIs were acquired at three different b values which included two lower b values (b = 50,900 s/mm2) and one higher b value (aHBV at 2000 s/mm2). The acquired data were postprocessed to generate two different types of trace-weighted images—using conventional magnitude-averaging and complex-averaging. Using lower b values (b = 50,900 s/mm2) from both conventional and complex-averaged image sets, cHBV images (b = 2000 s/mm2) and ADC maps were derived. All image sets were reviewed by two radiologists in different reading sessions to assess image quality and PIRADS. The diagnostic accuracy of different image sets for the detection of prostate lesions was performed by correlating PIRADS and Gleason scores.
Results
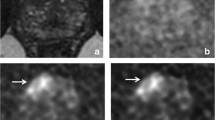
Complex-averaging did not impact ADC values of the prostate lesions compared to magnitude-averaging (P = 0.08). Complex-averaging improved image quality of acquired high b value and calculated high b value images (P < 0.0001). Complex-averaging also improved the level of confidence (LOC) of the acquired high b value for both readers (P < 0.0001, P < 0.05), but only for reader A in calculated high b value (P < 0.0001). The image quality of calculated high b value images was not significantly different than acquired high b value images. The dataset combining complex-averaging and calculated high b value provided the highest diagnostic accuracy (but not statistically significant) for detection of the significant prostate lesion compared to the magnitude-averaged acquired high b value (79.55% vs. 72.73%; P = 0.317). The mean acquisition time for b = 2000 s/mm2 sequence (aHBV) was 6 min 30 s (± 1 min 16 s) out of a total of 28 min 31 s (± 4 min 26 s) for the entire mp-MRI protocol (approximately 25% of total scan time).
Conclusion
Complex-averaging provides better image quality and level of confidence without significant impact on ADC values and diagnostic accuracy for detection of the significant prostate lesions . The calculated high b value images are also comparable to (and can substitute) the acquired high b value images which can help in reducing the imaging time.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Torre LA, Bray F, Siegel RL, Ferlay J, Lortet-Tieulent J, Jemal A. Global cancer statistics, 2012. CA Cancer J Clin. 2015 Mar 1;65(2):87–108.
Fütterer JJ, Briganti A, Visschere PD, Emberton M, Giannarini G, Kirkham A, et al. Can Clinically Significant Prostate Cancer Be Detected with Multiparametric Magnetic Resonance Imaging? A Systematic Review of the Literature. Eur Urol. 2015 Dec 1;68(6):1045–53.
Thoeny HC, Forstner R, De Keyzer F. Genitourinary Applications of Diffusion-weighted MR Imaging in the Pelvis. Radiology. 2012 May 1;263(2):326–42.
Baliyan V, Das CJ, Sharma S, Gupta AK. Diffusion-weighted imaging in urinary tract lesions. Clin Radiol. 2014 Aug 1;69(8):773–82.
Baliyan V, Das CJ, Sharma R, Gupta AK. Diffusion weighted imaging: Technique and applications. World J Radiol. 2016 Sep 28;8(9):785–98.
Kim CK, Park BK, Kim B. High-b-Value Diffusion-Weighted Imaging at 3 T to Detect Prostate Cancer: Comparisons Between b Values of 1,000 and 2,000 s/mm2. Am J Roentgenol. 2010 Jan 1;194(1):W33–7.
Maurer MH, Heverhagen JT. Diffusion weighted imaging of the prostate—principles, application, and advances. Transl Androl Urol. 2017 Jun;6(3):490–8.
Grant KB, Agarwal HK, Shih JH, Bernardo M, Pang Y, Daar D, et al. Comparison of calculated and acquired high b value diffusion-weighted imaging in prostate cancer. Abdom Imaging. 2015 Mar;40(3):578–86.
Agarwal HK, Mertan FV, Sankineni S, Bernardo M, Senegas J, Keupp J, et al. Optimal high b‐value for diffusion weighted MRI in diagnosing high risk prostate cancers in the peripheral zone. J Magn Reson Imaging. 2016 Jul 7;45(1):125–31.
Feng Q, Yan Y-Q, Zhu J, Tong J-L, Xu J-R. Optimal b value of diffusion-weighted imaging on a 3.0T magnetic resonance scanner in Crohn’s disease. World J Gastroenterol WJG. 2014 Sep 21;20(35):12621–7.
Zhuang J, Lu Z-L, Vidal CB, Damasio H. Correction of eddy current distortions in high angular resolution diffusion imaging. J Magn Reson Imaging. 2013;37(6):1460–1467.
Shenoy-Bhangle A, Baliyan V, Kordbacheh H, Guimaraes AR, Kambadakone A. Diffusion weighted magnetic resonance imaging of liver: Principles, clinical applications and recent updates. World J Hepatol. 2017 Sep 18;9(26):1081–91.
Ogura A, Koyama D, Hayashi N, Hatano I, Osakabe K, Yamaguchi N. Optimal b Values for Generation of Computed High-b-Value DW Images. Am J Roentgenol. 2016 Jan 21;206(4):713–8.
Maas MC, Fütterer JJ, Scheenen TWJ. Quantitative evaluation of computed high B value diffusion-weighted magnetic resonance imaging of the prostate. Invest Radiol. 2013 Nov;48(11):779–86.
Rosenkrantz AB, Chandarana H, Hindman N, Deng F-M, Babb JS, Taneja SS, et al. Computed diffusion-weighted imaging of the prostate at 3 T: impact on image quality and tumour detection. Eur Radiol. 2013 Nov;23(11):3170–7.
Ueno Y, Takahashi S, Kitajima K, Kimura T, Aoki I, Kawakami F, et al. Computed diffusion-weighted imaging using 3-T magnetic resonance imaging for prostate cancer diagnosis. Eur Radiol. 2013 Dec;23(12):3509–16.
Blackledge MD, Leach MO, Collins DJ, Koh D-M. Computed diffusion-weighted MR imaging may improve tumor detection. Radiology. 2011 Nov;261(2):573–81.
Walsh DO, Gmitro AF, Marcellin MW. Adaptive reconstruction of phased array MR imagery. Magn Reson Med. 2000 May 1;43(5):682–90.
Garcia-Reyes K, Passoni NM, Palmeri ML, Kauffman CR, Choudhury KR, Polascik TJ, et al. Detection of prostate cancer with multiparametric MRI (mpMRI): effect of dedicated reader education on accuracy and confidence of index and anterior cancer diagnosis. Abdom Imaging. 2015 Jan;40(1):134–42.
Purysko AS, Rosenkrantz AB, Barentsz JO, Weinreb JC, Macura KJ. PI-RADS Version 2: A Pictorial Update. RadioGraphics. 2016 Jul 29;36(5):1354–72.
PIRADS-V2.pdf [Internet]. [cited 2019 Feb 9]. Available from: https://www.acr.org/-/media/ACR/Files/RADS/Pi-RADS/PIRADS-V2.pdf
Bittencourt LK, Attenberger UI, Lima D, Strecker R, de Oliveira A, Schoenberg SO, et al. Feasibility study of computed vs measured high b-value (1400 s/mm2) diffusion-weighted MR images of the prostate. World J Radiol. 2014 Jun 28;6(6):374–80.
Funding
There is no source of funding for this original article. The author biography information is provided on the title page that is separate from the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Disclosure
Ravi Teja Seethamraju: Employee of Siemens Medical Solutions USA, Inc. Elisabeth Weiland: Employee of Siemens Healthcare GmbH. Berthold Kiefer: Employee of Siemens Healthcare GmbH. Marcel Dominik Nickel: Employee of Siemens Healthcare GmbH.
Ethical approval
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kordbacheh, H., Seethamraju, R.T., Weiland, E. et al. Image quality and diagnostic accuracy of complex-averaged high b value images in diffusion-weighted MRI of prostate cancer. Abdom Radiol 44, 2244–2253 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00261-019-01961-0
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00261-019-01961-0