Abstract
Purpose
To compare 2D gradient-recalled echo (GRE) and 2D spin-echo (SE) echo-planar imaging (EPI) MR elastography (MRE) for measurement of hepatic stiffness in adult patients with known or suspected liver disease at 3 Tesla.
Materials and methods
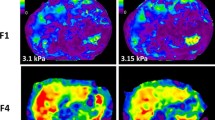
Three hundred and eighty-seven consecutive patients underwent MRE of the liver at 3 Tesla with 2D-GRE and 2D-SE-EPI sequences. ‘Mean liver stiffness (LS)’ calculated by averaging 3 ROIs in the right lobe, ‘Maximum LS’ calculated by an ROI in the right lobe; and ‘Freehand LS’ calculated by an ROI in the entire liver were measured by two independent readers. Inter-observer and inter-class variability in stiffness measurements were assessed. Stiffness values were correlated with degree of liver fibrosis (METAVIR scores) in 97 patients who underwent biopsy. The diagnostic performance was compared by a receiver-operating characteristic analysis.
Results
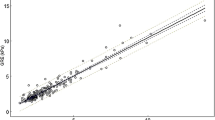
The technical failure rate was 2.8% for 2D-SE-EPI (11/387) and 4.1% for 2D-GRE (16/387, 9 had R2* > 80 s−1 indicating iron overload). There is high reproducibility for both GRE and SE-EPI variants (ICC = 0.84–0.94 for both GRE and SE-EPI MRE). The highest sensitivity, specificity, and accuracy of differentiating mild fibrosis (F0–F2) from advanced fibrosis (F3–F4) are 0.84 (GRE Freehand measurement), 0.92 (GRE Maximum stiffness measurement), and 0.88 (GRE Freehand measurement), respectively.
Conclusions
High intra-class correlation and intra-reader correlation are seen on measured hepatic stiffness for both 2D-GRE and 2D-SE-EPI MRE. 2D-SE-EPI has lower failure rate. Diagnostic performance of both sequences is equivalent, with highest sensitivity for 2D-GRE Freehand stiffness measurement, and highest specificity 2D-GRE Maximum stiffness measurement.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Browning, J.D., L.S. Szczepaniak, R. Dobbins, P. Nuremberg, J.D. Horton, et al. (2004) Prevalence of hepatic steatosis in an urban population in the United States: impact of ethnicity. Hepatology, 40(6): p. 1387-95.
Younossi, Z.M., M. Stepanova, M. Afendy, Y. Fang, Y. Younossi, et al. (2011) Changes in the prevalence of the most common causes of chronic liver diseases in the United States from 1988 to 2008. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol, 9(6): p. 524-530 e1; quiz e60.
Everhart, J.E., E.C. Wright, Z.D. Goodman, J.L. Dienstag, J.C. Hoefs, et al. (2010) Prognostic value of Ishak fibrosis stage: findings from the hepatitis C antiviral long-term treatment against cirrhosis trial. Hepatology, 51(2): p. 585-94.
Garcia-Tsao, G., A.J. Sanyal, N.D. Grace, W. Carey, D. Practice Guidelines Committee of the American Association for the Study of Liver, et al. (2007) Prevention and management of gastroesophageal varices and variceal hemorrhage in cirrhosis. Hepatology, 46(3): p. 922-38.
Bruix, J., M. Sherman, and D. American Association for the Study of Liver (2011) Management of hepatocellular carcinoma: an update. Hepatology, 53(3): p. 1020-2.
Ratziu, V., F. Charlotte, A. Heurtier, S. Gombert, P. Giral, et al. (2005) Sampling variability of liver biopsy in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Gastroenterology, 128(7): p. 1898-906.
Mannelli, L., E. Godfrey, M.J. Graves, A.J. Patterson, P. Beddy, et al. (2012) Magnetic resonance elastography: feasibility of liver stiffness measurements in healthy volunteers at 3T. Clin Radiol, 67(3): p. 258-62.
Muthupillai, R., D.J. Lomas, P.J. Rossman, J.F. Greenleaf, A. Manduca, et al. (1995) Magnetic resonance elastography by direct visualization of propagating acoustic strain waves. Science, 269(5232): p. 1854-7.
Yin, M., J.A. Talwalkar, K.J. Glaser, A. Manduca, R.C. Grimm, et al. (2007) Assessment of hepatic fibrosis with magnetic resonance elastography. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol, 5(10): p. 1207-1213 e2.
Dulai, P.S., C.B. Sirlin, and R. Loomba (2016) MRI and MRE for non-invasive quantitative assessment of hepatic steatosis and fibrosis in NAFLD and NASH: Clinical trials to clinical practice. J Hepatol, 65(5): p. 1006-1016.
Loomba, R., C.B. Sirlin, B. Ang, R. Bettencourt, R. Jain, et al. (2015) Ezetimibe for the treatment of nonalcoholic steatohepatitis: assessment by novel magnetic resonance imaging and magnetic resonance elastography in a randomized trial (MOZART trial). Hepatology, 61(4): p. 1239-50.
Chen, J., J.A. Talwalkar, M. Yin, K.J. Glaser, S.O. Sanderson, et al. (2011) Early detection of nonalcoholic steatohepatitis in patients with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease by using MR elastography. Radiology, 259(3): p. 749-56.
Trout, A.T., R.M. Sheridan, S.D. Serai, S.A. Xanthakos, W. Su, et al. (2018) Diagnostic Performance of MR Elastography for Liver Fibrosis in Children and Young Adults with a Spectrum of Liver Diseases. Radiology, 287(3): p. 824-832.
Yin, M., K.J. Glaser, J.A. Talwalkar, J. Chen, A. Manduca, et al. (2016) Hepatic MR Elastography: Clinical Performance in a Series of 1377 Consecutive Examinations. Radiology, 278(1): p. 114-24.
Serai, S.D., J.R. Dillman, and A.T. Trout (2017) Spin-echo Echo-planar Imaging MR Elastography versus Gradient-echo MR Elastography for Assessment of Liver Stiffness in Children and Young Adults Suspected of Having Liver Disease. Radiology, 282(3): p. 761-770.
Felker, E.R., K.S. Choi, K. Sung, H.H. Wu, S.S. Raman, et al. (2018) Liver MR Elastography at 3 T: Agreement Across Pulse Sequences and Effect of Liver R2* on Image Quality. AJR Am J Roentgenol: p. 1-7.
Mariappan, Y.K., B. Dzyubak, K.J. Glaser, S.K. Venkatesh, C.B. Sirlin, et al. (2017) Application of Modified Spin-Echo-based Sequences for Hepatic MR Elastography: Evaluation, Comparison with the Conventional Gradient-Echo Sequence, and Preliminary Clinical Experience. Radiology, 282(2): p. 390-398.
Kim, Y.S., J.S. Song, S. Kannengiesser, and S.Y. Seo (2017) Comparison of spin-echo echoplanar imaging and gradient recalled echo-based MR elastography at 3 Tesla with and without gadoxetic acid administration. Eur Radiol, 27(10): p. 4120-4128.
Lee, Y., J.M. Lee, J.E. Lee, K.B. Lee, E.S. Lee, et al. (2014) MR elastography for noninvasive assessment of hepatic fibrosis: reproducibility of the examination and reproducibility and repeatability of the liver stiffness value measurement. J Magn Reson Imaging, 39(2): p. 326-31.
Toguchi, M., M. Tsurusaki, N. Yada, K. Sofue, T. Hyodo, et al. (2017) Magnetic resonance elastography in the assessment of hepatic fibrosis: a study comparing transient elastography and histological data in the same patients. Abdom Radiol (NY), 42(6): p. 1659-1666.
Banerjee, R., M. Pavlides, E.M. Tunnicliffe, S.K. Piechnik, N. Sarania, et al. (2014) Multiparametric magnetic resonance for the non-invasive diagnosis of liver disease. J Hepatol, 60(1): p. 69-77.
Wagner, M., I. Corcuera-Solano, G. Lo, S. Esses, J. Liao, et al. (2017) Technical Failure of MR Elastography Examinations of the Liver: Experience from a Large Single-Center Study. Radiology, 284(2): p. 401-412.
Garteiser, P., R.S. Sahebjavaher, L.C. Ter Beek, S. Salcudean, V. Vilgrain, et al. (2013) Rapid acquisition of multifrequency, multislice and multidirectional MR elastography data with a fractionally encoded gradient echo sequence. NMR Biomed, 26(10): p. 1326-35.
Guenthner, C. and S. Kozerke (2018) Encoding and readout strategies in magnetic resonance elastography. NMR Biomed, 31(10): p. e3919.
Dhyani, M., A. Anvari, and A.E. Samir (2015) Ultrasound elastography: liver. Abdom Imaging, 40(4): p. 698-708.
Chung, S., E. Breton, L. Mannelli, and L. Axel (2011) Liver stiffness assessment by tagged MRI of cardiac-induced liver motion. Magn Reson Med, 65(4): p. 949-55.
Mannelli, L., G.J. Wilson, T.J. Dubinsky, C.A. Potter, P. Bhargava, et al. (2012) Assessment of the liver strain among cirrhotic and normal livers using tagged MRI. J Magn Reson Imaging, 36(6): p. 1490-5.
Ichikawa, S., U. Motosugi, T. Ichikawa, K. Sano, H. Morisaka, et al. (2012) Magnetic resonance elastography for staging liver fibrosis in chronic hepatitis C. Magn Reson Med Sci, 11(4): p. 291-7.
, A.A., S.G. Sheth, and S. Chopra (2001) Liver biopsy. N Engl J Med, 344(7): p. 495-500.
Regev, A., M. Berho, L.J. Jeffers, C. Milikowski, E.G. Molina, et al. (2002) Sampling error and intraobserver variation in liver biopsy in patients with chronic HCV infection. Am J Gastroenterol, 97(10): p. 2614-8.
Runge, J.H., A.E. Bohte, J. Verheij, V. Terpstra, A.J. Nederveen, et al. (2014) Comparison of interobserver agreement of magnetic resonance elastography with histopathological staging of liver fibrosis. Abdom Imaging, 39(2): p. 283-90.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
Stephan Kannengiesser and Matthias Fenchel are the Employee of Siemens Healthineers. All other author declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
This study is IRB-approved and HIPAA-compliant.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhan, C., Kannengiesser, S., Chandarana, H. et al. MR elastography of liver at 3 Tesla: comparison of gradient-recalled echo (GRE) and spin-echo (SE) echo-planar imaging (EPI) sequences and agreement across stiffness measurements. Abdom Radiol 44, 1825–1833 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00261-019-01932-5
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00261-019-01932-5