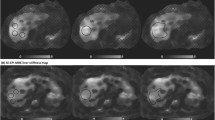
Abstract
Untreated hepatic iron overload causes hepatic fibrosis and cirrhosis and can predispose to hepatocellular carcinoma. MR elastography (MRE) provides a non-invasive means to measure liver stiffness, which correlates with liver fibrosis but standard gradient recalled echo (GRE)-based MRE techniques fail in patients with high iron due to very low hepatic signal. Short echo time (TE) 2D spin echo echoplanar imaging (SE-EPI)-based MRE may allow measurement of stiffness in the iron loaded liver. The purpose of this study was to describe the use of such an MRE sequence in patients undergoing liver iron quantification by MRI. In our preliminary study of 43 patients with mean LIC of 9.3 mg/g (range 1.8–21.5 mg/g), liver stiffness measurements could be made in 77% (33/43) of patients with a short TE, SE-EPI based MRE sequence. On average, mean LIC in patients with failed MRE was higher than in those with successful MRE (15.9 mg/g dry weight vs. 7.3 mg/g), but a cut-off value for successful MRE could not be established. Seven patients (21% of those with successful MRE) had liver stiffness values suggestive of the presence of significant fibrosis (> 2.49 kPa). A short TE, SE-EPI based MR elastography sequence allows successful measurement of liver stiffness in a majority of patients with liver iron loading, potentially allowing non-invasive screening for fibrosis.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Brown K, Subramony C, May W, et al. (2009) Hepatic iron overload in children with sickle cell anemia on chronic transfusion therapy. J Pediatr Hematol Oncol 31(5):309–312
Ware HM, Kwiatkowski JL (2013) Evaluation and treatment of transfusional iron overload in children. Pediatr Clin North Am 60(6):1393–1406
Ghavamzadeh A, Mirzania M, Kamalian N, Sedighi N, Azimi P (2015) Hepatic iron overload and fibrosis in patients with beta thalassemia major after hematopoietic stem cell transplantation: a pilot study. Int Journal Hematol Oncol Stem Cell Res 9(2):55–59
Arthur MJ (1996) Iron overload and liver fibrosis. J Gastroenterol Hepatol 11(12):1124–1129
Towbin AJ, Serai SD, Podberesky DJ (2013) Magnetic resonance imaging of the pediatric liver: imaging of steatosis, iron deposition, and fibrosis. Magn Reson Imaging Clin N Am 21(4):669–680
Serai SD, Trout AT, Sirlin CB (2017) Elastography to assess the stage of liver fibrosis in children: concepts, opportunities, and challenges. Clin Liver Dis 9(1):5–10
Serai SD, Towbin AJ, Podberesky DJ (2012) Pediatric liver MR elastography. Dig Dis Sci 57(10):2713–2719
Serai SD, Dillman JR, Trout AT (2017) Spin-echo echo-planar imaging MR elastography versus gradient-echo MR elastography for assessment of liver stiffness in children and young adults suspected of having liver disease. Radiology 282(3):761–770
Mariappan YK, Dzyubak B, Glaser KJ, et al. (2016) Application of modified spin-echo-based sequences for hepatic MR elastography: evaluation, comparison with the conventional gradient-echo sequence, and preliminary clinical experience. Radiology. 282:390–398
Mariappan YK, Glaser KJ, Hubmayr RD, et al. (2011) MR elastography of human lung parenchyma: technical development, theoretical modeling and in vivo validation. J Magn Reson Imaging 33(6):1351–1361
Wood JC, Enriquez C, Ghugre N, et al. (2005) MRI R2 and R2* mapping accurately estimates hepatic iron concentration in transfusion-dependent thalassemia and sickle cell disease patients. Blood 106(4):1460–1465
Serai SD, Fleck RJ, Quinn CT, Zhang B, Podberesky DJ (2015) Retrospective comparison of gradient recalled echo R2* and spin-echo R2 magnetic resonance analysis methods for estimating liver iron content in children and adolescents. Pediatr Radiol 45(11):1629–1634
Serai SD, Smith EA, Trout AT, Dillman JR (2017) Agreement between manual relaxometry and semi-automated scanner-based multi-echo Dixon technique for measuring liver T2* in a pediatric and young adult population. Pediatr Radiol. 48:94–100
Serai SD, Obuchowski NA, Venkatesh SK, et al. (2017) Repeatability of MR elastography of liver: a meta-analysis. Radiology. 285:92–100
Xanthakos SA, Podberesky DJ, Serai SD, et al. (2014) Use of magnetic resonance elastography to assess hepatic fibrosis in children with chronic liver disease. J Pediatr 164(1):186–188
Garbowski MW, Carpenter JP, Smith G, et al. (2014) Biopsy-based calibration of T2* magnetic resonance for estimation of liver iron concentration and comparison with R2 Ferriscan. J Cardiovasc Magn Reson 16:40
Dillman JR, Trout AT, Costello EN, et al. (2018) Quantitative liver MRI-biopsy correlation in pediatric and young adult patients with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease: can one be used to predict the other? AJR Am J Roentgenol 210(1):166–174
Yin M, Chen J, Glaser KJ, Talwalkar JA, Ehman RL (2009) Abdominal magnetic resonance elastography. Top Magn Reson Imaging 20(2):79–87
Trout ATSR, Serai SD, Xanthakos SA, et al. (2018) Diagnostic performance of MR elastography for liver fibrosis in children and young adults with a spectrum of liver diseases. Radiology. 287:824–832
Maira D, Cassinerio E, Marcon A, et al. (2017) Progression of liver fibrosis can be controlled by adequate chelation in transfusion-dependent thalassemia (TDT). Ann Hematol 96(11):1931–1936
Sirlin CB, Reeder SB (2010) Magnetic resonance imaging quantification of liver iron. Magn Reson Imaging Clin N Am. 18(3):359–381
Wood JC (2014) Use of Magnetic resonance imaging to monitor iron overload. Hematol Oncol Clin N Am 28(4):747–764
Joshi M, Dillman JR, Singh K, et al. (2017) Quantitative MRI of fatty liver disease in a large pediatric cohort: correlation between liver fat fraction, stiffness, volume, and patient-specific factors. Abdom Radiol. 43:1168–1179
Joshi M, Dillman JR, Towbin AJ, Serai SD, Trout AT (2017) MR elastography: high rate of technical success in pediatric and young adult patients. Pediatr Radiol 47(7):838–843
Trout AT, Sheridan RM, Serai SD, et al. (2018) Diagnostic performance of MR elastography for liver fibrosis in children and young adults with a spectrum of liver diseases. Radiology 287(3):824–832
Paparo F, Cevasco L, Zefiro D, et al. (2013) Diagnostic value of real-time elastography in the assessment of hepatic fibrosis in patients with liver iron overload. Eur J Radiol 82(12):e755–e761
Hamidieh AA, Shazad B, Ostovaneh MR, et al. (2014) Noninvasive measurement of liver fibrosis using transient elastography in pediatric patients with major thalassemia who are candidates for hematopoietic stem cell transplantation. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant 20(12):1912–1917
Pipaliya N, Solanke D, Parikh P, et al. (2017) Comparison of tissue elastography with magnetic resonance imaging T2* and serum ferritin quantification in detecting liver iron overload in patients with thalassemia major. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 15(2):292
Serai S, Towbin AJ, Podberesky DJ (2012) Non-contrast MRA using an inflow-enhanced, inversion recovery SSFP technique in pediatric abdominal imaging. Pediatr Radiol 42(3):364–368
Elalfy MS, Esmat G, Matter RM, Abdel Aziz HE, Massoud WA (2013) Liver fibrosis in young Egyptian beta-thalassemia major patients: relation to hepatitis C virus and compliance with chelation. Ann Hepatol. 12(1):54–61
Acknowledgements
We thank Richard L. Ehman, MD, PhD, Scott Kruse, BS, and Kevin Glaser, PhD, of Mayo Clinic (Rochester, MN) for their support and technical assistance related to MRE.
Funding
There were no grants or other financial assistance for this research.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Funding
Not applicable.
Disclosure of potential conflict of interest
None.
Ethical approval
All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and/or national research committee and with the 1964 Helsinki Declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards.
Informed consent
This was a retrospective study and informed consent was waived by the IRB.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Serai, S.D., Trout, A.T. Can MR elastography be used to measure liver stiffness in patients with iron overload?. Abdom Radiol 44, 104–109 (2019). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00261-018-1723-9
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00261-018-1723-9