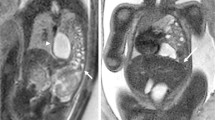
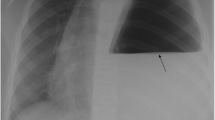
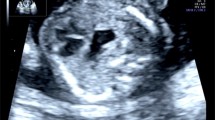
Abstract
The initial outcome in infants with congenital diaphragmatic hernia is mainly related to the associated lung hypoplasia. However, these patients frequently present with additional gastrointestinal pathology that also influences their quality of life and final prognosis. Congenital gastrointestinal anomalies are often observed and the displacement of the liver, the stomach and/or the intestines into the thorax may cause distortion of the vascular axis of these organs, increasing the risk of congestion and/or ischemia. Some of these gastrointestinal complications are already visible at imaging studies performed in utero and/or in newborns.This pictorial essay describes the imaging findings of the most frequently detected gastrointestinal complications in fetuses and infants with congenital diaphragmatic hernia, focusing on prenatal exams.







Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- US:
-
Ultrasound
- MRI:
-
Magnetic resonance Imaging
- CDH:
-
Congenital diaphragmatic hernia
References
Langham MR, Kays DW, Ledbetter DJ, et al. (1996) Congenital diaphragmatic hernia. Epidemiology and outcome. Clin Perinatol 23:671–688
Philip N, Gambarelli D, Guys JM, Camboulives J, Ayme S (1991) Epidemiological study of congenital diaphragmatic defects with special reference to aetiology. Eur J Pediatr 150:726–729
Skari H, Bjornland K, Haugen G, Egeland T, Emblem R (2000) Congenital diaphragmatic hernia: a meta-analysis of mortality factors. J Pediatr Surg 35:1187–1197. doi:10.1053/jpsu.2000.8725
Dillon E, Renwick M (1993) Antenatal detection of congenital diaphragmatic hernias: the northern region experience. Clin Radiol 48:264–267
Zalla JM, Stoddard GJ, Yoder BA (2015) Improved mortality rate for congenital diaphragmatic hernia in the modern era of management: 15 year experience in a single institution. J Pediatr Surg 50:524–527. doi:10.1016/j.jpedsurg.2014.11.002
Stege G, Fenton A, Jaffray B (2003) Nihilism in the 1990s: the true mortality of congenital diaphragmatic hernia. Pediatrics 112:532–535
Stoll C, Alambik Y, Dott B, Roth MP (2015) Associated non diaphragmatic anomalies among cases with congenital diaphragmatic hernia. Genet Couns 26(3):281–298
Taybi H, Lachmann RS (2007) Radiology of syndromes, metabolic disorders and skeletal dysplasias. St. Louis: Mosby Elsevier
Mehollin-Ray AR, Cassady CI, Cass DL, Olutoye OO (2012) Fetal MR imaging of congenital diaphragmatic hernia. Radiographics 32:1067–1084. doi:10.1148/rg.324115155
Chavhan GB, Babyn PS, Cohen RA, Langer JC (2010) Multimodality imaging of the pediatric diaphragm: anatomy and pathologic conditions. Radiographics 30:1797–1817. doi:10.1148/rg.307105046
Stoll C, Alembik Y, Dott B, Roth MP (2015) Associated non diaphragmatic anomalies among cases with congenital diaphragmatic hernia. Genet Couns 26:281–298
Datin-Dorriere V, Rouzies S, Taupin P, et al. (2008) Prenatal prognosis in isolated congenital diaphragmatic hernia. Am J Obstet Gynecol 198:80e1–80e5. doi:10.1016/j.ajog.2007.06.069
Zamora IJ, Olutoye OO, Cass DL, et al. (2014) Prenatal MRI fetal lung volumes and percent liver herniation predict pulmonary morbidity in congenital diaphragmatic hernia (CDH). J Pediatr Surg 49:688–693. doi:10.1016/j.jpedsurg.2014.02.048
Mayer S, Klaritsch P, Petersen S, et al. (2011) The correlation between lung volume and liver herniation measurements by fetal MRI in isolated congenital diaphragmatic hernia: a systematic review and meta-analysis of observational studies. Prenat Diagn 31:1086–1096. doi:10.1002/pd.2839
Garne E, Haeusler M, Barisic I, et al. (2002) Euroscan Study Group, Congenital diaphragmatic hernia: evaluation of prenatal diagnosis in 20 European regions. Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol 19:329–333. doi:10.1046/j.1469-0705.2002.00635.x
Hidaka N, Ishii K, Furutake Y, et al. (2014) Magnetic resonance fetal right lung volumetry and its efficacy in predicting postnatal short-term outcomes of congenital left-sided diaphragmatic hernia. J Obstet Gynaecol Res 40:429–438. doi:10.1111/jog.12210
Hubbard AM, Crombleholme TM, Adzick NS, et al. (1999) Prenatal MRI evaluation of congenital diaphragmatic hernia. Am J Perinatol 16:407–413
Oluyomi-Obi T, Kuret V, Puligandla P, et al. (2017) Antenatal predictors of outcome in prenatally diagnosed congenital diaphragmatic hernia (CDH). J Pediatr Surg 52:881–888
Nawapun K, Eastwood M, Sandaite I, et al. (2015) Correlation of observed-to-expected total fetal lung volume with intrathoracic organ herniation on magnetic resonance imaging in fetuses with isolated left-sided congenital diaphragmatic hernia: MRI o/e-TFLV and intrathoracic organ herniation in isolated CDH. Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol 46:162–167. doi:10.1002/uog.14701
Pérez-Egido L, Parente A, Cerdá JA (2015) Acute gastric volvulus and congenital diaphragmatic hernia, case report and review. Afr J Paediatr Surg AJPS 12:200–202. doi:10.4103/0189-6725.170230
Fox C, Stewart M, King SK, Patel N (2016) Acute gastrointestinal compromise in neonates with congenital diaphragmatic hernia prior to repair. J Pediatr Surg 51:1917–1920. doi:10.1016/j.jpedsurg.2016.09.012
Farhataziz N, Engels JE, Ramus RM, Zaretsky M, Twickler DM (2005) Fetal MRI of urine and meconium by gestational age for the diagnosis of genitourinary and gastrointestinal abnormalities. AJR 184:1891–1897. doi:10.2214/ajr.184.6.01841891
Cordier AG, Cannie MM, Guilbaud L, De Laveaucoupet J, et al. (2015) Stomach position versus liver-to-thoracic volume ratio in left-sided congenital diaphragmatic hernia. J Matern Fetal Neonatal Med 28:190–195. doi:10.3109/14767058.2014.906576
Alamo L, Gudinchet R, Meuli R (2015) Imaging findings in fetal diaphragmatic anomalies. Pediatr Radiol 45:1887–1900
Ackerman KG, Vargas SO, Wilson JA, et al. (2012) Congenital diaphragmatic defects: proposal for a new classification based on observations in 234 patients. Pediatr Dev Pathol 15:265–274. doi:10.2350/11-05-1041-OA.1
Taylor GA, Atalabi OM, Estroff JA (2009) Imaging of congenital diaphragmatic hernias. Pediatr Radiol 39:1–16. doi:10.1007/s00247-008-0917-7
Partridge EA, Peranteau WH, Herkert L, et al. (2016) Right- versus left-sided congenital diaphragmatic hernia: a comparative outcomes analysis. J Pediatr Surg 51:900–902. doi:10.1016/j.jpedsurg.2016.02.049
Kotecha S, Barbato A, Bush A, et al. (2012) Congenital diaphragmatic hernia. Eur Respir J 39:820–829. doi:10.1183/09031936.00066511
Visrutaratna P, Singhavejsakul J (2010) Intrathoracic gastric volvulus. Pediatr Radiol 40:230. doi:10.1007/s00247-009-1375-6
Pelizzo G, Lembo MA, Franchella A, et al. (2001) Gastric volvulus associated with congenital diaphragmatic hernia, wandering spleen, and intrathoracic left kidney: CT findings. Abdom Imaging 26:306–308
Ito TE, Hasnie R, Crosby DL, et al. (2012) Gastric volvulus complication in an infant with undiagnosed congenital diaphragmatic hernia presenting with acute respiratory distress. Pediatr Emerg Care 28:1078–1080. doi:10.1097/PEC.0b013e31826cedaf
Singh S, Wakhlu A, Pandey A, Kureel SN, Rawat JD (2013) Delayed presentation of strangulated congenital diaphragmatic hernia: learning from our experience. Hernia J Hernias Abdom Wall Surg 17:403–407. doi:10.1007/s10029-011-0882-1
Al-Faraj D, Al-Haddad M, Al-Hadeedi O, Al-Subaie S (2015) A case of acute mesentero-axial gastric volvulus in a patient with a diaphragmatic hernia: experience with a laparoscopic approach. J Surg Case Rep . doi:10.1093/jscr/rjv119
Akinkuotu AC, Cruz SM, Cass DL, et al. (2015) Revisiting outcomes of right congenital diaphragmatic hernia. J Surg Res 198:413–417. doi:10.1016/j.jss.2015.03.090
Fisher JC, Jefferson RA, Arkovitz MS, Stolar CJH (2008) Redefining outcomes in right congenital diaphragmatic hernia. J Pediatr Surg 43:373–379. doi:10.1016/j.jpedsurg.2007.10.049
Jani P, Bidarkar SS, Walker K, et al. (2014) Right-sided congenital diaphragmatic hernia: a tertiary centre’s experience over 25 years. J Neonatal-Perinat Med 7:39–45. doi:10.3233/NPM-1474313
Recio Rodríguez M, Martinez de Vega V, Cano Alonso R, et al. (2012) MR imaging of thoracic abnormalities in the fetus. RadioGraphics 32(7):E305–E321. doi:10.1148/rg.327125053
Slavotinek AM, Warmerdam B, Lin AE, Shaw GM (2007) Population-based analysis of left- and right-sided diaphragmatic hernias demonstrates different frequencies of selected additional anomalies. Am J Med Genet A 143A:3127–3136. doi:10.1002/ajmg.a.32100
Furey EA, Bailey Twickler (2016) Fetal MR imaging of gastrointestinal abnormalities. Radiographics 36:904–917. doi:10.1148/rg.2016150109
Kitano Y, Okuyama H, Saito M, et al. (2011) Re-evaluation of stomach position as a simple prognostic factor in fetal left congenital diaphragmatic hernia: a multicenter survey in Japan. Ultrasound Obstet Gynecol 37:277–282
Basta AM, Lusk LA, Keller RL, Filly RA (2016) Fetal stomach position predicts neonatal outcome in isolated left-sided congenital diaphragmatic hernia. Fetal Diagn Ther 39:248–255
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Funding
No funding was received for this study.
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and/or national research committee and with the 1964 Helsinki declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards. This article does not contain any studies with animals performed by any of the authors. All the image files were anonymized.
Informed consent
Statement of informed consent was not applicable since the manuscript does not contain any patient data.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Minkner, K., Alamo, L. Pre- and neonatal imaging of gastrointestinal complications in congenital diaphragmatic hernia. Abdom Radiol 43, 574–582 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00261-017-1246-9
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00261-017-1246-9