Abstract
Purpose
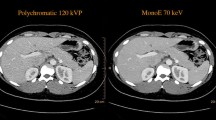
We aimed to determine optimal window settings for poly-energetic (PolyE) and virtual mono-energetic images (MonoE) derived from abdominal angiographic studies on a novel dual-layer spectral detector CT (SDCT) system.
Methods
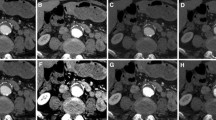
From 50 patients, SDCT datasets PolyE and MonoE at 70 and 40 keV levels were reconstructed and best individual window width and level (BI-W/L) manually assessed. Through regression analysis, the so-called optimized individual (OI-W/L) values were obtained. Subjective image quality parameters and vessel diameters were measured to determine influences of different W/L settings.
Results
Image noise was lower and attenuation and contrast-to-noise ratio were higher in MonoE compared to PolyE (all p ≤ 0.002). Mean BI-W/L values for PolyE, 70, and 40 keV were 637/284, 647/291, and 1568/691, respectively. Mean OI-W/L values were 631/276, 628/286, and 1516/667, respectively. Compared to standard settings, all adjusted W/L settings varied significantly and yielded higher subjective scoring. No between-group differences were found between manually adjusted and mathematically calculated W/L settings.
Conclusion
PolyE and MonoE from abdominal angiographic SDCT studies require appropriate W/L settings especially at low energy reconstruction levels. Individual adjustment reaches the best image quality but is time consuming. From our data, predefined W/L settings of 640/280 (PolyE/MonoE 70 keV) and 1570/690 (MonoE 40 keV) as a non-individualized starting point for abdominal angiographic studies from the novel SDCT system are suggested.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Carrascosa P, Leipsic JA, Capunay C, et al. (2015) Monochromatic image reconstruction by dual energy imaging allows half iodine load computed tomography coronary angiography. Eur J Radiol 84(10):1915–1920. doi:10.1016/j.ejrad.2015.06.019
He J, Wang Q, Ma X, Sun Z (2015) Dual-energy CT angiography of abdomen with routine concentration contrast agent in comparison with conventional single-energy CT with high concentration contrast agent. Eur J Radiol 84(2):221–227. doi:10.1016/j.ejrad.2014.11.025
Stolzmann P, Frauenfelder T, Pfammatter T, et al. (2008) Endoleaks after endovascular abdominal aortic aneurysm repair: detection with dual-energy dual-source CT. Radiology 249(2):682–691. doi:10.1148/radiol.2483080193
Brockmann C, Jochum S, Sadick M, et al. (2009) Dual-energy CT angiography in peripheral arterial occlusive disease. Cardiovasc Intervent Radiol 32(4):630–637. doi:10.1007/s00270-008-9491-5
Huang SY, Nelson RC, Miller MJ, et al. (2012) Assessment of vascular contrast and depiction of stenoses in abdominopelvic and lower extremity vasculature: comparison of dual-energy MDCT with digital subtraction angiography. Acad Radiol 19(9):1149–1157. doi:10.1016/j.acra.2012.04.014
Alvarez RE, Macovski A (1976) Energy-selective reconstructions in X-ray computerized tomography. Phys Med Biol 21(5):733–744
Yu L, Leng S, McCollough CH (2012) Dual-energy CT-based monochromatic imaging. AJR Am J Roentgenol 199(5 Suppl):S9–S15. doi:10.2214/AJR.12.9121
Apfaltrer P, Sudarski S, Schneider D, et al. (2014) Value of monoenergetic low-kV dual energy CT datasets for improved image quality of CT pulmonary angiography. Eur J Radiol 83(2):322–328. doi:10.1016/j.ejrad.2013.11.005
Silva AC, Morse BG, Hara AK, et al. (2011) Dual-energy (spectral) CT: applications in abdominal imaging. Radiographics 31(4):1031–1046; discussion 1047–1050. doi:10.1148/rg.314105159
McCollough CH, Leng S, Yu L, Fletcher JG (2015) Dual- and multi-energy CT: principles, technical approaches, and clinical applications. Radiology 276(3):637–653. doi:10.1148/radiol.2015142631
Dilmanian FA, Wu XY, Parsons EC, et al. (1997) Single-and dual-energy CT with monochromatic synchrotron x-rays. Phys Med Biol 42(2):371–387
Meier A, Wurnig M, Desbiolles L, et al. (2015) Advanced virtual monoenergetic images: improving the contrast of dual-energy CT pulmonary angiography. Clin Radiol 70(11):1244–1251. doi:10.1016/j.crad.2015.06.094
Saba L, Mallarin G (2009) Window settings for the study of calcified carotid plaques with multidetector CT angiography. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 30(7):1445–1450. doi:10.3174/ajnr.A1509
Caruso D, Parinella AH, Schoepf UJ, et al. (2016) Optimization of window settings for standard and advanced virtual monoenergetic imaging in abdominal dual-energy CT angiography. Abdom Radiol (NY) . doi:10.1007/s00261-016-0963-9
Bae KT, Mody GN, Balfe DM, et al. (2005) CT depiction of pulmonary emboli: display window settings. Radiology 236(2):677–684. doi:10.1148/radiol.2362041558
Albrecht MH, Trommer J, Wichmann JL, et al. (2016) Comprehensive comparison of virtual monoenergetic and linearly blended reconstruction techniques in third-generation dual-source dual-energy computed tomography angiography of the thorax and abdomen. Invest Radiol 51(9):582–590. doi:10.1097/RLI.0000000000000272
Flohr TG, McCollough CH, Bruder H, et al. (2006) First performance evaluation of a dual-source CT (DSCT) system. Eur Radiol 16(2):256–268. doi:10.1007/s00330-005-2919-2
Leipsic J, Labounty TM, Heilbron B, et al. (2010) Adaptive statistical iterative reconstruction: assessment of image noise and image quality in coronary CT angiography. AJR Am J Roentgenol 195(3):649–654. doi:10.2214/AJR.10.4285
Schabel C, Bongers M, Sedlmair M, et al. (2014) Assessment of the hepatic veins in poor contrast conditions using dual energy CT: evaluation of a novel monoenergetic extrapolation software algorithm. RoFo 186(6):591–597. doi:10.1055/s-0034-1366423
Sudarski S, Apfaltrer P, Nance JW Jr, et al. (2013) Optimization of keV-settings in abdominal and lower extremity dual-source dual-energy CT angiography determined with virtual monoenergetic imaging. Eur J Radiol 82(10):e574–581. doi:10.1016/j.ejrad.2013.04.040
Weiss J, Notohamiprodjo M, Bongers M, et al. (2016) Effect of noise-optimized monoenergetic postprocessing on diagnostic accuracy for detecting incidental pulmonary embolism in portal-venous phase dual-energy computed tomography. Invest Radiol . doi:10.1097/RLI.0000000000000319
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
All procedures performed in studies involving human participants were in accordance with the ethical standards of the institutional and/or national research committee and with the 1964 Helsinki declaration and its later amendments or comparable ethical standards. For this type of study formal consent is not required.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Doerner, J., Luetkens, J.A., Iuga, AI. et al. Poly-energetic and virtual mono-energetic images from a novel dual-layer spectral detector CT: optimization of window settings is crucial to improve subjective image quality in abdominal CT angiographies. Abdom Radiol 43, 742–750 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00261-017-1241-1
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00261-017-1241-1