Abstract
Purpose
To assess single energy metal artifact reduction (SEMAR) and spectral energy metal artifact reduction (MARS) algorithms in reducing artifacts generated by different metal implants.
Materials and method
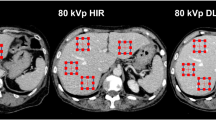
Phantom was scanned with and without SEMAR (Aquilion One, Toshiba) and MARS (Discovery CT750 HD, GE), with various metal implants. Images were evaluated objectively by measuring standard deviation in regions of interests and subjectively by two independent reviewers grading on a scale of 0 (no artifact) to 4 (severe artifact). Reviewers also graded new artifacts introduced by metal artifact reduction algorithms.
Results
SEMAR and MARS significantly decreased variability of the density measurement adjacent to the metal implant, with median SD (standard deviation of density measurement) of 52.1 HU without SEMAR, vs. 12.3 HU with SEMAR, p < 0.001. Median SD without MARS of 63.1 HU decreased to 25.9 HU with MARS, p < 0.001. Median SD with SEMAR is significantly lower than median SD with MARS (p = 0.0011). SEMAR improved subjective image quality with reduction in overall artifacts grading from 3.2 ± 0.7 to 1.4 ± 0.9, p < 0.001. Improvement of overall image quality by MARS has not reached statistical significance (3.2 ± 0.6 to 2.6 ± 0.8, p = 0.088). There was a significant introduction of artifacts introduced by metal artifact reduction algorithm for MARS with 2.4 ± 1.0, but minimal with SEMAR 0.4 ± 0.7, p < 0.001.
Conclusion
CT iterative reconstruction algorithms with single and spectral energy are both effective in reduction of metal artifacts. Single energy-based algorithm provides better overall image quality than spectral CT-based algorithm. Spectral metal artifact reduction algorithm introduces mild to moderate artifacts in the far field.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Sofue, K, Yoshikawa, T, Negi, N, et al. Abdominal CT with single-energy metal artifact reduction (SEMAR): initial experiences. Poster session presented at: European Congress of Radiology, 2014 March 6–10, Vienna, Austria
Morsbach F, Bickelhaupt S, Wanner GA, et al. (2013) Reduction of metal artifacts from hip prostheses on CT images of the pelvis: value of iterative reconstructions. Radiology 268(1):237–244
Brook OR, Gourtsoyianni S, Brook A, et al. (2012) Spectral CT with metal artifacts reduction software for improvement of tumor visibility in the vicinity of gold fiducial markers. Radiology 263(3):696–705
Yang Q, Peng S, Wu J, et al. (2015) Spectral CT with monochromatic imaging and metal artifacts reduction software for artifacts reduction of (125)I radioactive seeds in liver brachytherapy. Jpn J Radiol 33(11):694–705
Funama Y, Taguchi K, Utsunomiya D, et al. (2015) A newly-developed metal artifact reduction algorithm improves the visibility of oral cavity lesions on 320-MDCT volume scans. Phys Med 31(1):66–71
Sonoda A, Nitta N, Ushio N, et al. (2015) Evaluation of the quality of CT images acquired with the single energy metal artifact reduction (SEMAR) algorithm in patients with hip and dental prostheses and aneurysm embolization coils. Jpn J Radiol 33(11):710–716
Andersson KM, Nowik P, Persliden J, et al. (2015) Metal artefact reduction in CT imaging of hip prostheses—an evaluation of commercial techniques provided by four vendors. Br J Radiol 88(1052):20140473
Barrett JF, Keat N (2004) Artifacts in CT: recognition and avoidance. Radiographics 24(6):1679–1691
Yu L, Li H, Mueller J, et al. (2009) Metal artifact reduction from reformatted projections for hip prostheses in multislice helical computed tomography: techniques and initial clinical results. Investig Radiol 44(11):691–696
Watzke O, Kalender WA (2004) A pragmatic approach to metal artifact reduction in CT: merging of metal artifact reduced images. Eur Radiol 14(5):849–856
Boas FE, Fleischmann D (2011) Evaluation of two iterative techniques for reducing metal artifacts in computed tomography. Radiology 259(3):894–902
Meyer E, Raupach R, Lell M, et al. (2010) Normalized metal artifact reduction (NMAR) in computed tomography. Med Phys 37(10):5482–5493
Prell D, Kyriakou Y, Kachelrie M, et al. (2010) Reducing metal artifacts in computed tomography caused by hip endoprostheses using a physics-based approach. Investig Radiol 45(11):747–754
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Funding
No funding was received for this study.
Conflicts of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Ethical approval
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any of the authors. For this type of study formal consent is not required.
Informed consent
Statement of informed consent was not applicable since the manuscript does not contain any patient data.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Fang, J., Zhang, D., Wilcox, C. et al. Metal implants on CT: comparison of iterative reconstruction algorithms for reduction of metal artifacts with single energy and spectral CT scanning in a phantom model. Abdom Radiol 42, 742–748 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00261-016-1023-1
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00261-016-1023-1