Abstract
Purpose
The purpose of this study was to compare high b-value (b = 2000 s/mm2) acquired diffusion-weighted imaging (aDWI) with computed DWI (cDWI) obtained using four diffusion models—mono-exponential (ME), intra-voxel incoherent motion (IVIM), stretched exponential (SE), and diffusional kurtosis (DK)—with respect to lesion visibility, conspicuity, contrast, and ability to predict significant prostate cancer (PCa).
Methods
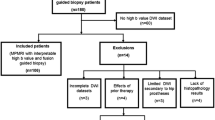
Ninety four patients underwent 3 T MRI including acquisition of b = 2000 s/mm2 aDWI and low b-value DWI. High b = 2000 s/mm2 cDWI was obtained using ME, IVIM, SE, and DK models. All images were scored on quality independently by three radiologists. Lesions were identified on all images and graded for lesion conspicuity. For a subset of lesions for which pathological truth was established, lesion-to-background contrast ratios (LBCRs) were computed and binomial generalized linear mixed model analysis was conducted to compare clinically significant PCa predictive capabilities of all DWI.
Results
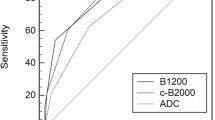
For all readers and all models, cDWI demonstrated higher ratings for image quality and lesion conspicuity than aDWI except DK (p < 0.001). The LBCRs of ME, IVIM, and SE were significantly higher than LBCR of aDWI (p < 0.001). Receiver Operating Characteristic curves obtained from binomial generalized linear mixed model analysis demonstrated higher Area Under the Curves for ME, SE, IVIM, and aDWI compared to DK or PSAD alone in predicting significant PCa.
Conclusion
High b-value cDWI using ME, IVIM, and SE diffusion models provide better image quality, lesion conspicuity, and increased LBCR than high b-value aDWI. Using cDWI can potentially provide comparable sensitivity and specificity for detecting significant PCa as high b-value aDWI without increased scan times and image degradation artifacts.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
SEER Stat Fact Sheets: Prostate Cancer (2015). National Cancer Institute website. http://seer.cancer.gov/statfacts/html/prost.html
Loch T, Eppelmann U, Lehmann J, et al. (2004) Transrectal ultrasound guided biopsy of the prostate: random sextant versus biopsies of sono-morphologically suspicious lesions. World J Urol 22(5):357–360
Ukimura O, Faber K, Gill IS (2012) Intraprostatic targeting. Curr Opin Urol 22(2):97–103. doi:10.1097/MOU.0b013e32835017fa
Barentsz JO, Richenberg J, Clements R, et al. (2012) ESUR prostate MR guidelines 2012. Eur Radiol 22(4):746–757. doi:10.1007/s00330-011-2377-y
Verma S, Rajesh A (2011) A clinically relevant approach to imaging prostate cancer: review. Am J Roentgenol 196(3 Suppl):S1–S10 (Quiz S11-4). doi:10.2214/AJR.09.7196
Marks L, Young S (2013) MRI-ultrasound fusion for guidance of targeted prostate biopsy. Curr Opin Urol 23(1):43–50. doi:10.1097/MOU.0b013e32835ad3ee
Mouraviev V, Verma S, Kalyanaraman B, et al. (2013) The feasibility of multiparametric magnetic resonance imaging for targeted biopsy using novel navigation systems to detect early stage prostate cancer: the preliminary experience. J Endourol 27(7):820–825. doi:10.1089/end.2012.0215
Moore CM, Robertson NL, Arsanious N, et al. (2013) Image-guided prostate biopsy using magnetic resonance imaging-derived targets: a systematic review. Eur Urol 63(1):125–140. doi:10.1016/j.eururo.2012.06.004
Bhavsar A, Verma S (2014) Anatomic Imaging of the Prostate. Biomed Res Int. 2014:728539. doi:10.1155/2014/728539
Prostate Imaging Reporting and Data System: Version 2 (2015). American College of Radiology website. http://www.acr.org/~/media/ACR/Documents/PDF/QualitySafety/Resources/PIRADS/PIRADS%20V2.pdf
Chatterjee A, Watson G, Myint E, et al. (2015) Changes in epithelium, stroma, and lumen space correlate more strongly with gleason pattern and are stronger predictors of prostate ADC changes than cellularity metrics. Radiology 277(3):751–762. doi:10.1148/radiol.2015142414
Rosenkrantz AB, Hindman N, Lim RP, et al. (2013) Diffusion-weighted imaging of the prostate: comparison of b1000 and b2000 image sets for index lesion detection. J Magn Reson Imaging . doi:10.1002/jmri.24016
Ben-Amitay S, Jones DK, Assaf Y (2012) Motion correction and registration of high b-value diffusion weighted images. Magn Reson Med 67:1694–1702
Blackledge MD, Leach MO, Collins DJ, Koh DM (2011) Computed diffusion-weighted MR imaging may improve tumor detection. Radiology 261(2):573–581. doi:10.1148/radiol.11101919
Bittencourt LK, Attenberger UI, Lima D, et al. (2014) Feasibility study of computed vs. measured high b-value (1400 s/mm2) diffusion-weighted MR images of the prostate. World J Radiol 6(6):374–380. doi:10.4329/wjr.v6.i6.374
Maas MC, Futterer JJ, Scheenen TW (2013) Quantitative evaluation of computed high B value diffusion-weighted magnetic resonance imaging of the prostate. Investig Radiol 48(11):779–786. doi:10.1097/RLI.0b013e31829705bb
Rosenkrantz AB, Chandarana H, Hindman N, et al. (2013) Computed diffusion-weighted imaging of the prostate at 3 T: impact on image quality and tumour detection. Eur Radiol 23:3170–3177. doi:10.1007/s00330-013-2917-8
Quentin M, Blondin D, Klasen J, et al. (2012) Comparison of different mathematical models of diffusion-weighted prostate MR imaging. Magn Reson Imaging. 30(10):1468–1474. doi:10.1016/j.mri.2012.04.025
Le Bihan D, Breton E, Lallemand D, et al. (1988) Separation of diffusion and perfusion in intravoxel incoherent motion MR imaging. Radiology 168(2):497–505
Mazaheri Y, Afaq A, Rowe DB, Lu Y, et al. (2012) Diffusion-weighted magnetic resonance imaging of the prostate: improved robustness with stretched exponential modeling. J Comput Assist Tomogr 36(6):695–703. doi:10.1097/RCT.0b013e31826bdbbd
Rosenkrantz AB, Sigmund EE, Johnson G, et al. (2012) Prostate cancer: feasibility and preliminary experience of a diffusional kurtosis model for detection and assessment of aggressiveness of peripheral zone cancer. Radiology 264(1):126–135. doi:10.1148/radiol.12112290
Natarajan S, Marks LS, Margolis DJ, et al. (2011) Clinical application of a 3D ultrasound-guided prostate biopsy system. Urol Oncol 29(3):334–342. doi:10.1016/j.urolonc.2011.02.014
Bourne RM, Panagiotaki E, Bongers A, et al. (2014) Information theoretic ranking of four models of diffusion attenuation in fresh and fixed prostate tissue ex vivo. Magn Reson Med. 72(5):1418–1426. doi:10.1002/mrm.25032
Jambor I, Merisaari H, Taimen P, et al. (2015) Evaluation of different mathematical models for diffusion-weighted imaging of normal prostate and prostate cancer using high b-values: a repeatability study. Magn Reson Med. 73(5):1988–1998. doi:10.1002/mrm.25323
Metens T, Miranda D, Absil J, Matos C (2012) What is the optimal b value in diffusion-weighted MR imaging to depict prostate cancer at 3T? Eur Radiol 22(3):703–709. doi:10.1007/s00330-011-2298-9
Ohgiya Y, Suyama J, Seino N, et al. (2012) Diagnostic accuracy of ultra-high-b-value 3.0-T diffusion-weighted MR imaging for detection of prostate cancer. Clin Imaging 36(5):526–531. doi:10.1016/j.clinimag.2011.11.016
Ueno Y, Takahashi S, Kitajima K, et al. (2013) Computed diffusion-weighted imaging using 3-T magnetic resonance imaging for prostate cancer diagnosis. Eur Radiol 23(12):3509–3516. doi:10.1007/s00330-013-2958-z
Grant KB, Agarwal HK, Shih JH, et al. (2015) Comparison of calculated and acquired high b value diffusion-weighted imaging in prostate cancer. Abdom Imaging 40:578–586. doi:10.1007/s00261-014-0246-2
Liu X, Zhou L, Peng W, Wang H, Zhang Y (2015) Comparison of stretched-Exponential and monoexponential model diffusion-Weighted imaging in prostate cancer and normal tissues. J Magn Reson Imaging . doi:10.1002/jmri.24872
Boesen L, Chabanova E, Løgager V, et al. (2015) Apparent diffusion coefficient ratio correlates significantly with prostate cancer gleason score at final pathology. J Magn Reson Imaging. 42(2):446–453. doi:10.1002/jmri.24801
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of Interest
The authors Sadhna Verma, Jason Young, Anil Bhavsar, Nilesh Patil, James Donovan, and Krishnanath Gaitonde declare that they have no conflict of interest. The authors Saradwata Sarkar, Rajesh Venkataraman, and Xu Yang are employed at Eigen, Grass Valley, CA.
Additional information
Sadhna Verma and Saradwata Sarkar are first author.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Verma, S., Sarkar, S., Young, J. et al. Evaluation of the impact of computed high b-value diffusion-weighted imaging on prostate cancer detection. Abdom Radiol 41, 934–945 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00261-015-0619-1
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00261-015-0619-1