Abstract
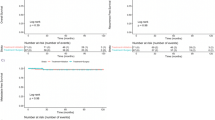
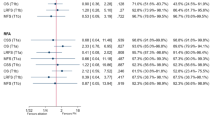
Laparoscopic radial nephrectomy (LRN) and microwave ablation (MWA) are optional treatment for renal cell carcinoma (RCC). However, the comparative study with two techniques remains lacking. The aim of this study was to evaluate midterm results of MWA vs. LRN in patients with small RCC. A total of 426 patients with ≤4 cm RCC were included from April 2006 to October 2012. Ninety-eight patients underwent MWA and 328 patients LRN. The survival, recurrence, and renal function changes were compared between two treatments. Although overall survival after MWA (82.6% at 5 years) was lower than those after LRN (98.6% at 5 years, p = 0.0004), the RCC-related survival (97% at 5 years) was comparable to those following LRN (98% at 5 years, p = 0.38). One local tumor progress occurred at 32 months after MWA and none after LRN. The major complication rates were comparable between two techniques (1.7% in MWA vs. 1.5% in LRN, p = 0.75), but MWA showed less renal function damage than LRN (p < 0.0001). The multivariate analysis showed the presence of postablation extrarenal metastasis may become a predictor of the oncologic outcome (p = 0.059) and treatment modality had no influence (p = 0.965). This study demonstrates that MWA and LRN provide comparable results in small RCC outcomes.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ljungberg B, Campbell SC, Choi HY, et al. (2011) The epidemiology of renal cell carcinoma. Eur Urol 60(4):615–621
Krajewski KM, Giardino AA, Zukotynski K, Van den Abbeele AD, Pedrosa I (2011) Imaging in renal cell carcinoma. Hematol Oncol Clin North Am 25(4):687–715
Marszalek M, Meixl H, Polajnar M, et al. (2009) Laparoscopic and open partial nephrectomy: a matched-pair comparison of 200 patients. Eur Urol 55(5):1171–1178
Park YH, Byun SS, Kang SH, et al. (2009) Comparison of hand-assisted laparoscopic radical nephrectomy with open radical nephrectomy for pT1-2 clear cell renal-cell carcinoma: a multi-institutional study. J Endourol 23(9):1485–1489
Takaki H, Yamakado K, Soga N, et al. (2010) Midterm results of radiofrequency ablation versus nephrectomy for small renal cell carcinoma. Jpn J Radiol 28(6):460–468
Choueiri TK, Schutz FA, Hevelone ND, et al. (2011) Thermal ablation vs surgery for localized kidney cancer: a Surveillance, Epidemiology, and End Results (SEER) database analysis. Urology 78(1):93–98
Park SY, Park BK, Kim CK (2012) Thermal ablation in renal cell carcinoma: what affects renal function? Int J Hyperth 28(8):729–734
Liang P, Yu J, Yu XL, et al. (2011) Percutaneous cooled-tip microwave ablation under ultrasound guidance for primary liver cancer: a multicentre analysis of 1363 treatment-naive lesions in 1007 patients in China. Gut 61(7):1100–1101
Carrafiello G, Mangini M, Fontana F, et al. (2010) Single-antenna microwave ablation under contrast-enhanced ultrasound guidance for treatment of small renal cell carcinoma: preliminary experience. Cardiovasc Interv Radiol 33:367–374
Yu J, Liang P, Yu XL, et al. (2012) US-guided percutaneous microwave ablation of renal cell carcinoma: intermediate-term results. Radiology 263(3):900–908
Castle SM, Salas N, Leveillee RJ (2011) Initial experience using microwave ablation therapy for renal tumor treatment: 18-month follow-up. Urology 77(4):792–797
Ai H, Wu S, Gao H, et al. (2012) Temperature distribution analysis of tissue water vaporization during microwave ablation: experiments and simulations. Int J Hyperth 28(7):674–685
Yu J, Liang P, Yu X, et al. (2011) A comparison of microwave ablation and bipolar radiofrequency ablation both with an internally cooled probe: results in ex vivo and in vivo porcine livers. Eur J Radiol 79(1):124–130
Ljungberg B, Cowan NC, Hanbury DC, et al. (2010) EAU guidelines on renal cell carcinoma: the 2010 update. Eur Urol 58(3):398–406
Campbell SC, Novick AC, Belldegrun A, et al. (2009) Guideline for management of the clinical T1 renal mass. J Urol 182(4):1271–1279
Clark TW, Millward SF, Gervais DA, et al. (2009) Reporting standards for percutaneous thermal ablation of renal cell carcinoma. J Vasc Interv Radiol 20(7 Suppl):S409–S416
Goldberg SN, Grassi CJ, Cardella JF, et al. (2005) Image-guided tumor ablation: standardization of terminology and reporting criteria. Radiology 235(3):728–739
Dindo D, Demartines N, Clavien PA (2004) Classification of surgical complications: a new proposal with evaluation in a cohort of 6336 patients and results of a survey. Ann Surg 240:205–213
Jemal A, Siegel R, Ward E, et al. (2010) Estimates of cancer incidence and mortality in Europe in 2008. Eur J Cancer 46:765–781
Jemal A, Siegel R, Ward E, et al. (2007) Cancer statistics, 2007. CA Cancer J Clin 57:43–66
Brown DB (2005) Concepts, considerations, and concerns on the cutting edge of radiofrequency ablation. J Vasc Interv Radiol 16:597–613
Wright AS, Sampson LA, Warner TF (2005) Radiofrequency versus microwave ablation in a hepatic porcine model. Radiology 236:132–139
Lucas SM, Stern JM, Adibi M, et al. (2008) Renal function outcomes in patients treated for renal masses smaller than 4 cm by ablative and extirpative techniques. J Urol 179:75–79
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by three Grants 81430039, 81127006, and 81401436 from the National Scientific Foundation Committee of China, one Grant 7144246 from the Beijing Natural Science Foundation and supported from the State Key Laboratory of Kidney Diseases.
Conflict of interest
All authors have made a substantial contribution to the information or material submitted for publication. All have read and approved the final manuscript. All have no direct or indirect commercial financial incentive associated with publishing the article. The manuscript or portions thereof are not under consideration by another journal or electronic publication and have not been previously published.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Jie Yu and Guoming Zhang have contributed equally to the manuscript.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yu, J., Zhang, G., Liang, P. et al. Midterm results of percutaneous microwave ablation under ultrasound guidance versus retroperitoneal laparoscopic radial nephrectomy for small renal cell carcinoma. Abdom Imaging 40, 3248–3256 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00261-015-0500-2
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00261-015-0500-2