Abstract
Purpose
To evaluate the performance of a prototype, fully-automated post-processing solution for whole-liver and lobar segmentation based on MDCT datasets.
Materials and methods
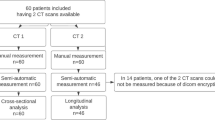
A polymer liver phantom was used to assess accuracy of post-processing applications comparing phantom volumes determined via Archimedes’ principle with MDCT segmented datasets. For the IRB-approved, HIPAA-compliant study, 25 patients were enrolled. Volumetry performance compared the manual approach with the automated prototype, assessing intraobserver variability, and interclass correlation for whole-organ and lobar segmentation using ANOVA comparison. Fidelity of segmentation was evaluated qualitatively.
Results
Phantom volume was 1581.0 ± 44.7 mL, manually segmented datasets estimated 1628.0 ± 47.8 mL, representing a mean overestimation of 3.0%, automatically segmented datasets estimated 1601.9 ± 0 mL, representing a mean overestimation of 1.3%. Whole-liver and segmental volumetry demonstrated no significant intraobserver variability for neither manual nor automated measurements. For whole-liver volumetry, automated measurement repetitions resulted in identical values; reproducible whole-organ volumetry was also achieved with manual segmentation, p ANOVA 0.98. For lobar volumetry, automated segmentation improved reproducibility over manual approach, without significant measurement differences for either methodology, p ANOVA 0.95–0.99. Whole-organ and lobar segmentation results from manual and automated segmentation showed no significant differences, p ANOVA 0.96–1.00. Assessment of segmentation fidelity found that segments I–IV/VI showed greater segmentation inaccuracies compared to the remaining right hepatic lobe segments.
Conclusion
Automated whole-liver segmentation showed non-inferiority of fully-automated whole-liver segmentation compared to manual approaches with improved reproducibility and post-processing duration; automated dual-seed lobar segmentation showed slight tendencies for underestimating the right hepatic lobe volume and greater variability in edge detection for the left hepatic lobe compared to manual segmentation.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Selver MA, Kocaoglu A, Demir GK, et al. (2008) Patient oriented and robust automatic liver segmentation for pre-evaluation of liver transplantation. Comput Biol Med 38:765–784
Suzuki K, Kohlbrenner R, Epstein ML, et al. (2010) Computer-aided measurement of liver volumes in CT by means of geodesic active contour segmentation coupled with level-set algorithms. Med Phys 37:2159–2166
Gao L, Heath DG, Kuszyk BS, et al. (1996) Automatic liver segmentation technique for three-dimensional visualization of CT data. Radiology 201:359–364
Okada T, Shimada R, Hori M, et al. (2008) Automated segmentation of the liver from 3D CT images using probabilistic atlas and multilevel statistical shape model. Acad Radiol 15:1390–1403
Nakayama Y, Li Q, Katsuragawa S, et al. (2006) Automated hepatic volumetry for living related liver transplantation at multisection CT. Radiology 240:743–748
Suzuki K, Epstein ML, Kohlbrenner R, et al. (2011) Quantitative radiology: automated CT liver volumetry compared with interactive volumetry and manual volumetry. AJR Am J Roentgenol 197:W706–W712
Karlo C, Reiner CS, Stolzmann P, et al. (2010) CT- and MRI-based volumetry of resected liver specimen: comparison to intraoperative volume and weight measurements and calculation of conversion factors. Eur J Radiol 75:e107–e111
Lemke AJ, Brinkmann MJ, Pascher A, et al. (2003) Accuracy of the CT-estimated weight of the right hepatic lobe prior to living related liver donation (LRLD) for predicting the intraoperatively measured weight of the graft. Rofo 175:1232–1238
Lemke AJ, Brinkmann MJ, Schott T, et al. (2006) Living donor right liver lobes: preoperative CT volumetric measurement for calculation of intraoperative weight and volume. Radiology 240:736–742
Lemke AJ, Hosten N, Neumann K, et al. (1997) CT volumetry of the liver before transplantation. Rofo 166:18–23
Soler L, Delingette H, Malandain G, et al. (2001) Fully automatic anatomical, pathological, and functional segmentation from CT scans for hepatic surgery. Comput Aided Surg 6:131–142
Samuel GA, Gregory VG, Lawrence HS (2013) Quantitative imaging biomarkers alliance (QIBA)
Fischer L, Thorn M, Neumann JO, et al. (2005) The segments of the hepatic veins-is there a spatial correlation to the Couinaud liver segments? Eur J Radiol 53:245–255
Ward TJ, Madoff DC, Weintraub JL (2013) Interventional radiology in the multidisciplinary management of liver lesions: pre- and postoperative roles. Semin Liver Dis 33:213–225
Sangro B, Bilbao JI, Inarrairaegui M, et al. (2009) Treatment of hepatocellular carcinoma by radioembolization using 90Y microspheres. Dig Dis 27:164–169
Shin CI, Kim SH, Rhim JH, et al. (2013) Feasibility of commercially available, fully automated hepatic CT volumetry for assessing both total and territorial liver volumes in liver transplantation. J Korean Soc Radiol 68:125–136
Bae KT, Giger ML, Chen CT, et al. (1993) Automatic segmentation of liver structure in CT images. Med Phys 20:71–78
Heimann T, van GB, Styner MA, et al. (2009) Comparison and evaluation of methods for liver segmentation from CT datasets. IEEE Trans Med Imaging 28:1251–1265
Conflict of interest
None.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Fananapazir, G., Bashir, M.R., Marin, D. et al. Computer-aided liver volumetry: performance of a fully-automated, prototype post-processing solution for whole-organ and lobar segmentation based on MDCT imaging. Abdom Imaging 40, 1203–1212 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00261-014-0276-9
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00261-014-0276-9