Abstract
Purpose
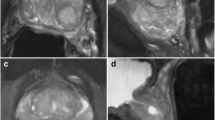
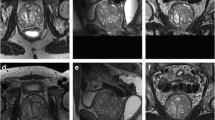
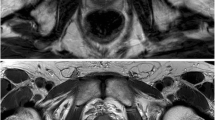
To retrospectively compare standard and BLADE T2-weighted imaging (T2WI) sequences of the prostate in terms of image quality and tumor assessment.
Methods
49 prostate cancer patients (64 ± 6 years) who underwent 3 T phased-array coil MRI before prostatectomy were included. T2WI was acquired using standard rectilinear and BLADE techniques. Two readers (R1, R2) independently localized the dominant lesion using T2WI alone and using multi-parametric imaging; recorded presence of extraprostatic extension (EPE) in each lobe; and scored lesion conspicuity and absence of motion artifact (1–5 scale; 5 = highest quality). A third reader, unblinded to pathology, placed ROIs to record tumor-to-peripheral-zone contrast. Standard and BLADE T2WI were compared using paired Wilcoxon tests.
Results
BLADE showed a trend toward improved motion artifact for R1 (3.4 ± 1.3 vs. 2.9 ± 1.5; p = 0.054) but not R2 (4.0 ± 1.0 vs. 3.9 ± 1.1; p = 0.880). Dominant lesions showed significantly lower conspicuity using BLADE for R1 (2.8 ± 2.0 vs. 3.2 ± 2.0; p = 0.011) but not R2 (2.3 ± 1.6 vs. 2.4 ± 1.7; p = 0.353), and significantly lower tumor-to-peripheral-zone contrast using BLADE (0.35 ± 0.13 vs. 0.42 ± 0.15; p ≤ 0.001). R1 and R2 correctly localized four and three fewer dominant tumors, respectively, using BLADE than standard T2WI, although both correctly localized a similar fraction of dominant tumors using multi-parametric sequences. While R1 detected EPE in 10 of 11 patients using both sequences, R2 detected EPE in 3 more patients using BLADE.
Conclusion
BLADE may help reduce motion artifact of prostate T2WI and assist EPE detection, although at expense of reduced image contrast. In practice, BLADE may be useful in patients in whom initial T2WI is degraded by motion.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Barentsz JO, Richenberg J, Clements R, et al. (2012) ESUR prostate MR guidelines 2012. Eur Radiol 22(4):746–757. doi:10.1007/s00330-011-2377-y
Hoeks CM, Barentsz JO, Hambrock T, et al. (2011) Prostate cancer: multiparametric MR imaging for detection, localization, and staging. Radiology 261(1):46–66. doi:10.1148/radiol.11091822
Pipe JG (1999) Motion correction with PROPELLER MRI: application to head motion and free-breathing cardiac imaging. Magn Reson Med 42(5):963–969
Lavdas E, Mavroidis P, Kostopoulos S, et al. (2013) Improvement of image quality using BLADE sequences in brain MR imaging. Magn Reson Imaging 31(2):189–200. doi:10.1016/j.mri.2012.08.001
Finkenzeller T, Menzel C, Fellner FA, et al. (2014) BLADE sequences in sagittal T2-weighted MR imaging of the cervical spine and spinal cord–lesion detection and clinical value. Rofo 186(1):47–53. doi:10.1055/s-0033-1350346
Rosenkrantz AB, Mannelli L, Mossa D, et al. (2011) Breath-hold T2-weighted MRI of the liver at 3T using the BLADE technique: impact upon image quality and lesion detection. Clin Radiol 66(5):426–433. doi:10.1016/j.crad.2010.10.018
Michaely HJ, Kramer H, Weckbach S, et al. (2008) Renal T2-weighted turbo-spin-echo imaging with BLADE at 3.0 Tesla: initial experience. J Magn Reson Imaging 27(1):148–153. doi:10.1002/jmri.21240
Lane BF, Vandermeer FQ, Oz RC, et al. (2011) Comparison of sagittal T2-weighted BLADE and fast spin-echo MRI of the female pelvis for motion artifact and lesion detection. AJR Am J Roentgenol 197(2):W307–W313. doi:10.2214/AJR.10.5918
Froehlich JM, Metens T, Chilla B, et al. (2012) Should less motion sensitive T2-weighted BLADE TSE replace Cartesian TSE for female pelvic MRI? Insights Imaging 3(6):611–618. doi:10.1007/s13244-012-0193-9
Rosenkrantz AB, Sabach A, Babb JS, et al. (2013) Prostate cancer: comparison of dynamic contrast-enhanced MRI techniques for localization of peripheral zone tumor. AJR Am J Roentgenol 201(3):W471-W478. doi:10.2214/AJR.12.9737
Rosenkrantz AB, Kim S, Lim RP, et al. (2013) Prostate cancer localization using multiparametric MR imaging: comparison of Prostate Imaging Reporting and Data System (PI-RADS) and Likert scales. Radiology 269(2):482-492. doi:10.1148/radiol.13122233
Landis JR, Koch GG (1977) The measurement of observer agreement for categorical data. Biometrics 33(1):159–174
Nanko S, Oshima H, Watanabe T, et al. (2009) Usefulness of the application of the BLADE technique to reduce motion artifacts on navigation-triggered prospective acquisition correction (PACE) T2-weighted MRI (T2WI) of the liver. J Magn Reson Imaging 30(2):321–326. doi:10.1002/jmri.21855
Bomers JG, Barentsz JO (2014) Standardization of Multiparametric Prostate MR Imaging Using PI-RADS. BioMed Res Int 2014:431680. doi:10.1155/2014/431680
Acknowledgments
The authors acknowledge the Joseph and Diane Steinberg Charitable Trust.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Rosenkrantz, A.B., Bennett, G.L., Doshi, A. et al. T2-weighted imaging of the prostate: Impact of the BLADE technique on image quality and tumor assessment. Abdom Imaging 40, 552–559 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00261-014-0225-7
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00261-014-0225-7