Abstract
Objectives
To investigate the diagnostic performance of the acoustic radiation force impulse (ARFI) elastography for the assessment of the liver fibrosis in alcoholic liver disease (ALD).
Methods
We included 112 patients with ALD in whom liver biopsy, ARFI elastography, and aspartate-to-platelet ratio index (APRI) measurements were performed.
Results
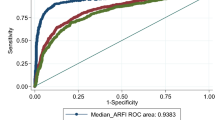
ARFI elastography correlated significantly with histological fibrosis (r = 0.685, P < 0.001) in patients with ALD. The diagnostic accuracies expressed as areas under receiver operating characteristic (AUROC) curves for ARFI elastography and APRI were 0.846 and 0.763 for the diagnosis of significant fibrosis (S ≥ 2), 0.875 and 0.688 for the diagnosis of severe fibrosis (S ≥ 3), and 0.893 and 0.648 for the diagnosis of liver cirrhosis, respectively. The AUROC values of ARFI elastography were significantly better than those of APRI for predicting severe fibrosis (P = 0.02) and cirrhosis (P = 0.04). The optimum cutoff values for ARFI elastography were 1.33 m/s for S ≥ 2, 1.40 m/s for S ≥ 3, and 1.65 m/s for S = 4 in patients with elevated alanine aminotransferase (ALT) levels; these decreased to 1.24 m/s for S ≥ 2, 1.27 m/s for S ≥ 3, and 1.41 m/s for S = 4 in patients with normal ALT.
Conclusion
ARFI elastography is an acceptable method for predicting the severity of fibrosis in patients with ALD. ARFI elastography is influenced by elevated aminotransferase levels in ALD.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
World Health Organization (2011) Global status report on alcohol and health. Geneva: World Health Organization, p 286
Jaurigue MM, Cappell MS (2014) Therapy for alcoholic liver disease. World J Gastroenterol 20(9):2143–2158
Thampanitchawong P, Piratvisuth T (1999) Liver biopsy: complications and risk factors. World J Gastroenterol 5(4):301–304
Regev A, Berho M, Jeffers LJ, et al. (2002) Sampling error and intraobserver variation in liver biopsy in patients with chronic HCV infection. Am J Gastroenterol 97(10):2614–2618
Bedossa P, Dargere D, Paradis V (2003) Sampling variability of liver fibrosis in chronic hepatitis. Hepatology 38(6):1449–1457
Ferraioli G, Tinelli C, Dal Bello B, et al. (2013) Performance of liver stiffness measurements by transient elastography in chronic hepatitis. World J Gastroenterol 19(1):49–56
Morikawa H, Fukuda K, Kobayashi S, et al. (2011) Real-time tissue elastography as a tool for the noninvasive assessment of liver stiffness in patients with chronic hepatitis C. J Gastroenterol 46(3):350–358
Sporea I, Sirli R, Bota S, et al. (2011) Is ARFI elastography reliable for predicting fibrosis severity in chronic HCV hepatitis. World J Radiol 3(7):188–193
Ferraioli G, Parekh P, Levitov AB, Filice C (2014) Shear wave elastography for evaluation of liver fibrosis. J Ultrasound Med 33(2):197–203
Friedrich-Rust M, Buggisch P, de Knegt RJ, et al. (2013) Acoustic radiation force impulse imaging for non-invasive assessment of liver fibrosis in chronic hepatitis B. J Viral Hepat 20(4):240–247
Fierbinteanu Braticevici C, Sporea I, Panaitescu E, Tribus L (2013) Value of acoustic radiation force impulse imaging elastography for non-invasive evaluation of patients with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease. Ultrasound Med Biol 39(11):1942–1950
Tapper EB, Cohen EB, Patel K, et al. (2012) Levels of alanine aminotransferase confound use of transient elastography to diagnose fibrosis in patients with chronic hepatitis C virus infection. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol 10(8):932–937
Fung J, Lai CL, Cheng C, et al. (2011) Mild-to-moderate elevation of alanine aminotransferase increases liver stiffness measurement by transient elastography in patients with chronic hepatitis B. Am J Gastroenterol 106(3):492–496
Nightingale K, Soo MS, Nightingale R, Trahey G (2002) Acoustic radiation force impulse imaging: in vivo demonstration of clinical feasibility. Ultrasound Med Biol 28:227–235
Theise ND (2007) Liver biopsy assessment in chronic viral hepatitis: a personal, practical approach. Mod Pathol 20(suppl):S3–S14
Colloredo G, Guido M, Sonzogni A, Leandro G (2003) Impact of liver biopsy size on histological evaluation of chronic viral hepatitis: the smaller the sample, the milder the disease. J Hepatol 39(2):239–244
Piccinino F, Sagnelli E, Pasquale G, Giusti G (1986) Complications following percutaneous liver biopsy. A multicentre retrospective study on 68,276 biopsies. J Hepatol 2(2):165–173
Friedman LS (2004) Controversies in liver biopsy: who, where, when, how, why? Curr Gastroenterol Rep 6(1):30–36
Sporea I, Bota S, Peck-Radosavljevic M, et al. (2012) Acoustic radiation force impulse elastography for fibrosis evaluation in patients with chronic hepatitis C: an international multicenter study. Eur J Radiol 81(12):4112–4118
Ye XP, Ran HT, Cheng J, et al. (2012) Liver and spleen stiffness measured by acoustic radiation force impulse elastography for noninvasive assessment of liver fibrosis and esophageal varices in patients with chronic hepatitis B. J Ultrasound Med 31(8):1245–1253
Nguyen-Khac E, Chatelain D, Tramier B, et al. (2008) Assessment of asymptomatic liver fibrosis in alcoholic patients using fibroscan: prospective comparison with seven non-invasive laboratory tests. Aliment Pharmacol Ther 28(10):1188–1198
Nahon P, Kettaneh A, Tengher-Barna I, et al. (2008) Assessment of liver fibrosis using transient elastography in patients with alcoholic liver disease. J Hepatol 49(6):1062–1068
Bota S, Herkner H, Sporea I, et al. (2013) Meta-analysis: ARFI elastography versus transient elastography for the evaluation of liver fibrosis. Liver Int 33(8):1138–1147
Boursier J, Isselin G, Fouchard-Hubert I, et al. (2010) Acoustic radiation force impulse: a new ultrasonographic technology for the widespread noninvasive diagnosis of liver fibrosis. Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol 22(9):1074–1084
Friedrich-Rust M, Wunder K, Kriener S, et al. (2009) Liver fibrosis in viral hepatitis: noninvasive assessment with acoustic radiation force impulse imaging versus transient elastography. Radiology 252(2):595–604
Foucher J, Castera L, Bernard PH, et al. (2006) Prevalence and factors associated with failure of liver stiffness measurement using FibroScan in a prospective study of 2114 examinations. Eur J Gastroenterol Hepatol 18(4):411–412
Yoon KT, Lim SM, Park JY, et al. (2012) Liver stiffness measurement using acoustic radiation force impulse (ARFI) elastography and effect of necroinflammation. Dig Dis Sci 57(6):1682–1691
Bota S, Sporea I, Peck-Radosavljevic M, Sirli R, et al. (2013) The influence of aminotransferase levels on liver stiffness assessed by acoustic radiation force impulse elastography: a retrospective multicentre study. Dig Liver Dis 45(9):762–768
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Dakun Zhang and Peng Li have contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, D., Li, P., Chen, M. et al. Non-invasive assessment of liver fibrosis in patients with alcoholic liver disease using acoustic radiation force impulse elastography. Abdom Imaging 40, 723–729 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00261-014-0154-5
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00261-014-0154-5