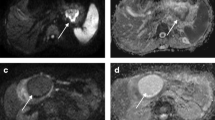
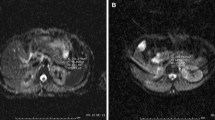
Abstract
Purpose
The purpose of this study was to evaluate the contribution of diffusion-weighted magnetic resonance imaging (DW-MRI) to the detection of infection in acute pancreatitis-related collections.
Methods
A total of 21 DW-MRI, and computed tomography (CT) were performed on 20 patients diagnosed as acute pancreatitis with acute peri-pancreatic fluid or necrotic collections. Collections were classified as infected or sterile according to the culture and follow-up results. Collections with gas bubbles on CT images were considered to be infected. Collections with peripheral bright signals on DW-MRI images were considered to be positive, whereas those without signals were considered to be negative. Apparent diffusion coefficient (ADC) values of the peripheral and central parts of the collections were measured. Student’s t test was used to compare the means of ADC values of independent groups.
Results
Apart from one false positive result, the presence of infection was detected by DW-MRI with 95.2% accuracy. The sensitivity and accuracy of DW-MRI were higher than CT for the detection of infection. The ADC values in the central parts of the collections were significantly different between the infected and sterile groups.
Conclusion
DW-MRI can be used as a non-invasive technique for the detection of infection in acute pancreatitis-associated collections.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Banks PA, Bollen TL, Dervenis C, et al. (2013) Classification of acute pancreatitis—2012: revision of the Atlanta classification and definitions by international consensus. Gut 62(1):102–111
Balthazar EJ, Robinson DL, Megibow AJ, Ranson JH (1990) Acute pancreatitis: value of CT in establishing prognosis. Radiology 174:331–336
Lenhart DK, Balthazar EJ (2008) MDCT of acute mild non-necrotizing pancreatitis: abdominal complications and fate of fluid collections. AJR 190:643–649
Renner IG, Savage WT, Pantoja JL, Renner VJ (1985) Death due to acute pancreatitis. A retrospective analysis of 405 autopsy cases. Dig Dis Sci 30:1005–1018
Beger H, Bittnner R, Block S, Büchler M (1986) Bacterial contamination of pancreatic necrosis. Gastroenterology 91:433–438
Schmid SW, Uhl W, Friess H, Malfertheiner P, Büchler MW (1999) The role of infection in acute pancreatitis. Gut 45(2):311–316
Triantopoulou C, Delis S, Dervenis C (2010) Imaging evaluation of post-pancreatitis infection. Infect Disord Drug Targets 10(1):15–20
Rattner DW, Legermate DA, Lee MJ, Mueller PR, Warshaw AL (1992) Early surgical debridement of symptomatic pancreatic necrosis is beneficial irrespective of infection. Am J Surg 163:105–109
Elfar M, Gaber LW, Sabek O, Fischer CP, Gaber AO (2007) The inflammatory cascade in acute pancreatitis: relevance to clinical disease. Surg Clin N Am 87:1325–1340
Maher MM, Lucey BC, Gervais DA, Mueller PR (2004) Acute pancreatitis: the role of imaging and interventional radiology. Cardiovasc Intervent Radiol 27:208–225
Qayyum A (2009) Diffusion-weighted imaging in the abdomen and pelvis: concepts and applications. RadioGraphics 29:1797–1810
Koh DM, Collins DJ (2007) Diffusion-weighted MRI in the body: applications and challenges in oncology. AJR 188(6):1622–1635
Kim YJ, Chang KH, Song IC, et al. (1998) Brain abscess and necrotic or cystic brain tumor: discrimination with signal intensity on diffusion-weighted MR imaging. AJR 171:1487–1490
Mürtz P, Flacke S, Traber F, et al. (2002) Abdomen: diffusion-weighted MR imaging with pulse-triggered single-shot sequences. Radiology 224:258–264
Chan JH, Tsui EY, Luk SH, et al. (2001) Diffusion-weighted MR imaging of the liver: distinguishing hepatic abscess from cystic or necrotic tumor. Abdom Imaging 26:161–165
Chan JH, Tsui EY, Luk SH, et al. (2001) MR diffusion-weighted imaging of kidney: differentiation between hydronephrosis and pyonephrosis. Clin Imaging 25:110–113
Unal O, Koparan HI, Avcu S, Kalender AM, Kisli E (2011) The diagnostic value of diffusion-weighted magnetic resonance imaging in soft tissue abscesses. Eur J Radiol 77:490–494
Oto A, Schmid-Tannwald C, Agrawal G, et al. (2011) Diffusion-weighted MR imaging of abdominopelvic abscesses. Emerg Radiol 18:515–524
Thomas S, Kayhan A, Lakadamyali H, Oto A (2012) Diffusion MRI of acute pancreatitis and comparison with normal individuals using ADC values. Emerg Radiol 19:5–9
Shinya S, Sasaki T, Nakagawa Y, et al. (2009) The efficacy of diffusion-weighted imaging for the detection and evaluation of acute pancreatitis. Hepatogastroenterology 56:1407–1410
Akisik MF, Sandrasegaran K, Jennings SG, et al. (2009) Diagnosis of chronic pancreatitis by using apparent diffusion coefficient measurements at 3.0-T MR following secretin stimulation. Radiology 252:418–425
Taniguchi T, Kobayashi H, Nishikawa K, et al. (2009) Diffusion-weighted magnetic resonance imaging in autoimmune pancreatitis. Jpn J Radiol 27:138–142
Ranson JH, Rifkind KM, Roses DF, et al. (1974) Prognostic signs and the role of operative management in acute pancreatitis. Surg Gynecol Obstet 139(1):69–78
Munro BH (1997) Statistical methods for health care research, 3rd edn. New York: Lippincott Williams & Wilkins
Landis JR, Koch GG (1977) The measurement of observer agreement for categorical data. Biometrics 33:159–174
Kylänpää L, Rakonczay Z Jr, O’Reilly DA (2012) The clinical course of acute pancreatitis and the inflammatory mediators that drive it. Int J Inflam 2012:360685
Buchler MW, Gloor B, Muller CA, et al. (2000) Acute necrotizing pancreatitis: treatment strategy according to the status of infection. Ann Surg 232:619–626
Morgan DE, Baron TH, Smith JK, Robbin ML, Kenney PJ (1997) Pancreatic fluid collections prior to intervention: evaluation with MR imaging compared with CT and US. Radiology 203:773–778
Freeny PC, Hauptmann E, Althaus SJ, Traverso LW, Sinanan M (1998) Percutaneous CT-guided catheter drainage of infected acute necrotizing pancreatitis. AJR 170:969–975
Seifert H, Biermer M, Schmitt W, et al. (2009) Transluminal endoscopic necrosectomy after acute pancreatitis: a multicentre study with long-term follow-up (the GEPARD Study). Gut 58:1260–1266
Xiao B, Zhang XM, Tang W, Zeng NL, Zhai ZH (2010) Magnetic resonance imaging for local complications of acute pancreatitis: a pictorial review. World J Gastroenterol 16:2735–2742
Balthazar E, Freeney PC, van Sonnenberg E (1994) Imaging and intervention in acute pancreatitis. Radiology 193:297–306
Wong AM, Zimmerman RA, Simon EM, Pollock AN, Bilaniuk LT (2004) Diffusion-weighted MR imaging of subdural empyemas in children. AJNR 25:1016–1021
Reddy JS, Mishra AM, Behari S, et al. (2006) The role of diffusion-weighted imaging in the differential diagnosis of intracranial cystic mass lesions: a report of 147 lesions. Surg Neurol 66:246–250
Han KT, Choi DS, Ryoo JW, et al. (2007) Diffusion-weighted MR imaging of pyogenic intraventricular empyema. Neuroradiology 49:813–818
Sepahdari AR, Aakalu VK, Kapur R, et al. (2009) MRI of orbital cellulitis and orbital abscess: the role of diffusion-weighted imaging. AJR 193:244–250
Bradley EL 3rd (1993) A clinically based classification system for acute pancreatitis. Summary of the International Symposium on Acute Pancreatitis, Atlanta, GA, September 11 through 13, 1992. Arch Surg 128:586–590
Mönkemüller KE, Harewood GC, Curioso WH, et al. (2005) Biochemical analysis of pancreatic fluid collections predicts bacterial infection. J Gastroenterol Hepatol 20:1667–1673
Acknowledgments
We thank Yigit Sirin for his comments.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Islim, F., Salik, A.E., Bayramoglu, S. et al. Non-invasive detection of infection in acute pancreatic and acute necrotic collections with diffusion-weighted magnetic resonance imaging: preliminary findings. Abdom Imaging 39, 472–481 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00261-014-0076-2
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00261-014-0076-2